Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (12): 1234-1240.DOI: 10.6023/A24090276 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
许木榕a, 周纯b, 王子慧a, 杨丽冰a, 李晨远a, 卓炜丰a, 王行之b,*( ), 杜克钊a,*(
), 杜克钊a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-09-12
发布日期:2024-12-01
基金资助:
Murong Xua, Chun Zhoub, Zihui Wanga, Libing Yanga, Chenyuan Lia, Weifeng Zhuoa, Xingzhi Wangb( ), Kezhao Dua(
), Kezhao Dua( )
)
Received:2024-09-12
Published:2024-12-01
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Murong Xu, Chun Zhou, Zihui Wang, Libing Yang, Chenyuan Li, Weifeng Zhuo, Xingzhi Wang, Kezhao Du. Solid-State Bromine for Bromide Synthesis, a Case Study of CrSBr[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(12): 1234-1240.
| 序号 | 溴源 | 管子长度 | 条件a | 实验结果 | 是否成功 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 24 cm | 溴源端分开 | CrSBr | √ | 针状黑色晶体产出 |
| 2 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 10 cm | 溴源端分开 | Cr0.67S | × | 两端温差为100 ℃, 不利于CrSBr合成 |
| 3 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开 | Cr0.67S | × | 无法较好释放溴素 |
| 4 | KBrO3+KBr | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开 | 爆管 | × | 原料对石英管具有一定腐蚀性 |
| 5 | KBrO3+KBr | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开, 镀膜b | Cr2O3 | × | KBrO3高温分解, 提供溴源不稳定 |
| 6 | CsBr3 | — | 溴源端未分开 | — | × | CsBr3不稳定, 未封管已变为白色CsBr |
| 7 | C16H36NBr3 | 13 cm | 溴源端未分开 | 爆管 | × | 有机物碳化, 导致气压上升 |
| 序号 | 溴源 | 管子长度 | 条件a | 实验结果 | 是否成功 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 24 cm | 溴源端分开 | CrSBr | √ | 针状黑色晶体产出 |
| 2 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 10 cm | 溴源端分开 | Cr0.67S | × | 两端温差为100 ℃, 不利于CrSBr合成 |
| 3 | Cs4Sb2Br12 | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开 | Cr0.67S | × | 无法较好释放溴素 |
| 4 | KBrO3+KBr | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开 | 爆管 | × | 原料对石英管具有一定腐蚀性 |
| 5 | KBrO3+KBr | 24 cm | 溴源端未分开, 镀膜b | Cr2O3 | × | KBrO3高温分解, 提供溴源不稳定 |
| 6 | CsBr3 | — | 溴源端未分开 | — | × | CsBr3不稳定, 未封管已变为白色CsBr |
| 7 | C16H36NBr3 | 13 cm | 溴源端未分开 | 爆管 | × | 有机物碳化, 导致气压上升 |
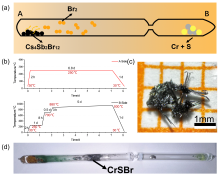




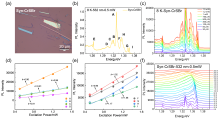

| [1] |
Wang, Q. H.; Bedoya-Pinto, A.; Blei, M.; Dismukes, A. H.; Hamo, A.; Jenkins, S.; Koperski, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q. C.; Telford, E. J.; Kim, H. H.; Augustin, M.; Vool, U.; Yin, J. X.; Li, L. H.; Falin, A.; Dean, C. R.; Casanova, F.; Evans, R. F. L.; Chshiev, M.; Mishchenko, A.; Petrovic, C.; He, R.; Zhao, L.; Tsen, A. W.; Gerardot, B. D.; Brotons-Gisbert, M.; Guguchia, Z.; Roy, X.; Tongay, S.; Wang, Z.; Hasan, M. Z.; Wrachtrup, J.; Yacoby, A.; Fert, A.; Parkin, S.; Novoselov, K. S.; Dai, P.; Balicas, L.; Santos, E. J. G. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6960.
|
| [2] |
Ziebel, M. E.; Feuer, M. L.; Cox, J.; Zhu, X.; Dean, C. R.; Roy, X. Nano Lett 2024, 24, 4319.
|
| [3] |
Dirnberger, F.; Quan, J.; Bushati, R.; Diederich, G. M.; Florian, M.; Klein, J.; Mosina, K.; Sofer, Z.; Xu, X.; Kamra, A.; García-Vidal, F. J.; Alù, A.; Menon, V. M. Nature 2023, 620, 533.
|
| [4] |
Bae, Y.; Wang, J.; Scheie, A.; Xu, J.-W.; Chica, D. G.; Diederich, G.; Cenker, J.; Ziebel, M. E.; Bai, Y.; Ren, H.; Dean, C.; Delor, M.; Xu, X.; Roy, X.; Kent, A.; Zhu, X. Nature 2022, 609, 282.
|
| [5] |
Boix-Constant, C.; Jenkins, S.; Rama-Eiroa, R.; Santos, E. J. G.; Mañas-Valero, S.; Coronado, E. Nat. Mater. 2023, 23, 212.
|
| [6] |
Burch, K. S.; Mandrus, D.; Park, J.-G. Nature 2018, 563, 47.
|
| [7] |
Gong, C.; Zhang, X. Science 2019, 363, 706.
|
| [8] |
Tabataba-Vakili, F.; Nguyen, H. P. G.; Rupp, A.; Mosina, K.; Papavasileiou, A.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Maletinsky, P.; Glazov, M. M.; Sofer, Z.; Baimuratov, A. S.; Högele, A. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4735.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49048-9 pmid: 38830857 |
| [9] |
Tschudin, M. A.; Broadway, D. A.; Siegwolf, P.; Schrader, C.; Telford, E. J.; Gross, B.; Cox, J.; Dubois, A. E. E.; Chica, D. G.; Rama-Eiroa, R.; Santos, E. J. G.; Poggio, M.; Ziebel, M. E.; Dean, C. R.; Roy, X.; Maletinsky, P. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6005.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49717-9 pmid: 39019853 |
| [10] |
Beck, J. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1990, 585, 157.
|
| [11] |
Lopez-Paz, S. A.; Guguchia, Z.; Pomjakushin, V. Y.; Witteveen, C.; Cervellino, A.; Luetkens, H.; Casati, N.; Morpurgo, A. F.; von Rohr, F. O. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4745.
|
| [12] |
Klein, J.; Pham, T.; Thomsen, J. D.; Curtis, J. B.; Denneulin, T.; Lorke, M.; Florian, M.; Steinhoff, A.; Wiscons, R. A.; Luxa, J.; Sofer, Z.; Jahnke, F.; Narang, P.; Ross, F. M. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5420.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32737-8 pmid: 36109520 |
| [13] |
Long, F.; Mosina, K.; Hübner, R.; Sofer, Z.; Klein, J.; Prucnal, S.; Helm, M.; Dirnberger, F.; Zhou, S. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 222401.
|
| [14] |
Scheie, A.; Ziebel, M.; Chica, D. G.; Bae, Y. J.; Wang, X.; Kolesnikov, A. I.; Zhu, X.; Roy, X. J. A. S. 2022, 9, 2202467.
|
| [15] |
Lin, H.; Ma, R.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, M.; Lin, Y.; Du, K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 62. (in Chinese)
|
|
(林航青, 马若茹, 江怡蓝, 许木榕, 林洋彭, 杜克钊, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 62.)
doi: 10.6023/A23080392 |
|
| [16] |
Lin, Y.-P.; Huang, X.-Y.; Du, K.-Z. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 280, 125820.
|
| [17] |
Lin, Y. P.; Xia, B.; Hu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y. E.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Wu, N.; Wu, Y. W.; Wu, X. H.; Huang, X. Y.; Xiao, Z.; Du, K. Z. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 535.
|
| [18] |
Lin, K.; Li, Y.; Ghorbani-Asl, M.; Sofer, Z.; Winnerl, S.; Erbe, A.; Krasheninnikov, A.; Helm, M.; Zhou, S.; Dan, Y.; Prucnal, S. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 6010.
|
| [19] |
Wilson, N. P.; Lee, K.; Cenker, J.; Xie, K.; Dismukes, A. H.; Telford, E. J.; Fonseca, J.; Sivakumar, S.; Dean, C.; Cao, T.; Roy, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1657.
|
| [20] |
Pawbake, A.; Pelini, T.; Wilson, N.; Mosina, K.; Sofer, Z.; Heid, R.; Faugeras, C. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 075421.
|
| [21] |
Torres, K.; Kuc, A.; Maschio, L.; Pham, T.; Reidy, K.; Dekanovsky, L.; Sofer, Z.; Ross, F. M.; Klein, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211366.
|
| [22] |
Lin, K.; Sun, X.; Dirnberger, F.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Wen, P.; Sofer, Z.; Söll, A.; Winnerl, S.; Helm, M.; Zhou, S.; Dan, Y.; Prucnal, S. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 2898.
|
| [23] |
Klein, J.; Song, Z.; Pingault, B.; Dirnberger, F.; Chi, H.; Curtis, J. B.; Dana, R.; Bushati, R.; Quan, J.; Dekanovsky, L.; Sofer, Z.; Alu, A.; Menon, V. M.; Moodera, J. S.; Loncar, M.; Narang, P.; Ross, F. M. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 288.
|
| [24] |
Klein, J.; Pingault, B.; Florian, M.; Heißenbüttel, M.-C.; Steinhoff, A.; Song, Z.; Torres, K.; Dirnberger, F.; Curtis, J. B.; Weile, M.; Penn, A.; Deilmann, T.; Dana, R.; Bushati, R.; Quan, J.; Luxa, J.; Sofer, Z.; Alù, A.; Menon, V. M.; Wurstbauer, U.; Rohlfing, M.; Narang, P.; Lončar, M.; Ross, F. M. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 5316.
|
| [25] |
Marques-Moros, F.; Boix-Constant, C.; Mañas-Valero, S.; Canet-Ferrer, J.; Coronado, E. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 13224.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c00375 pmid: 37442121 |
| [1] | Fen Zhang, Xiaoqi Li, Shiguo Han, Fafa Wu, Xitao Liu, Zhihua Sun, Junhua Luo. Bulk Single Crystal Growth of a Two-Dimensional Halide Perovskite Ferroelectric for Highly Polarized-Sensitive Photodetection※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 237-243. |
| [2] | Jiazheng Zhou, Xiao Xu, Biwen Duan, Jiangjian Shi, Yanhong Luo, Huijue Wu, Dongmei Li, Qingbo Meng. Research Progress of Metal(I) Substitution in Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 Thin Film Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 303-318. |
| [3] | Qian Chen, Qin Kuang, Zhaoxiong Xie. Research Progress of Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Based on Two-dimensional Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 10-22. |
| [4] | Wang Wenbin, Wen Qunlei, Liu Youwen, Zhai Tianyou. Research Progress of Surface and Interface Chemistry Regulate Two-dimensional Materials for Electrocatalytic Biomass Conversion [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(11): 1185-1199. |
| [5] | Zhang Dandan, Yuan Zhenzhou, Zhang Guoqing, Tian Nan, Liu Danmin, Zhang Yongzhe. Preparation and Characterization of Black Phosphorus [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(7): 537-542. |
| [6] | He Xuexia, Liu Fucai, Zeng Qingsheng, Liu Zheng. Electric-double-layer Transistors Based on Two Dimensional Materials [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(9): 924-935. |
| [7] | Wang Lu, Gao Junfeng, Ding Feng. Application of Crystal Growth Theory in Graphene CVD Nucleation and Growth [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014, 72(3): 345-358. |
| [8] | . Diffusion Mass Transfer in Lysozyme Crystal Growth [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 67(4): 307-312. |
| [9] | ZHAO Gang*,1; LIU Zhi-Feng2; YANG Rui3; CHENG Shu-Xia2. Study on Non-equilibrium Phase Transformation of Intracellular Wa-ter during Freezing Process [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2007, 65(4): 295-299. |
| [10] | DAI Guo-Liang*; PENG Ling; XIE Ying; KANG Qi; HU Wen-Rui. Effect of Intermolecular Interaction on Protein Crystal Growth [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2007, 65(17): 1767-1772. |
| [11] | YU Yong*,1, CHEN Wan-Chun1,2, KANG Qi, LIU Dao-Dan1,2, DAI Guo-Liang, CUI Hai-Liang. Study on Growth Mechanism of Lysozyme Crystal Grown by Batch Crystallization Method [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(12): 1284-1290. |
| [12] | DAI Guo-Liang*, DAI Lian-Hua, YU Yong, XIE Ying. Preparation and Crystallization Preinvestigation of the Fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate Derivatives of Chicken Egg White Lysozyme [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(7): 559-561. |
| [13] | DAI Guo-Liang, YU Yong, KANG Qi, HU Wen-Rui. Study of the Aggregates in Lysozyme Solution before Crystal Growth [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2004, 62(8): 757-761. |
| [14] | Dai Guoliang;Hu Wenrui. Effect of NaCl on Liquid/Liquid Diffusion Lysozyme Crystal Growth [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2003, 61(4): 520-525. |
| [15] | Dong Weiyang;Ren Yu;Zhou Weizheng;Long Yingcai. Studies on Zeolite Synthesis by Self-transformation of B-Containing Porous Glass in a Vapor Phase II . Self-transformation Kinetics [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2003, 61(2): 251-255. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||