Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (6): 778-786.DOI: 10.6023/A21010007 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
焦建超, 朱玉鑫, 彭晓薇, 金世航, 张云强*( ), 李梅*(
), 李梅*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-01-12
发布日期:2021-04-14
通讯作者:
张云强, 李梅
基金资助:
Jianchao Jiao, Yuxin Zhu, Xiaowei Peng, Shihang Jin, Yunqiang Zhang( ), Mei Li(
), Mei Li( )
)
Received:2021-01-12
Published:2021-04-14
Contact:
Yunqiang Zhang, Mei Li
About author:Supported by:Share
Jianchao Jiao, Yuxin Zhu, Xiaowei Peng, Shihang Jin, Yunqiang Zhang, Mei Li. Preparation of High Capacitive Performance Porous Carbon Assisted by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 778-786.
| Sample | SBETa/ (m2•g-1) | Smicrob/ (m2•g-1) | Smeso/macroc/ (m2•g-1) | Vtotd/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmicroe/ (cm3•g-1) | Average pore size/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFC-0 | 82.18 | 14.14 | 68.04 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 13.36 |
| MFC-SDS20 | 321.50 | 241.20 | 80.30 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 2.58 |
| MFC-SDS30 | 387.86 | 283.03 | 104.83 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 3.62 |
| MFC-SDS40 | 251.05 | 231.47 | 19.58 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 2.23 |
| Sample | SBETa/ (m2•g-1) | Smicrob/ (m2•g-1) | Smeso/macroc/ (m2•g-1) | Vtotd/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmicroe/ (cm3•g-1) | Average pore size/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFC-0 | 82.18 | 14.14 | 68.04 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 13.36 |
| MFC-SDS20 | 321.50 | 241.20 | 80.30 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 2.58 |
| MFC-SDS30 | 387.86 | 283.03 | 104.83 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 3.62 |
| MFC-SDS40 | 251.05 | 231.47 | 19.58 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 2.23 |


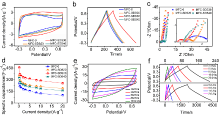


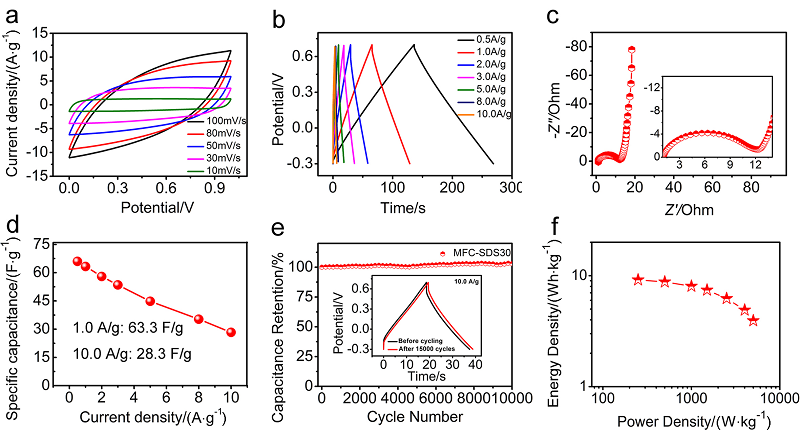
| [1] |
Díez, N.; Mysyk, R.; Zhang, W.; Goikolea, E.; Carriazo, D. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14619.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA01424D |
| [2] |
Li, H.; Gong, Y.; Fu, C.; Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; Guo, M.; Li, M.; Kuang, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3875.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA10786A |
| [3] |
Kwon, H.; Han, D. J.; Lee, B. Y. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41495.
doi: 10.1039/D0RA08064K |
| [4] |
Shinde, P. A.; Khan, M. F.; Rehman, M. A.; Jung, E.; Pham, Q. N.; Won, Y.; Jun, S. C. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 6360.
doi: 10.1039/D0CE01006E |
| [5] |
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, A. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4453.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR08784A |
| [6] |
Zhang, N.; Liu, F.; Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Yu, Q.; Liu, L. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 22631.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA07488C |
| [7] |
Yao, L.; Lin, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Deng, L.; Zheng, Z. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11086.
doi: 10.1039/C9NR02476J |
| [8] |
Benzigar, M. R.; Talapaneni, S. N.; Joseph, S.; Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Scaranto, J.; Ravon, U.; Al-Bahily, K.; Vinu, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2680.
doi: 10.1039/c7cs00787f pmid: 29577123 |
| [9] |
Du, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 1038.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA10266J |
| [10] |
Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Chinese J. Chem. 2020, 38, 353.
|
| [11] |
Xie, L.; Su, F.; Xie, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Kong, Q.; Sun, G.; Ahmad, A.; Li, X.; Yi, Z.; Chen, C. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2610.
doi: 10.1039/D0QM00180E |
| [12] |
Bi, R.; Mao, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, R.; Wang, D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1200. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20060215 |
|
(毕如一, 毛丹, 王江艳, 于然波, 王丹, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1200.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060215 |
|
| [13] |
Liu, Z.; Du, Z.; Xing, W.; Yan, Z. Mater. Lett. 2014, 117, 273.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2013.12.021 |
| [14] |
Wang, C.; Wu, D.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F.; Jiang, K. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 375.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.07.097 |
| [15] |
Li, G.; Mao, K.; Liu, M.; Yan, M.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, Q. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004632.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.52 |
| [16] |
Nasini, U. B.; Bairi, V. G.; Ramasahayam, S. K.; Bourdo, S. E.; Viswanathan, T.; Shaikh, A. U. J. Power Sources 2014, 250, 257.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.014 |
| [17] |
Tutunchi, A.; Kamali, R.; Kianvash, A. J. Adhesion 2015, 91, 663.
doi: 10.1080/00218464.2014.961187 |
| [18] |
Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 166, 310.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.078 |
| [19] |
Fic, K.; Lota, G.; Frackowiak, E. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 1333, 206.
|
| [20] |
Kailasam, K.; Jun, Y.; Katekomol, P.; Epping, J.; Hong, W.; Thomas, A. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 428.
doi: 10.1021/cm9029903 |
| [21] |
Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiang, H. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 517, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.11.042 |
| [22] |
Yang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gu, D.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 579.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.10.037 |
| [23] |
Li, W.; Li, B.; Shen, M.; Gao, Q.; Hou, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123309.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123309 |
| [24] |
Fic, K.; Lota, G.; Frackowiak, E. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7484.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2010.02.037 |
| [25] |
Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Chu, X.; Gu, B.; Huang, H.; Yang, W. Carbon 2019, 149, 105.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.04.023 |
| [26] |
Zhu, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, D.; Qian, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Chai, X.; Gan, L.; Liu, M. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 12334.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA02341G |
| [27] |
Mahbub, S.; Molla, M. R.; Saha, M.; Shahriar, I.; Hoque, M. A.; Halim, M. A.; Rub, M. A.; Khan, M. A.; Azum, N. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 263.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.03.045 |
| [28] |
Kim, J. H.; Ko, Y.; Kim, Y. A.; Kim, K. S.; Yang, C. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 855, 157282.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157282 |
| [29] |
Pang, Z.; Li, G.; Zou, X.; Sun, C.; Hu, C.; Tang, W.; Ji, L.; Hsu, H.; Xu, Q.; Lu, X. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 56, 512.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2020.08.042 |
| [30] |
Zheng, C.; Qian, W.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, M.; Tan, P. Carbon 2012, 50, 5167.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.06.058 |
| [31] |
Shan, Q.; Huo, W.; Shen, M.; Jing, C.; Peng, Y.; Pu, H.; Zhang, Y. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2245.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.02.003 |
| [32] |
Liu, X.; Lai, C.; Xiao, Z.; Zou, S.; Liu, K.; Yin, Y.; Liang, T.; Wu, Z. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2019, 2, 3185.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.9b00002 |
| [33] |
Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A. B. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5069.
doi: 10.1021/nn501124h pmid: 24731137 |
| [34] |
Bo, X.; Xiang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Guo, X. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 39, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.01.006 |
| [35] |
Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Shang, J.; Yu, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 19558.
doi: 10.1002/ange.v132.44 |
| [36] |
Du, W.; Wang, X.; Zhan, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, L.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Q.; Dong, M.; Liu, H.; Murugadoss, V.; Guo, Z. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296, 907.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.074 |
| [37] |
Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Jia, S.; Xu, H.; Zang, J. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 2222.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2983-z |
| [38] |
Benzigar, M. R.; Talapaneni, S. N.; Joseph, S.; Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Scaranto, J.; Ravon, U.; Al-Bahily, K.; Vinu, A. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2680.
doi: 10.1039/c7cs00787f pmid: 29577123 |
| [39] |
Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 797.
doi: 10.1039/C1CS15060J |
| [40] |
Ma, F.; Sun, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Huo, L.; Xia, T.; Gao, S. Chem. Res. Chinese U. 2013, 29, 735.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-013-3181-9 |
| [41] |
Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Lu, X.; Tong, Y.; Li, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 11444.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b02157 |
| [42] |
Deng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zou, K.; Ji, X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1144.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA08620E |
| [43] |
Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 166, 310.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.078 |
| [44] |
Wei, T.; Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Xiao, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, H. J. Power Sources 2016, 331, 373.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.09.053 |
| [45] |
Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.; Hua, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Wei, B. Carbon 2018, 127, 85.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.10.084 |
| [46] |
Chen, H.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Guan, S. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 148, 187.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.10.042 |
| [47] |
Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Luo, J.; Peng, Y.; Ji, Q.; Dai, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2763.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05947 |
| [48] |
Miao, L.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Duan, H.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Chai, X.; Gan, L. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 274, 378.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.04.100 |
| [49] |
Díez, N.; Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A. B. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3798.
doi: 10.1002/celc.v7.18 |
| [50] |
Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Miao, R.; Yao, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2286.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA09073C |
| [51] |
Wang, H.; Yi, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Fan, H. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 658.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.03.033 |
| [52] |
Zhao, Y.; Lu, M.; Tao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, H. J. Power Sources 2016, 307, 391.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.01.020 |
| [53] |
Zhao, J.; Gong, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, K.; Ye, K.; Zhu, K.; Yan, J.; Cao, D.; Wang, G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 31. (in Chinese)
|
|
(赵婧, 龚俊伟, 李一举, 程魁, 叶克, 朱凯, 闫俊, 曹殿学, 王贵领, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 31.)
|
| [1] | Gu Xiaoyu, Hong Ye, Ai Guo, Wang Chaoyang, Mao Wenfeng. All Graphene Lithium Ion Capacitor with High-Energy-Power Density Performance [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2018, 76(8): 644-648. |
| [2] | . Mesoscopic Simulation Study on the Aggregation Behavior between Lauryl Alcohol Polyoxyethylene and Sodium Lauryl Sulfate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 67(6): 483-487. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||