Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (10): 1410-1423.DOI: 10.6023/A22070314 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
田宋炜†,a,b, 周丽雪†,a,c, 张秉乾a,b, 张建军a,*( ), 杜晓璠a, 张浩a,b, 胡思伽a, 苑志祥a, 韩鹏献a, 李素丽d, 赵伟d, 周新红b,*(
), 杜晓璠a, 张浩a,b, 胡思伽a, 苑志祥a, 韩鹏献a, 李素丽d, 赵伟d, 周新红b,*( ), 崔光磊a,*(
), 崔光磊a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
张建军, 周新红, 崔光磊
作者简介: |
田宋炜, 男, 青岛科技大学化学与分子工程学院硕士, 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所联合培养硕士生. 主要从事高电压钠金属电池及水系钠离子电池电解质的研究. |
 |
周丽雪, 女, 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所材料工程专业硕士研究生. 主要从事高电压水系锂/钠离子电池电解质的研究. |
 |
张秉乾, 男, 青岛科技大学材料科学与工程学院博士, 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所联合培养博士, 主要从事新能源材料的合成与器件制备. |
 |
张建军, 男, 中国共产党党员, 副研究员, 硕士生导师, 中国科学院青年创新促进会会员. 2011年进入中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所工作, 主要研究方向是: 高电压聚合物固态锂(钠)二次电池技术及其关键材料. 主持承担国家自然科学基金面上项目(2项)、国家自然科学基金青年基金(1项)等多个项目. 以第一作者(含共一)或通讯作者在Advanced Energy Materials、Small、Energy & Environmental Science等国际权威学术期刊发表SCI论文29篇(其中4篇入选ESI高被引论文), 总引用次数2495次. 申请PCT国际专利2项, 获得授权欧洲专利1项;获得授权中国发明专利20项, 获得授权中国实用新型专利3项. 2017年获得青岛市自然科学奖一等奖(第五完成人); 2018年获得山东省自然科学奖一等奖(第五完成人); 2021年获得青岛市科学进步奖一等奖(第五完成人). |
 |
周新红, 2005年毕业于清华大学化学系, 获理学博士学位. 目前主要从事于能源化学、材料和新型能源器件的研究. 重点研究新能源器件的电极以及电解质材料体系, 致力于推动基础研究成果的实际应用. 作为项目负责人, 现主持国家自然科学基金面上项目一项; 先后主持完成国家自然科学青年基金, 山东省自然科学基金面上项目. 近年来, 以第一作者或通讯作者在能源材料、化学、器件等方面的国际权威杂志Nat. Commun.、Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.、Adv. Mater.、ACS Energy Lett.等发表学术论文20余篇. |
 |
崔光磊, 研究员, 博士生导师, 国务院特殊津贴专家, 国家杰青和WR计划, 中科院深海智能技术先导专项副总师(固态电池基深海能源体系), 青岛市储能产业技术研究院院长, 国际聚合物电解质委员会理事. 2005年于中国科学院化学所获得有机化学博士学位, 2005年9月至2009年2月先后在德国马普协会高分子所和固态所从事博士后研究. 2009年2月起于中科院青岛生物能源与过程所工作. 2009年入选中国科学院“百人计划”(终期评估优秀), 2009年获山东省自然科学杰出青年基金资助, 2015年入选山东省“泰山学者特聘专家”, 2016年获国家自然科学杰出青年基金资助, 2018年至2021年, 十三五国家重点研发计划新能源汽车专项, 高比能固态电池项目负责人. 主要从事低成本高效能源储存与转换器件的研究. 作为负责人/课题负责人承担国家自然科学杰出青年基金, 国家973计划, 863计划, 国家自然科学基金面上项目, 省部级及中科院先导专项, 企业横向项目等多项科研项目. 在Nat. Commun.、J. Am. Chem. Soc.、Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.、Adv. Mater.等发表论文300余篇, 引用2万余次, 申请国家专利210余项, 授权113项, 申请PCT专利6项, 授权欧洲专利1项, 出版《动力锂电池中聚合物关键材料》一部. 获得2017年青岛市自然科学奖一等奖(第一完成人); 获得2018年山东省自然科学奖一等奖(第一完成人); 获得2021年青岛市科学进步奖一等奖(第一完成人). |
基金资助:
Songwei Tian†,a,b, Lixue Zhou†,a,c, Bingqian Zhanga,b, Jianjun Zhanga( ), Xiaofan Dua, Hao Zhanga,b, Sijia Hua, Zhixiang Yuana, Pengxian Hana, Suli Lid, Wei Zhaod, Xinhong Zhoub(
), Xiaofan Dua, Hao Zhanga,b, Sijia Hua, Zhixiang Yuana, Pengxian Hana, Suli Lid, Wei Zhaod, Xinhong Zhoub( ), Guanglei Cuia(
), Guanglei Cuia( )
)
Received:2022-07-18
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
Jianjun Zhang, Xinhong Zhou, Guanglei Cui
About author:Supported by:Share
Songwei Tian, Lixue Zhou, Bingqian Zhang, Jianjun Zhang, Xiaofan Du, Hao Zhang, Sijia Hu, Zhixiang Yuan, Pengxian Han, Suli Li, Wei Zhao, Xinhong Zhou, Guanglei Cui. Key Advances of High-voltage Solid-state Lithium Metal Batteries Based on Poly(ethylene oxide) Polymer Electrolytes[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(10): 1410-1423.
| 序号 | 提升方案 | 固态聚合物电解质组份, 以及正极组成 (负极均为锂金属) | 充放电电压区间和测试温度 | 循环性能及容量保持率 (包含对比样) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1[ | 高电压正极片表面修饰超薄聚合物层 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 固态电解质组成: PEO/LiDFOB/SN(质量比为10:1:9), 将PEO电解质浇铸于纤维素膜; 实验样: PECA-coated LCO/SP/PVDF/PEO(质量比为85:5:7:3), PECA为聚氰基丙烯酸酯; 对比样: 未经PECA修饰的钴酸锂正极, 配比同上. | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.45 V. 80 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环50圈容量保持率为67%; 对比样: 0.1 C循环50圈容量接近0. |
| 2[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆1 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000 ; 电解质: PEO-LiTFSI (EO/Li物质的量比18), PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: 1% (w) LATP(磷酸钛铝锂)包覆钴酸锂粉末; PEO/PVDF(质量比为2:1)分散于溶剂NMP中形成混合液; 包覆后钴酸锂/ SP/PEO/PVDF(质量比为75:10:10:5); 对比样正极: 未包覆的原始钴酸锂. | LCO/Li, 3~4.2 V; LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/Li, 3~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: LCO/Li: 0.2 C循环50圈容量保持率为88.6%; 实验样: LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/Li: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为90.3%; 对比样: 分别采用LiPF6、LiClO4、LiBOB、LiODFB四种锂盐, 在LCO/Li电池0.2 C倍率下分别循环24圈、22圈、27圈、3圈后, 放电容量已经接近0. |
| 3[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆2 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000; 固态电解质组成: PEO-LiTFSI (EO/Li物质的量比18); PEO自支撑膜; 正极组分: 1% (w) LATP包覆钴酸锂粉末; 包覆后钴酸锂/SP/PEO/PVDF(质量比为75:10:10:5). | LCO/Li, 3~4.5 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环7圈容量保持率为84%. |
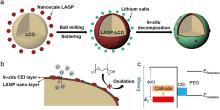
| 4[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆3 | 原料: PEO, Mn: 10000; PEGDME, Mw: 500; 电解质: PEO-PEGDME-LiTFSI-LiBOB-LiPF6 其中LiTFSI/LiBOB/LiPF6(物质的量比为12:8:1); PEO/PEGDME(质量比为1:1); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极: 3.5% (w) LAGP(磷酸锗铝锂)包覆钴酸锂粉末, 包覆后钴酸锂/SP/PVDF(质量比为85:8:7); 对比样正极: 未包覆的钴酸锂; 锂盐: LiTFSI、LiBOB、LiPF6. | LCO/Li, 3~4.25 V; 3~4.3 V; 3~4.4 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 充电截止电压为4.25 V时, 0.5 C循环400圈容量保持率为81.9%; 充电截止电压为4.3 V时, 0.5 C循环200圈容量保持率为84.7%; 充电截止电压为4.4 V时, 0.5 C循环70圈容量保持率为88.1%; 对比样: 充电截止电压为4.3 V时0.5 C循环50圈容量保持率50%. |
| 5[ | 对碳黑颗粒进行包覆 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 固态聚合物电解质: PEO/LiClO4/LLZTO(质量比为1.2:0.19:0.24); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: 原子层沉积(ALD)技术将钛酸锂沉积于碳黑表面以及钴酸锂极片表面, 沉积20次; 然后LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为90:6:4); 对比样正极组成: 原子层沉积技术将钛酸锂沉积于钴酸锂粉末表面. | LCO/Li, 2.7~4.5 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为80%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为32%. |
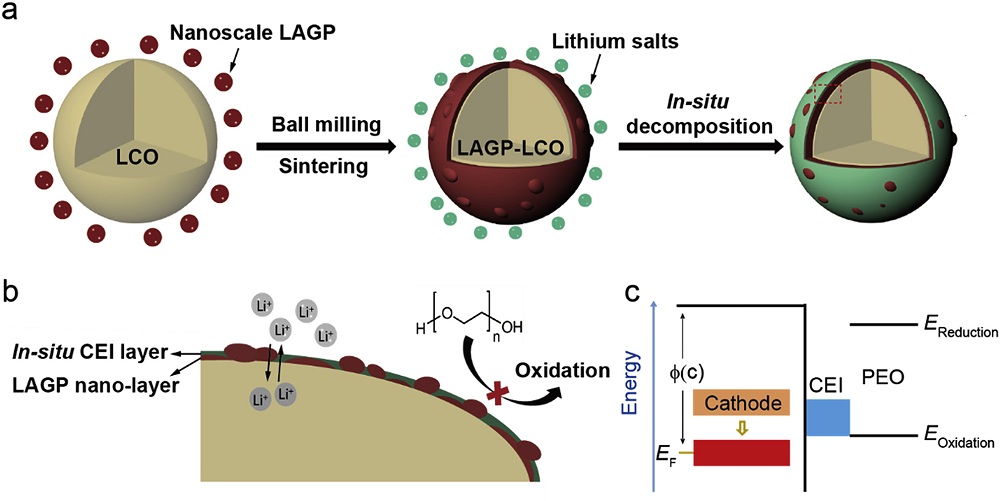
| 6[ | 使用富含羧基的水性粘结剂 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 电解质: PEO/LiClO4/LLZTO; PEO自支撑膜; (质量比为0.6:0.19:0.12); 实验样正极组成: LCO/SP/海藻酸钠(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/CMC羟甲基纤维素钠(质量比为8:1:1); 对比样正极组成: LCO/SP/PEO(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1). | LCO/Li, 2.7~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 对于粘结剂为Na-alginat及CMC的锂金属电池, 0.4 C循环1000圈容量保持率分别为63%及68%; 对比样: 对于粘结剂为PEO及PVDF的锂金属电池对比样, 0.4 C循环300圈容量保持率分别为40.1%及46%. |
| 7[ | 不对称固态聚合物电解质结构设计1 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 正极组成: LCO/SP/PMA/LiTFSI (质量比为50:6:10:5); 实验样: 双层电解质: PEO/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP(质量比为4:2:0.34), 靠近锂金属; PMA/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP(质量比为4:2:0.34), 靠近高电压正极; 对比样: PEO/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP (质量比为4:2:0.34). | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.25 V. 65 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为91.2%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环20圈容量保持率为67%. |
| 序号 | 提升方案 | 固态聚合物电解质组份, 以及正极组成 (负极均为锂金属) | 充放电电压区间和测试温度 | 循环性能及容量保持率 (包含对比样) |
| 8[ | 不对称固态聚合物电解质结构设计2 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 正极组成: LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 实验样三层电解质: PEO/LiTFSI质量比3:1 (添加5% (w) LiTFPFB), 靠近锂金属; PEO/LiTFSI/SN质量比7:7:6, 中间层; PEO/SN/LiTFPFB质量比7:7:6, 靠近高电压正极; 对比样1: 单层固态电解质PEO/LiTFSI/SN质量比7:7:6; 对比样2: 单层固态电解质PEO/LiTFSI质量比3:1; 电解质浇铸于纤维素无纺布. | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.3 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环100圈容量保持率为83.3%; 对比样1: 0.1 C循环46圈容量接近0; 对比样2: 0.1 C循环100圈容量保持率为43%. |
| 9[ | 原位形成耐高电压界面层 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 电解质: PEO/LiTFSI(质量比为1:0.65, 并向其中加入15%质量分数的二氧化硅纳米颗粒, 直径14 nm); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: NCM111/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LFP/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 将聚合后的PVC/LiTFSI溶液(质量比为1:0.287)浇铸于正极表面进行热聚合; 对比样正极组成: 没有VC聚合修饰的 NCM111/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1). | NCM111/Li, 2.8~4.25 V; LCO/Li, 2.8~4.2 V; LFP/Li, 2.8~3.8 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 采用NCM111、LCO、LFP三种正极材料的锂金属电池, 1 C下循环100圈容量保持率分别为75%、90%、99%; 对比样: NCM111正极材料1 C下循环100圈放电比容量接近0. |
| 10[ | -OCH3官能团封端PEO | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; PEG, Mn=400, 2000, 20000; PEGDME, Mn=20000; 正极组成: NCM532/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LFP/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 实验样电解质: PEGDME/LITFSI/LiFSI (其中, LITFSI/LiFSI的最优质量比为4:1; 整体EG/Li物质的量比12:1); PEO自支撑膜; 对比样电解质: PEO/LITFSI/LiFSI (LiTFSI/LiFSI质量比4:1; 整体EO/Li物质的量比12:1). | LFP/Li, 2.7~4.0 V; NCM532/Li, 2.5~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: LFP/Li: 0.33 C循环210圈容量保持率为97%; 实验样: NCM532/Li: 0.1 C循环110圈容量保持率为90%; 对比样: NCM532/Li: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为20%. |
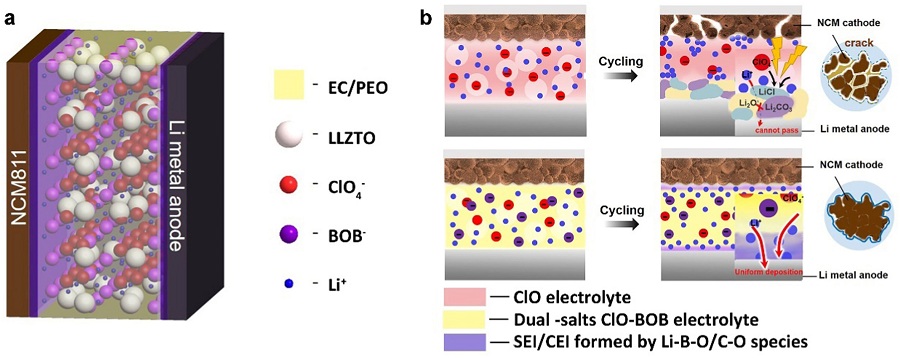
| 11[ | 含硼锂盐做添加剂 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000; 正极: NCM811; 实验样电解质组成: PEO/EC/LiClO4/LiBOB/LLZTO(质量比为8:4:1:0.4:1.6); PEO自支撑膜; 对比样电解质组成: PEO/EC/LiClO4/LLZTO(质量比为8:4:1:1.6). | NCM811/Li, 2.8~4.3 V. 25 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环200圈容量保持率为87%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环30圈左右比容量接近0. |
| 序号 | 提升方案 | 固态聚合物电解质组份, 以及正极组成 (负极均为锂金属) | 充放电电压区间和测试温度 | 循环性能及容量保持率 (包含对比样) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1[ | 高电压正极片表面修饰超薄聚合物层 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 固态电解质组成: PEO/LiDFOB/SN(质量比为10:1:9), 将PEO电解质浇铸于纤维素膜; 实验样: PECA-coated LCO/SP/PVDF/PEO(质量比为85:5:7:3), PECA为聚氰基丙烯酸酯; 对比样: 未经PECA修饰的钴酸锂正极, 配比同上. | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.45 V. 80 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环50圈容量保持率为67%; 对比样: 0.1 C循环50圈容量接近0. |
| 2[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆1 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000 ; 电解质: PEO-LiTFSI (EO/Li物质的量比18), PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: 1% (w) LATP(磷酸钛铝锂)包覆钴酸锂粉末; PEO/PVDF(质量比为2:1)分散于溶剂NMP中形成混合液; 包覆后钴酸锂/ SP/PEO/PVDF(质量比为75:10:10:5); 对比样正极: 未包覆的原始钴酸锂. | LCO/Li, 3~4.2 V; LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/Li, 3~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: LCO/Li: 0.2 C循环50圈容量保持率为88.6%; 实验样: LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/Li: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为90.3%; 对比样: 分别采用LiPF6、LiClO4、LiBOB、LiODFB四种锂盐, 在LCO/Li电池0.2 C倍率下分别循环24圈、22圈、27圈、3圈后, 放电容量已经接近0. |
| 3[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆2 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000; 固态电解质组成: PEO-LiTFSI (EO/Li物质的量比18); PEO自支撑膜; 正极组分: 1% (w) LATP包覆钴酸锂粉末; 包覆后钴酸锂/SP/PEO/PVDF(质量比为75:10:10:5). | LCO/Li, 3~4.5 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环7圈容量保持率为84%. |
| 4[ | 高电压正极颗粒 包覆3 | 原料: PEO, Mn: 10000; PEGDME, Mw: 500; 电解质: PEO-PEGDME-LiTFSI-LiBOB-LiPF6 其中LiTFSI/LiBOB/LiPF6(物质的量比为12:8:1); PEO/PEGDME(质量比为1:1); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极: 3.5% (w) LAGP(磷酸锗铝锂)包覆钴酸锂粉末, 包覆后钴酸锂/SP/PVDF(质量比为85:8:7); 对比样正极: 未包覆的钴酸锂; 锂盐: LiTFSI、LiBOB、LiPF6. | LCO/Li, 3~4.25 V; 3~4.3 V; 3~4.4 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 充电截止电压为4.25 V时, 0.5 C循环400圈容量保持率为81.9%; 充电截止电压为4.3 V时, 0.5 C循环200圈容量保持率为84.7%; 充电截止电压为4.4 V时, 0.5 C循环70圈容量保持率为88.1%; 对比样: 充电截止电压为4.3 V时0.5 C循环50圈容量保持率50%. |
| 5[ | 对碳黑颗粒进行包覆 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 固态聚合物电解质: PEO/LiClO4/LLZTO(质量比为1.2:0.19:0.24); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: 原子层沉积(ALD)技术将钛酸锂沉积于碳黑表面以及钴酸锂极片表面, 沉积20次; 然后LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为90:6:4); 对比样正极组成: 原子层沉积技术将钛酸锂沉积于钴酸锂粉末表面. | LCO/Li, 2.7~4.5 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为80%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为32%. |
| 6[ | 使用富含羧基的水性粘结剂 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 电解质: PEO/LiClO4/LLZTO; PEO自支撑膜; (质量比为0.6:0.19:0.12); 实验样正极组成: LCO/SP/海藻酸钠(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/CMC羟甲基纤维素钠(质量比为8:1:1); 对比样正极组成: LCO/SP/PEO(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1). | LCO/Li, 2.7~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 对于粘结剂为Na-alginat及CMC的锂金属电池, 0.4 C循环1000圈容量保持率分别为63%及68%; 对比样: 对于粘结剂为PEO及PVDF的锂金属电池对比样, 0.4 C循环300圈容量保持率分别为40.1%及46%. |
| 7[ | 不对称固态聚合物电解质结构设计1 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 正极组成: LCO/SP/PMA/LiTFSI (质量比为50:6:10:5); 实验样: 双层电解质: PEO/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP(质量比为4:2:0.34), 靠近锂金属; PMA/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP(质量比为4:2:0.34), 靠近高电压正极; 对比样: PEO/LiTFSI/PVDF-HFP (质量比为4:2:0.34). | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.25 V. 65 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为91.2%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环20圈容量保持率为67%. |
| 序号 | 提升方案 | 固态聚合物电解质组份, 以及正极组成 (负极均为锂金属) | 充放电电压区间和测试温度 | 循环性能及容量保持率 (包含对比样) |
| 8[ | 不对称固态聚合物电解质结构设计2 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 300000; 正极组成: LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 实验样三层电解质: PEO/LiTFSI质量比3:1 (添加5% (w) LiTFPFB), 靠近锂金属; PEO/LiTFSI/SN质量比7:7:6, 中间层; PEO/SN/LiTFPFB质量比7:7:6, 靠近高电压正极; 对比样1: 单层固态电解质PEO/LiTFSI/SN质量比7:7:6; 对比样2: 单层固态电解质PEO/LiTFSI质量比3:1; 电解质浇铸于纤维素无纺布. | LCO/Li, 2.5~4.3 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 0.1 C循环100圈容量保持率为83.3%; 对比样1: 0.1 C循环46圈容量接近0; 对比样2: 0.1 C循环100圈容量保持率为43%. |
| 9[ | 原位形成耐高电压界面层 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; 电解质: PEO/LiTFSI(质量比为1:0.65, 并向其中加入15%质量分数的二氧化硅纳米颗粒, 直径14 nm); PEO自支撑膜; 实验样正极组成: NCM111/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LCO/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LFP/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 将聚合后的PVC/LiTFSI溶液(质量比为1:0.287)浇铸于正极表面进行热聚合; 对比样正极组成: 没有VC聚合修饰的 NCM111/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1). | NCM111/Li, 2.8~4.25 V; LCO/Li, 2.8~4.2 V; LFP/Li, 2.8~3.8 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: 采用NCM111、LCO、LFP三种正极材料的锂金属电池, 1 C下循环100圈容量保持率分别为75%、90%、99%; 对比样: NCM111正极材料1 C下循环100圈放电比容量接近0. |
| 10[ | -OCH3官能团封端PEO | 原料: PEO, Mw: 1000000; PEG, Mn=400, 2000, 20000; PEGDME, Mn=20000; 正极组成: NCM532/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); LFP/SP/PVDF(质量比为8:1:1); 实验样电解质: PEGDME/LITFSI/LiFSI (其中, LITFSI/LiFSI的最优质量比为4:1; 整体EG/Li物质的量比12:1); PEO自支撑膜; 对比样电解质: PEO/LITFSI/LiFSI (LiTFSI/LiFSI质量比4:1; 整体EO/Li物质的量比12:1). | LFP/Li, 2.7~4.0 V; NCM532/Li, 2.5~4.2 V. 60 ℃ | 实验样: LFP/Li: 0.33 C循环210圈容量保持率为97%; 实验样: NCM532/Li: 0.1 C循环110圈容量保持率为90%; 对比样: NCM532/Li: 0.2 C循环100圈容量保持率为20%. |
| 11[ | 含硼锂盐做添加剂 | 原料: PEO, Mw: 600000; 正极: NCM811; 实验样电解质组成: PEO/EC/LiClO4/LiBOB/LLZTO(质量比为8:4:1:0.4:1.6); PEO自支撑膜; 对比样电解质组成: PEO/EC/LiClO4/LLZTO(质量比为8:4:1:1.6). | NCM811/Li, 2.8~4.3 V. 25 ℃ | 实验样: 0.2 C循环200圈容量保持率为87%; 对比样: 0.2 C循环30圈左右比容量接近0. |








| [1] |
Cao, X.; Jia, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.-G. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 010522.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd60e |
| [2] |
Jiang, L. L.; Yan, C.; Yao, Y. X.; Cai, W.; Huang, J. Q.; Zhang, Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3402.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202009738 |
| [3] |
Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Paek, E.; Wang, Y.; Mitlin, D. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 382.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE02423F |
| [4] |
Nikiforidis, G.; Raghibi, M.; Sayegh, A.; Anouti, M. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1911.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03736 pmid: 33591750 |
| [5] |
Wei, C.; Tan, L.; Tao, Y.; An, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Feng, J.; Qian, Y. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 34, 12.
|
| [6] |
Chai, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Ma, J.; Du, H.; Yue, L.; Zhao, J.; Wen, H.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5191.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA00828C |
| [7] |
Chatterjee, K.; Pathak, A. D.; Lakma, A.; Sharma, C. S.; Sahu, K. K.; Singh, A. K. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9606.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66341-x pmid: 32541876 |
| [8] |
Hou, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Ohma, A.; Ren, D.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ootani, I.; Han, X.; Ren, W.; He, X.; Nitta, Y.; Ouyang, M. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5100.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18868-w |
| [9] |
Wang, J.; Yamada, Y.; Sodeyama, K.; Watanabe, E.; Takada, K.; Tateyama, Y.; Yamada, A. Nat. Energy 2017, 3, 22.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-017-0033-8 |
| [10] |
Liu, K.; Liu, Y. Y.; Lin, D. C.; Pei, A.; Cui, Y. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 11.
|
| [11] |
He, M.; Su, C.-C.; Peebles, C.; Zhang, Z. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 010505.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd44b |
| [12] |
Köps, L.; Leibing, C.; Hess, L. H.; Balducci, A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 010513.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd604 |
| [13] |
Taskovic, T.; Thompson, L. M.; Eldesoky, A.; Lumsden, M. D.; Dahn, J. R. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 010514.
doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd833 |
| [14] |
Xia, L.; Miao, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 9936.
doi: 10.1002/er.6488 |
| [15] |
Dong, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; Chai, J.; Du, H.; Wang, L.; Wen, H.; Zang, X.; Du, A.; Jia, Q.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1197.
doi: 10.1039/C7EE03365F |
| [16] |
Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903939.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903939 |
| [17] |
Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cui, G. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800337.
doi: 10.1002/mame.201800337 |
| [18] |
Cheng, H.; Zhu, C.-B.; Yang, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2007, 65, 2832. (in Chinese)
|
|
(程琥, 朱昌宝, 杨勇, 化学学报, 2007, 65, 2832.)
|
|
| [19] |
Liao, R.-X.; Shen, Z.-C.; Xie, W.-H.; Zhong, J.-W.; Shi, Z.-C. Sci. Sinica Chim. 2022, 52, 38. (in Chinese)
|
|
(廖睿熹, 沈之川, 谢文浩, 钟嘉炜, 施志聪, 中国科学:化学, 2022, 52, 38.)
|
|
| [20] |
Zheng, P.-X.; Wang, X.-W.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.-W. Acta Polym. Sinica 2021, 52, 94. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郑鹏轩, 王向伟, 王栋, 于志伟, 高分子学报, 2021, 52, 94.)
|
|
| [21] |
Wang, X.; Yang, J.-J.; Shao, L.; Li, J.-J.; Zhao, W.-F.; Ma, A.-J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W.-X. Sci. Sinica Chim. 2019, 49, 360. (in Chinese)
|
|
(汪勋, 杨晶晶, 邵乐, 李娇娇, 赵卫峰, 马爱洁, 张改, 陈卫星, 中国科学:化学, 2019, 49, 360.)
|
|
| [22] |
Wan, J.; Xie, J.; Kong, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Shi, F.; Pei, A.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zong, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Q.; Qin, J.; Cui, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 705.
doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0465-3 |
| [23] |
Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Engelhard, M. H.; Ding, M. S.; El-Khoury, P. Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Xu, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.-G.; Xu, W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902108.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201902108 |
| [24] |
Xu, S.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, G.; Cheng, H.-M.; Li, F. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2007172.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.202007172 |
| [25] |
Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Yue, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A3454.
doi: 10.1149/2.0221714jes |
| [26] |
Qiu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Gan, L.; Lee, S.-J.; Nordlund, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Bai, X.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909392.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909392 |
| [27] |
Nie, K.; Wang, X.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 826.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02739 |
| [28] |
Li, Z.; Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Lin, R.; Jin, T.; Cheng, Q.; Xiao, X.; Lee, W.-K.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Zangiabadi, A.; Waluyo, I.; Hunt, A.; Zhai, H.; Borovilas, J. J.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.-Q.; Chuan, X.; Yang, Y. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104655.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104655 |
| [29] |
Liang, J. N.; Sun, Y. P.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhao, F. P.; Lin, X. T.; Li, X.; Li, R. Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S. G.; Huang, H.; Sun, X. L. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2769.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA08607B |
| [30] |
Liang, J.; Chen, D.; Adair, K.; Sun, Q.; Holmes, N. G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Lu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Singh, C. V.; Sun, X. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002455.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.202002455 |
| [31] |
Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Pu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xin, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Goodenough, J. B. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805574.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201805574 |
| [32] |
Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Li, J.; Dong, S.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901036.
doi: 10.1002/advs.201901036 |
| [33] |
Bae, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Yu, G. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1184.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04959 |
| [34] |
Yang, X.; Jiang, M.; Gao, X.; Bao, D.; Sun, Q.; Holmes, N.; Duan, H.; Mukherjee, S.; Adair, K.; Zhao, C.; Liang, J.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Lu, Q.; Li, R.; Singh, C. V.; Sun, X. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 1318.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE00342E |
| [35] |
Samson, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F. Y.; Zhao, L.; Fan, R.; Chung, C. Y.; Tang, J. N.; Zeng, X. R.; He, Y. B. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105562.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105562 |
| [36] |
Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Jiang, F.; Sun, X.; Du, A.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900355.
doi: 10.1002/advs.201900355 |
| [37] |
Xu, G.; Pang, C.; Chen, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Chai, J.; Wang, Q.; An, W.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701398.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201701398 |
| [38] |
Xia, Y.; Fujieda, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Prosini, P.; Sakai, T. J. Power Sources 2001, 92, 234.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00533-4 |
| [39] |
Han, Y.; Zhu, X.; He, Y.; Wang, C. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501590.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201501590 |
| [1] | Xia Lan, Yu Linpo, Hu Di, Chen Z. George. Research Progress and Perspectives on High Voltage, Flame Retardant Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(12): 1183-1195. |
| [2] | WANG Rong, Gu-Zheng-Beng, DONG E-Lei, CHEN Xin-Guo, XIE Hua, MA Jun, ZHANG Jiang, ZHANG Jun-Chi, XIN Xiao-Ting, LI Wen-Bin, WANG Juan. Mechanism of the DNA Separation with High Performance Capillary Electrophoresis in Poly(ethylene oxide) Matrix [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2010, 68(03): 269-275. |
| [3] | ZHENG Yun*,1, ZHANG Xue-Qin, XIE Hong-Feng, YANG Hu, WANG Zhi-Liu, CHENG Rong-Shi*,1,2. Formation of Multicolored Ring Stripes on PEO Spherulites [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(9): 829-832. |
| [4] | ZHOU Jie1,2, FU Xiang-Kai*,1,2, SUN Mei-Dan1,2, LUO Wei1,2. Study of the Preparation and Electrochromic Performance of PEO-Doped NiO Films by Sol-Gel Method [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(10): 1004-1010. |
| [5] | ZHOU Shi-Yi, LEI Jing-Xin*, SUN Zhong-Wu, LI Qi-Man. Study on Novel Soft Poly(vinyl Chloride) with Antistatic Property [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(10): 979-982. |
| [6] | SUN Ming-Bo1,2, HOU Wan-Guo*,1, SUN De-Jun, DAI Xiao-Nan. Interaction Mechanism Study on Poly(ethylene oxide)-Clay-Alkali Metal Ion Intercalation Composites [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(7): 562-566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||