Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (5): 690-702.DOI: 10.6023/A21120624 Previous Articles
Special Issue: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
Review
投稿日期:2021-12-31
发布日期:2022-05-31
通讯作者:
李娜
作者简介: |
宋攀奇, 硕士, 助理工程师, 毕业于北京理工大学, 现于国家蛋白质科学研究(上海)设施工作, 负责同步辐射生物小角散射线站的运行、管理工作, 参与线站的用户服务和技术支持. 主要研究方向为基于同步辐射BioSAXS技术进行方法学开发研究. |
 |
张建桥, 硕士, 助理工程师, 毕业于西南科技大学, 现于国家蛋白质科学研究(上海)设施工作, 负责协助开展BL19U2生物小角X射线散射(BioSAXS)线站的运行、维护和管理工作. |
 |
李怡雯, 博士, 工程师, 同步辐射生物小角X射线散射线站用户负责人, 毕业于中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 获核科学与技术专业博士学位, 主要从事脂质体药物结构研究、X射线小角散射实验方法学研究. 作为项目骨干参与国家重点研发项目1项、中科院基础设施维修改造项目1项, 主持国家自然科学基金青年项目1项. |
 |
刘广峰, 博士, 副研究员, 同步辐射生物小角X-射线散射线站运行负责人, 毕业于中国科学院高能物理研究所, 主要从事生物小角散射线站的运行维护工作. 作为项目骨干参加了中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(B类)生物小角X射线散射技术及国家自然科学基金大科学装置联合基金重点项目, 主持自然科学基金青年项目1项, 入选2020年中科院青年创新促进会会员. |
 |
李娜, 博士, 副研究员, 同步辐射生物小角X射线散射线站团队负责人. 现担任中国晶体学会小角散射委员会委员、中国生物物理学会分子生物物理委员会委员、中国科学院青年创新促进会会员. 2011年加入国家蛋白质科学研究(上海)设施. 主要研究方向为基于同步辐射溶液散射技术方法开发以及溶液散射技术在软物质领域中的应用研究. 曾作为第四完成人获得中国水产科学研究院科技进步二等奖. 已在国际知名期刊发表论文68篇. 已提交专利申请4项, 获批1项. 现已出版科普译著1部、科普专著1部; 同时参与撰写学术专著1部; 主持完成学术译著1部. 作为项目负责人主持科研项目11项; 作为技术骨干参与科研项目4项; 多次组织生物小角散射技术相关的国际培训课程及国际会议, 录制生物小角散射专业技术微课, 于2019年12月份上线中科院继续教育网络课程. |
基金资助:
Panqi Song, Jianqiao Zhang, Yiwen Li, Guangfeng Liu, Na Li( )
)
Received:2021-12-31
Published:2022-05-31
Contact:
Na Li
About author:Supported by:Share
Panqi Song, Jianqiao Zhang, Yiwen Li, Guangfeng Liu, Na Li. Solution Small-Angle Scattering in Soft Matter: Application and Prospective※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 690-702.
| Beamline | Synchrotron | Source type | Energy range/keV | Flux/(phs•s–1) | Beam size (mm×mm) | Detectable spatial size (Max)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1W2A | BSRF | Wiggler | 8 | ≈1011 | 1.4×0.2 | 200 |
| Pinkbeam SAXS | HEPS | Undulator | 8~12 | ≈1013~1015 | 0.5×0.5/0.05×0.05 | 5000 |
| BL16B1 | SSRF | Bending magnet | 5~20 | ≈1011 | 0.16×0.24 | 240 |
| BL19U2 | SSRF | Undulator | 7~15 | ≈1012 | 0.33×0.05/0.01×0.01 | 300 |
| BL10U1 | SSRF | Undulator | 8~15 | ≈1013 | 0.4×0.45/0.008×0.006 | 2100 |
| Beamline | Synchrotron | Source type | Energy range/keV | Flux/(phs•s–1) | Beam size (mm×mm) | Detectable spatial size (Max)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1W2A | BSRF | Wiggler | 8 | ≈1011 | 1.4×0.2 | 200 |
| Pinkbeam SAXS | HEPS | Undulator | 8~12 | ≈1013~1015 | 0.5×0.5/0.05×0.05 | 5000 |
| BL16B1 | SSRF | Bending magnet | 5~20 | ≈1011 | 0.16×0.24 | 240 |
| BL19U2 | SSRF | Undulator | 7~15 | ≈1012 | 0.33×0.05/0.01×0.01 | 300 |
| BL10U1 | SSRF | Undulator | 8~15 | ≈1013 | 0.4×0.45/0.008×0.006 | 2100 |
| Spectrometer | Neutron source | λ range/nm | Flux/(cm–2•s–1) | Beam size (mm×mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suanni | CMRR | 0.25~2, 0.35~2 | 1.18×107 | Aperture Φ 4~10 |
| CNGD | CARR | 0.4~2 | 104~107 | Aperture Φ 5~25 |
| SANS | CSNS | 0.12~0.95, 0.12~1.1 | 1.08×108/6.46×106 | 20×30 |
| VSANS | CSNS | 0.24~1.14 | 2.2×105 | 20×30 |
| Spectrometer | Neutron source | λ range/nm | Flux/(cm–2•s–1) | Beam size (mm×mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suanni | CMRR | 0.25~2, 0.35~2 | 1.18×107 | Aperture Φ 4~10 |
| CNGD | CARR | 0.4~2 | 104~107 | Aperture Φ 5~25 |
| SANS | CSNS | 0.12~0.95, 0.12~1.1 | 1.08×108/6.46×106 | 20×30 |
| VSANS | CSNS | 0.24~1.14 | 2.2×105 | 20×30 |
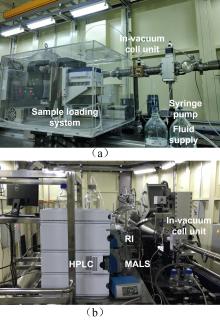



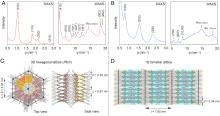

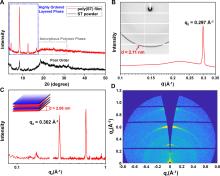

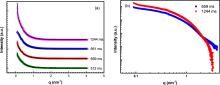




| [1] |
Hamley, I. W. Introduction to Soft Matter: Synthetic and Biological Self-Assembling Materials, Revised Edition, Wiley, Chichester, UK, 2013, 13, 3.
|
| [2] |
de Gennes, P. G. Science 1992, 64, 645.
doi: 10.1126/science.64.1670.645 |
| [3] |
Narayanan, T.; Wacklin, H.; Konovalov, O.; Lund, R. Crystallogr. Rev. 2017, 23, 160.
doi: 10.1080/0889311X.2016.1277212 |
| [4] |
Campbell, E. C.; Correy, G. J.; Mabbitt, P. D.; Buckle, A. M.; Tokuriki, N.; Jackson, C. J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2018, 50, 49.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.09.005 |
| [5] |
Li, M.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Svoboda, V.; Oung, H. M. O.; Mullendore, D. L.; Kirchhoff, H. Plant. Direct. 2020, 4, e00280.
|
| [6] |
Engel, B. D.; Schaffer, M.; Kuhn Cuellar, L.; Villa, E.; Plitzko, J. M.; Baumeister, W. Elife 2015, 4, e04889.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.04889 |
| [7] |
Mazur, R.; Mostowska, A.; Szach, J.; Gieczewska, K.; Wojtowicz, J.; Bednarska, K.; Garstka, M.; Kowalewska, L. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4689.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz219 |
| [8] |
Koch, M. H.; Vachette, P.; Svergun, D. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2003, 36, 147.
doi: 10.1017/S0033583503003871 |
| [9] |
Lombardo, D.; Calandra, P.; Kiselev, M. Molecules 2020, 25, 5624.
doi: 10.3390/molecules25235624 |
| [10] |
Hura, G. L.; Menon, A. L.; Hammel, M.; Rambo, R. P.; Poole, F. L., 2nd; Tsutakawa, S. E.; Jenney, F. E.; Jr
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1353 |
| [11] |
Perera, S.; Chawla, U.; Shrestha, U. R.; Bhowmik, D.; Struts, A. V.; Qian, S.; Chu, X. Q.; Brown, M. F. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 7064.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b03048 |
| [12] |
Guinier, A. Phys. Today 1969, 22, 25.
|
| [13] |
Nagar, B.; Kuriyan, J. Structure 2005, 13, 169.
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2005.01.001 |
| [14] |
Perez, J.; Nishino, Y. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 670.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.07.014 |
| [15] |
Liu, L.; Boldon, L.; Urquhart, M.; Wang, X. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 71, e4160.
|
| [16] |
Round, A.; Felisaz, F.; Fodinger, L.; Gobbo, A.; Huet, J.; Villard, C.; Blanchet, C. E.; Pernot, P.; McSweeney, S.; Roessle, M.; Svergun, D. I.; Cipriani, F. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 67.
doi: 10.1107/S1399004714026959 |
| [17] |
Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, N. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2018, 51, 1633.
doi: 10.1107/S160057671801316X |
| [18] |
Li, Y.-W.; Liu, G.-F.; Wu, H.-J.; Zhou, P.; Hong, C.-X.; Li, N.; Bian, F.-G. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2020, 31, 116.
doi: 10.1007/s41365-020-00822-6 |
| [19] |
Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Onuk, E.; Badger, J.; Makowski, L. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1009, 131.
|
| [20] |
Kwok, L. W.; Shcherbakova, I.; Lamb, J. S.; Park, H. Y.; Andresen, K.; Smith, H.; Brenowitz, M.; Pollack, L. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 355, 282.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.10.070 |
| [21] |
Lamb, J.; Kwok, L.; Qiu, X.; Andresen, K.; Park, H. Y.; Pollack, L. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 1046.
doi: 10.1107/S0021889808028264 |
| [22] |
Ansari, M. A.; Kim, K.-Y.; Anwar, K.; Kim, S. M. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 055007.
doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/20/5/055007 |
| [23] |
Rai, D. K.; Gillilan, R. E.; Huang, Q.; Miller, R.; Ting, E.; Lazarev, A.; Tate, M. W.; Gruner, S. M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 111.
doi: 10.1107/S1600576720014752 |
| [24] |
Gruzinov, A. Y.; Schroer, M. A.; Manalastas-Cantos, K.; Kikhney, A. G.; Hajizadeh, N. R.; Schulz, F.; Franke, D.; Svergun, D. I.; Blanchet, C. E. J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 2021, 28, 812.
doi: 10.1107/S1600577521003404 pmid: 33949989 |
| [25] |
Li, Y.-W.; Bian, F.-G.; Wang, J. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2016, 27, 920.
|
| [26] |
Narayanan, T.; Konovalov, O. Materials (Basel) 2020, 13, 752.
doi: 10.3390/ma13030752 |
| [27] |
Luoxi, T.; James, G.; Brian, H.; Elizabeth, G.; Jonathan, N. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 363.
doi: 10.1107/S1600576720015526 |
| [28] |
Ingo, B.; Joachim, K.; Thünemann, A. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1587.
doi: 10.1107/S1600576715016544 |
| [29] |
Karen, M.; Petr, V.; Nelly, R.; Alexey, G.; Maxim, V.; Dmitry, S.; Alejandro, P.; Haydyn, D.; Andrey, G.; Clemente, B.; Cy, M.; Dmitri, I. S.; Daniel, F. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 343.
doi: 10.1107/S1600576720013412 |
| [30] |
Panjkovich, A.; Svergun, D. I. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1944.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx846 pmid: 29300836 |
| [31] |
Hammouda, B. Probing Nanoscale Structures-The SANS Toolbox, National Institute of Standards and Technology Center for Neutron Research, Gaithersburg, 2010, pp. 210-225.
|
| [32] |
Grant, T. D. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 191.
|
| [33] |
Yang, L.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7196.
doi: 10.1021/cr500633b |
| [34] |
Ogi, S.; Sugiyasu, K.; Manna, S.; Samitsu, S.; Takeuchi, M. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 188.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1849 |
| [35] |
Prabhu, D. D.; Aratsu, K.; Kitamoto, Y.; Ouchi, H.; Ohba, T.; Hollamby, M. J.; Shimizu, N.; Takagi, H.; Haruki, R.; Adachi, S. I.; Yagai, S. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat8466.
|
| [36] |
Poon, J. K.; Chen, Z.; Leung, S. Y.; Leung, M. Y.; Yam, V. W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2022829118.
|
| [37] |
Aida, T.; Meijer, E. W.; Stupp, S. I. Science 2012, 335, 813.
doi: 10.1126/science.1205962 pmid: 22344437 |
| [38] |
Webber, M. J.; Appel, E. A.; Meijer, E. W.; Langer, R. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 13.
doi: 10.1038/nmat4474 |
| [39] |
Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y. X.; Luo, H. X.; Shi, C. Y.; Geise, G. M.; Feringa, B. L.; Tian, H.; Qu, D. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12804.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05740 pmid: 31348651 |
| [40] |
Thanh, N. T.; Maclean, N.; Mahiddine, S. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7610.
doi: 10.1021/cr400544s |
| [41] |
Liu, Y. B.; Yang, R. H.; Pelster, T.; Lee, T. T.; Wang, Y. J.; Hong, C. X.; Luo, G. S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 21853.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c06846 |
| [42] |
Lai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, W.; Yin, P. Polym. Compos. 2019, 41, 306.
doi: 10.1002/pc.25370 |
| [43] |
Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Lai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Halbert, C.; Browning, J. F.; Liu, D.; Yin, P. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 15656.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c05544 |
| [44] |
Lai, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, M.; Yin, P. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 7178.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00295 |
| [45] |
Yin, J. F.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L.; Guo, Q. Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Sun, T. L.; Liu, G. X.; Huang, C.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Russell, T. P.; Yin, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4894.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202013361 |
| [46] |
Heftberger, P.; Kollmitzer, B.; Heberle, F. A.; Pan, J.; Rappolt, M.; Amenitsch, H.; Kucerka, N.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 173.
doi: 10.1107/S1600576713029798 |
| [47] |
Ye, Y. N.; Cui, K.; Hong, W.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Hourdet, D.; Nakajima, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J. P. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2014694118.
|
| [48] |
Bonaccorsi, L.; Calandra, P.; Kiselev, M. A.; Amenitsch, H.; Proverbio, E.; Lombardo, D. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7079.
doi: 10.1021/la400951s pmid: 23651236 |
| [49] |
Wang, M.; Dai, L.; Duan, J.; Ding, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Xing, H.; Tian, Y. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2020, 59, 6389.
|
| [50] |
Petoukhov, M. V.; Svergun, D. I. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 562.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.06.009 |
| [51] |
Gilman, B.; Tijerina, P.; Russell, R. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1313.
doi: 10.1042/BST20170095 |
| [52] |
Tria, G.; Mertens, H. D.; Kachala, M.; Svergun, D. I. IUCrJ 2015, 2, 207.
doi: 10.1107/S205225251500202X |
| [53] |
Ma, J.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Valle, J.; Fan, S.; Zuo, X.; Lasa, I.; Fang, X. EMBO J. 2021, 40, 3510.
|
| [54] |
Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, H.; Guddat, L. W.; Yang, H.; Rao, Z. Cell 2019, 176, 636.
doi: S0092-8674(19)30036-4 pmid: 30682372 |
| [55] |
Cui, W.; Braun, E.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Slater, B.; Li, N.; Chen, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Duan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ti, R.; Hotter, D.; Ji, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, J.; Xiong, Y.; Sauter, D.; Wang, Z.; Kirchhoff, F.; Yang, H. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2022269118.
|
| [56] |
Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Xie, F.; Kuang, S.; Zhan, B.; Gao, W.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qian, F.; Ding, C.; Gan, J.; Ji, C.; Xu, X. W.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, J.; He, H. H.; Li, J. Adv. Sci (Weinh). 2020, 7, 2000532.
|
| [57] |
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Fang, X. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47016.
|
| [58] |
Brezski, R. J.; Georgiou, G. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 40, 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.03.002 |
| [59] |
Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Lu, B.; Jin, T.; Li, F. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4206.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12097-6 |
| [60] |
Guan, D.; Kao, H. Y. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 60.
doi: 10.1186/s13578-015-0051-9 |
| [61] |
Bernardi, R.; Pandolfi, P. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 1006.
doi: 10.1038/nrm2277 |
| [62] |
Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Cheng, N.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Chen, S. J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, G. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3789.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11746-0 |
| [63] |
Josts, I.; Gao, Y.; Monteiro, D. C. F.; Niebling, S.; Nitsche, J.; Veith, K.; Grawert, T. W.; Blanchet, C. E.; Schroer, M. A.; Huse, N.; Pearson, A. R.; Svergun, D. I.; Tidow, H. Structure 2020, 28, 348.
doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.12.001 |
| [64] |
Mezzenga, R.; Schurtenberger, P.; Burbidge, A.; Michel, M. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 729.
doi: 10.1038/nmat1496 |
| [65] |
Pan, D. D.; Jane, J. I. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 126.
pmid: 11709834 |
| [66] |
Blazek, J.; Gilbert, E. P. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 85, 281.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.02.041 |
| [67] |
Donald, A. M.; Kato, K. L.; Perry, P. A.; Weigh, T. A. Starch-Starke 2001, 53, 504.
|
| [68] |
Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Wang, D. K.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Qiao, D.; Xiong, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.002 |
| [69] |
Vella, J.; Hemar, Y.; Gu, Q. F.; Wu, Z. R.; Li, N.; Sohnel, T. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110174.
doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110174 |
| [70] |
Sun, Y.; Tai, Z.; Yan, T.; Dai, Y.; Hemar, Y.; Li, N. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110653.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110653 |
| [71] |
Matsumoto, M.; Saito, S.; Ohmine, I. Nature 2002, 416, 409.
doi: 10.1038/416409a |
| [72] |
Fitzner, M.; Sosso, G. C.; Pietrucci, F.; Pipolo, S.; Michaelides, A. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2257.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02300-x pmid: 29273707 |
| [73] |
Bai, G.; Gao, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Nature 2019, 576, 437.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1827-6 |
| [74] |
Zhang, S.; Han, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, X.; Li, N.; de Souza, N. R.; Garcia Sakai, V.; Chu, X. Q. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 8, 054901.
doi: 10.1063/4.0000111 |
| [75] |
Qian, X.; Han, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, J.; Tyagi, M.; Li, Q.; Du, F.; Zheng, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J.; Huang, H.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Bernholc, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, L. Q.; Hong, L.; Zhang, Q. M. Nature 2021, 600, 664.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04189-5 |
| [1] | Lei Yang, Yujing Wu, Xuanjun Wu, Weiquan Cai. High-throughput Screening of Real Metal-organic Frameworks for Adsorption Separation of C4 Olefins [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 520-529. |
| [2] | Bian Lei, Li Wei, Wei Zhenzhen, Liu Xiaowei, Li Song. Formaldehyde Adsorption Performance of Selected Metal-Organic Frameworks from High-throughput Computational Screening [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(4): 303-310. |
| [3] | Wu Jinmei, Su Gaoxing, Zhang Bin, Yan Bing. Nanocombinatorial Chemistry in Nanomaterial Discovery and Nanomedicine [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(04): 493-500. |
| [4] | Zhang Yaling, Yang Bin, Xu Liangxin, Zhang Xiaoyong, Tao Lei, Wei Yen. Self-healing Hydrogels Based on Dynamic Chemistry and Their Biomedical Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(04): 485-492. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||