Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (4): 428-438.DOI: 10.6023/A24120375 Previous Articles
Review
投稿日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-02-14
作者简介: |
李帅, 博士, 分别于2018年和2023年获得天津大学化工学院学士和博士学位, 目前在天津大学浙江研究院进行博士后研究, 主要从事外泌体分离方法和癌症早期诊断研究. |
 |
刘亚婷, 于2021年取得安徽工程大学学士学位, 2024年取得沈阳医科大学硕士学位, 现为苏州亿弗生物科技有限公司研发工程师, 研究方向为外泌体分离技术和产品的研发. |
 |
仰大勇, 博士, 复旦大学“瑞清”特聘讲席教授, 天津大学兼职教授. 国家杰出青年科学基金、国家优秀青年科学基金获得者, 入选海外高层次人才计划. 研究方向为核酸化学与功能材料, 在Chem. Rev.、Acc. Chem. Res.、PNAS、J. Am. Chem. Soc.、Angew. Chem.、Nat. Commun.、Sci. Adv.、Nat. Protoc.和Adv. Mater.等杂志发表学术论文150余篇. |
基金资助:
Shuai Lia,b, Yating Liuc, Dayong Yanga( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Published:2025-02-14
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Shuai Li, Yating Liu, Dayong Yang. Recent Progress on Exosome Separation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(4): 428-438.

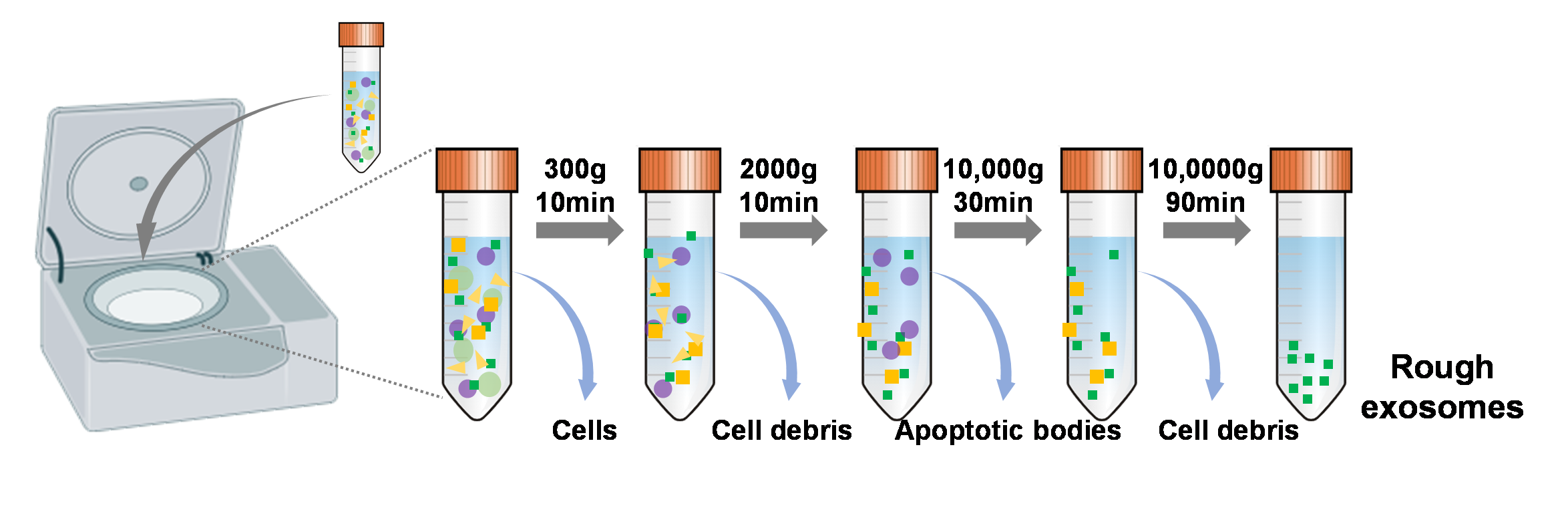
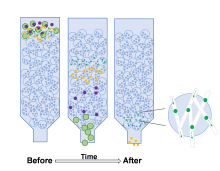

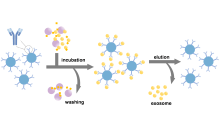




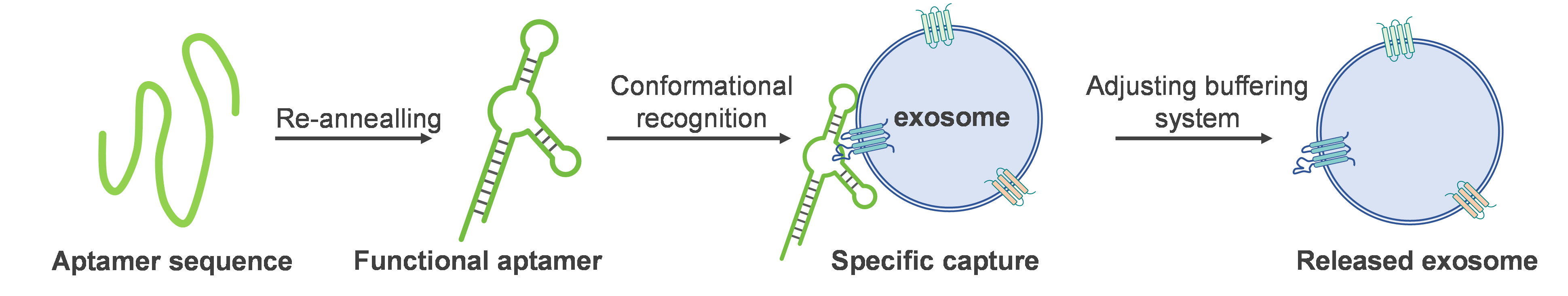
| 方法 | 纯度 | 得率 | 成本 | 分离时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 超速离心 | 低 | 中等 | 中等 | 长(4~6 h) |
| 超滤 | 较低 | 较高 | 较高 | 短(1~2 h) |
| 尺寸排阻色谱 | 较高 | 中等 | 较高 | 短(0.5~2 h) |
| 聚合物沉淀 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 长(2~12 h) |
| 免疫亲和 | 高 | 低 | 高 | 中等(2~4 h) |
| 微流控 | 高 | 高 | 高 | 短(0.5~1 h) |
| DNA适配体 亲和 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 中等(2~4 h) |
| 基于流体流动的分离 | 中等 | 中等 | 高 | 短(1~2 h) |
| 热泳 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 短(0.5~1 h) |
| 磷脂识别分离 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 中等(2~3 h) |
| 方法 | 纯度 | 得率 | 成本 | 分离时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 超速离心 | 低 | 中等 | 中等 | 长(4~6 h) |
| 超滤 | 较低 | 较高 | 较高 | 短(1~2 h) |
| 尺寸排阻色谱 | 较高 | 中等 | 较高 | 短(0.5~2 h) |
| 聚合物沉淀 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 长(2~12 h) |
| 免疫亲和 | 高 | 低 | 高 | 中等(2~4 h) |
| 微流控 | 高 | 高 | 高 | 短(0.5~1 h) |
| DNA适配体 亲和 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 中等(2~4 h) |
| 基于流体流动的分离 | 中等 | 中等 | 高 | 短(1~2 h) |
| 热泳 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 短(0.5~1 h) |
| 磷脂识别分离 | 高 | 中等 | 高 | 中等(2~3 h) |
| [1] |
Kimiz-Gebologlu, I.; Oncel, S. S. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 533.
|
| [2] |
Johnstone, R. M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J. R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412.
pmid: 3597417 |
| [3] |
Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V. S. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977.
|
| [4] |
Welsh, J. A.; Goberdhan, D. C. I.; O'Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E. I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T. A. P.; Erdbrügger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J. M.; Fu, Q. L.; Hill, A. F.; Lenassi, M.; Lim, S. K.; Mahoney, M. G.; Mohanty, S.; Möller, A.; Nieuwland, R.; Ochiya, T.; Sahoo, S.; Torrecilhas, A. C.; Zheng, L.; Zijlstra, A.; Abuelreich, S.; Bagabas, R.; Bergese, P.; Bridges, E. M.; Brucale, M.; Burger, D.; Carney, R. P.; Cocucci, E.; Crescitelli, R.; Hanser, E.; Harris, A. L.; Haughey, N. J.; Hendrix, A.; Ivanov, A. R.; Jovanovic-Talisman, T.; Kruh-Garcia, N. A.; Ku'ulei-Lyn Faustino, V.; Kyburz, D.; Lässer, C.; Lennon, K. M.; Lötvall, J.; Maddox, A. L.; Martens-Uzunova, E. S.; Mizenko, R. R.; Newman, L. A.; Ridolfi, A.; Rohde, E.; Rojalin, T.; Rowland, A.; Saftics, A.; Sandau, U. S.; Saugstad, J. A.; Shekari, F.; Swift, S.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Tosar, J. P.; Useckaite, Z.; Valle, F.; Varga, Z.; van der Pol, E.; van Herwijnen, M. J. C.; Wauben, M. H. M.; Wehman, A. M.; Williams, S.; Zendrini, A.; Zimmerman, A. J.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K. W. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404.
|
| [5] |
Rahimian, S.; Najafi, H.; Afzali, B.; Doroudian, M. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 123.
|
| [6] |
Hoshino, A.; Kim, H. S.; Bojmar, L.; Gyan, K. E.; Cioffi, M.; Hernandez, J.; Zambirinis, C. P.; Rodrigues, G.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; Mark, M. T.; Steiner, L.; Benito-Martin, A.; Lucotti, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Offer, K.; Nakajima, M.; Williams, C.; Nogues, L.; Vatter, F. A. P.; Hashimoto, A.; Davies, A. E.; Freitas, D.; Kenific, C. M.; Ararso, Y.; Buehring, W.; Lauritzen, P.; Ogitani, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Takahashi, N.; Aleckovic, M.; Bailey, K. A.; Jolissant, J. S.; Wang, H.; Harris, A.; Schaeffer, L. M.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Posner, Z.; Balachandran, V. P.; Khakoo, Y.; Raju, G. P.; Scherz, A.; Sagi, I.; Scherz-Shouval, R.; Yarden, Y.; Oren, M.; Malladi, M.; Petriccione, M.; De Braganca, K. C.; Donzelli, M.; Fischer, C.; Vitolano, S.; Wright, G. P.; Ganshaw, L.; Marrano, M.; Ahmed, A.; DeStefano, J.; Danzer, E.; Roehrl, M. H. A.; Lacayo, N. J.; Vincent, T. C.; Weiser, M. R.; Brady, M. S.; Meyers, P. A.; Wexler, L. H.; Ambati, S. R.; Chou, A. J.; Slotkin, E. K.; Modak, S.; Roberts, S. S.; Basu, E. M.; Diolaiti, D.; Krantz, B. A.; Cardoso, F.; Simpson, A. L.; Berger, M.; Rudin, C. M.; Simeone, D. M.; Jain, M.; Ghajar, C. M.; Batra, S. K.; Stanger, B. Z.; Bui, J.; Brown, K. A.; Rajasekhar, V. K.; Healey, J. H.; de Sousa, M.; Kramer, K.; Sheth, S.; Baisch, J.; Pascual, V.; Heaton, T. E.; La Quaglia, M. P.; Pisapia, D. J.; Schwartz, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Shukla, A.; Blavier, L.; DeClerck, Y. A.; LaBarge, M.; Bissell, M. J.; Caffrey, T. C.; Grandgenett, P. M.; Hollingsworth, M. A.; Bromberg, J.; Costa-Silva, B.; Peinado, H.; Kang, Y.; Garcia, B. A.; O'Reilly, E. M.; Kelsen, D.; Trippett, T. M.; Jones, D. R.; Matei, I. R.; Jarnagin, W. R.; Lyden, D. Cell 2020, 182, 1044.
doi: S0092-8674(20)30874-6 pmid: 32795414 |
| [7] |
Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56.
|
| [8] |
Yang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wu, K.; Li, D. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 2269.
|
| [9] |
Shi, J.; Sun, Y.; Fan, W.; Ren, W.; Liu, C. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 2151.
|
| [10] |
Mizenko, R. R.; Feaver, M.; Bozkurt, B. T.; Lowe, N.; Nguyen, B.; Huang, K.-W.; Wang, A.; Carney, R. P. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12510.
|
| [11] |
Rasihashemi, S. Z.; Sahrai, H.; Rezazadeh-Gavgani, E.; Yazdani, Y.; Khalaji, A.; Lotfinejad, P. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 183.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01781-1 pmid: 36071295 |
| [12] |
Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Larcher, L. M.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q.; Tran, P. H. L.; Chen, C.; Veedu, R. N.; Wang, T. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684.
|
| [13] |
Livshits, M. A.; Khomyakova, E.; Evtushenko, E. G.; Lazarev, V. N.; Kulemin, N. A.; Semina, S. E.; Generozov, E. V.; Govorun, V. M. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17319.
doi: 10.1038/srep17319 pmid: 26616523 |
| [14] |
Johnstone, R. M. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1992, 70, 179.
|
| [15] |
Jeppesen, D. K.; Hvam, M. L.; Primdahl-Bengtson, B.; Boysen, A. T.; Whitehead, B.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Orntoft, T. F.; Howard, K. A.; Ostenfeld, M. S. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 25011.
doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.25011 pmid: 25396408 |
| [16] |
Wan, Z.; Gu, J.; Balaji, U.; Bojmar, L.; Molina, H.; Heissel, S.; Pagano, A. E.; Peralta, C.; Shaashua, L.; Ismailgeci, D.; Narozniak, H. K.; Song, Y.; Jarnagin, W. R.; Kelsen, D. P.; Bromberg, J.; Pascual, V.; Zhang, H. J. Extracell. Bio. 2024, 3, e167.
|
| [17] |
Thery, C.; Witwer, K. W.; Aikawa, E.; Jose Alcaraz, M.; Anderson, J. D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G. K.; Ayre, D. C.; Bach, J.-M.; Bachurski, D.; Baharvand, H.; Balaj, L.; Baldacchino, S.; Bauer, N. N.; Baxter, A. A.; Bebawy, M.; Beckham, C.; Zavec, A. B.; Benmoussa, A.; Berardi, A. C.; Bergese, P.; Bielska, E.; Blenkiron, C.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Boilard, E.; Boireau, W.; Bongiovanni, A.; Borras, F. E.; Bosch, S.; Boulanger, C. M.; Breakefield, X.; Breglio, A. M.; Brennan, M. A.; Brigstock, D. R.; Brisson, A.; Broekman, M. L. D.; Bromberg, J. F.; Bryl-Gorecka, P.; Buch, S.; Buck, A. H.; Burger, D.; Busatto, S.; Buschmann, D.; Bussolati, B.; Buzas, E. I.; Byrd, J. B.; Camussi, G.; Carter, D. R. F.; Caruso, S.; Chamley, L. W.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Cheng, L.; Chin, A. R.; Clayton, A.; Clerici, S. P.; Cocks, A.; Cocucci, E.; Coffey, R. J.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Couch, Y.; Coumans, F. A. W.; Coyle, B.; Crescitelli, R.; Criado, M. F.; D'Souza-Schorey, C.; Das, S.; Chaudhuri, A. D.; de Candia, P.; De Santana Junior, E. F.; De Wever, O.; del Portillo, H. A.; Demaret, T.; Deville, S.; Devitt, A.; Dhondt, B.; Di Vizio, D.; Dieterich, L. C.; Dolo, V.; Dominguez Rubio, A. P.; Dominici, M.; Dourado, M. R.; Driedonks, T. A. P.; Duarte, F. V.; Duncan, H. M.; Eichenberger, R. M.; Ekstrom, K.; Andaloussi, S. E. L.; Elie-Caille, C.; Erdbrugger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J. M.; Fatima, F.; Fish, J. E.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Forsonits, A.; Frelet-Barrand, A.; Fricke, F.; Fuhrmann, G.; Gabrielsson, S.; Gamez-Valero, A.; Gardiner, C.; Gaertner, K.; Gaudin, R.; Gho, Y. S.; Giebel, B.; Gilbert, C.; Gimona, M.; Giusti, I.; Goberdhan, D. C. I.; Goergens, A.; Gorski, S. M.; Greening, D. W.; Gross, J. C.; Gualerzi, A.; Gupta, G. N.; Gustafson, D.; Handberg, A.; Haraszti, R. A.; Harrison, P.; Hegyesi, H.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A. F.; Hochberg, F. H.; Hoffmann, K. F.; Holder, B.; Holthofer, H.; Hosseinkhani, B.; Hu, G.; Huang, Y.; Huber, V.; Hunt, S.; Ibrahim, A. G.-E.; Ikezu, T.; Inal, J. M.; Isin, M.; Ivanova, A.; Jackson, H. K.; Jacobsen, S.; Jay, S. M.; Jayachandran, M.; Jenster, G.; Jiang, L.; Johnson, S. M.; Jones, J. C.; Jong, A.; Jovanovic-Talisman, T.; Jung, S.; Kalluri, R.; Kano, S.-i.; Kaur, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Keller, E. T.; Khamari, D.; Khomyakova, E.; Khvorova, A.; Kierulf, P.; Kim, K. P.; Kislinger, T.; Klingeborn, M.; Klinke, D. J.; II, Kornek, M.; Kosanovic, M. M.; Kovacs, A. F.; Kraemer-Albers, E.-M.; Krasemann, S.; Krause, M.; Kurochkin, I. V.; Kusuma, G. D.; Kuypers, S.; Laitinen, S.; Langevin, S. M.; Languino, L. R.; Lannigan, J.; Lasser, C.; Laurent, L. C.; Lavieu, G.; Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Le Lay, S.; Lee, M.-S.; Lee, Y. X. F.; Lemos, D. S.; Lenassi, M.; Leszczynska, A.; Li, I. T. S.; Liao, K.; Libregts, S. F.; Ligeti, E.; Lim, R.; Lim, S. K.; Line, A.; Linnemannstoens, K.; Llorente, A.; Lombard, C. A.; Lorenowicz, M. J.; Lorincz, A. M.; Lotvall, J.; Lovett, J.; Lowry, M. C.; Loyer, X.; Lu, Q.; Lukomska, B.; Lunavat, T. R.; Maas, S. L. N.; Malhi, H.; Marcilla, A.; Mariani, J.; Mariscal, J.; Martens-Uzunova, E. S.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Martinez, M. C.; Martins, V. R.; Mathieu, M.; Mathivanan, S.; Maugeri, M.; McGinnis, L. K.; McVey, M. J.; Meckes, D. G.; Jr.; Meehan, K. L.; Mertens, I.; Minciacchi, V. R.; Moller, A.; Jorgensen, M. M.; Morales-Kastresana, A.; Morhayim, J.; Mullier, F.; Muraca, M.; Musante, L.; Mussack, V.; Muth, D. C.; Myburgh, K. H.; Najrana, T.; Nawaz, M.; Nazarenko, I.; Nejsum, P.; Neri, C.; Neri, T.; Nieuwland, R.; Nimrichter, L.; Nolan, J. P.; Nolte-'t Hoen, E. N. M.; Noren Hooten, N.; O'Driscoll, L.; O'Grady, T.; O'Loghlen, A.; Ochiya, T.; Olivier, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, L. A.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Ostegaard, O.; Ostrowski, M.; Park, J.; Pegtel, D. M.; Peinado, H.; Perut, F.; Pfaffl, M. W.; Phinney, D. G.; Pieters, B. C. H.; Pink, R. C.; Pisetsky, D. S.; von Strandmann, E. P.; Polakovicova, I.; Poon, I. K. H.; Powell, B. H.; Prada, I.; Pulliam, L.; Quesenberry, P.; Radeghieri, A.; Raffai, R. L.; Raimondo, S.; Rak, J.; Ramirez, M. I.; Raposo, G.; Rayyan, M. S.; Regev-Rudzki, N.; Ricklefs, F. L.; Robbins, P. D.; Roberts, D. D.; Rodrigues, S. C.; Rohde, E.; Rome, S.; Rouschop, K. M. A.; Rughetti, A.; Russell, A. E.; Saa, P.; Sahoo, S.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Sanchez, C.; Saugstad, J. A.; Saul, M. J.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Schneider, R.; Schoyen, T. H.; Scott, A.; Shahaj, E.; Sharma, S.; Shatnyeva, O.; Shekari, F.; Shelke, G. V.; Shetty, A. K.; Shiba, K.; Siljander, P. R. M.; Silva, A. M.; Skowronek, A.; Snyder, O. L.; II, Soares, R. P.; Sodar, B. W.; Soekmadji, C.; Sotillo, J.; Stahl, P. D.; Stoorvogel, W.; Stott, S. L.; Strasser, E. F.; Swift, S.; Tahara, H.; Tewari, M.; Timms, K.; Tiwari, S.; Tixeira, R.; Tkach, M.; Toh, W. S.; Tomasini, R.; Torrecilhas, A. C.; Pablo Tosar, J.; Toxavidis, V.; Urbanelli, L.; Vader, P.; van Balkom, B. W. M.; van der Grein, S. G.; Van Deun, J.; van Herwijnen, M. J. C.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.; van Niel, G.; van Royen, M. E.; van Wijnen, A. J.; Helena Vasconcelos, M.; Vechetti, I. J.; Jr.; Veit, T. D.; Vella, L. J.; Velot, E.; Verweij, F. J.; Vestad, B.; Vinas, J. L.; Visnovitz, T.; Vukman, K. V.; Wahlgren, J.; Watson, D. C.; Wauben, M. H. M.; Weaver, A.; Webber, J. P.; Weber, V.; Wehman, A. M.; Weiss, D. J.; Welsh, J. A.; Wendt, S.; Wheelock, A. M.; Wiener, Z.; Witte, L.; Wolfram, J.; Xagorari, A.; Xander, P.; Xu, J.; Yan, X.; Yanez-Mo, M.; Yin, H.; Yuana, Y.; Zappulli, V.; Zarubova, J.; Zekas, V.; Zhang, J.-y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zheutlin, A. R.; Zickler, A. M.; Zimmermann, P.; Zivkovic, A. M.; Zocco, D.; Zuba-Surma, E. K. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750.
|
| [18] |
Tran, P. H. L.; Wang, T.; Yin, W.; Tran, T. T. D.; Nguyen, T. N. G.; Lee, B. J.; Duan, W. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118786.
|
| [19] |
Onodi, Z.; Pelyhe, C.; Nagy, C. T.; Brenner, G. B.; Almasi, L.; Kittel, A.; Mancek-Keber, M.; Ferdinandy, P.; Buzas, E. I.; Giricz, Z. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1479.
|
| [20] |
Seo, K.; Yoo, J. H.; Kim, J.; Min, S. J.; Heo, D. N.; Kwon, I. K.; Moon, H. J. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 5798.
|
| [21] |
Musumeci, T.; Leonardi, A.; Bonaccorso, A.; Pignatello, R.; Puglisi, G. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2018, 6, 48.
doi: 10.2174/2211738506666180306160921 pmid: 29510657 |
| [22] |
Lu, Y.; Eguchi, T.; Sogawa, C.; Taha, E. A.; Tran, M. T.; Nara, T.; Wei, P.; Fukuoka, S.; Miyawaki, T.; Okamoto, K. Cells 2021, 10, 1328.
|
| [23] |
Lane, R. E.; Korbie, D.; Trau, M.; Hill, M. M. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 111.
|
| [24] |
Lucchetti, D.; Fattorossi, A.; Sgambato, A. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, e1700716.
|
| [25] |
Visan, K. S.; Lobb, R. J.; Ham, S.; Lima, L. G.; Palma, C.; Edna, C. P. Z.; Wu, L. Y.; Gowda, H.; Datta, K. K.; Hartel, G.; Salomon, C.; Möller, A. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12266.
|
| [26] |
Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Hu, L.; Lou, D.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Lee, L. P.; Liu, F. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 212.
|
| [27] |
(a) Sidhom, K.; Obi, P. O.; Saleem, A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6466.
|
|
(b) Yousif, G.; Qadri, S.; Parray, A.; Akhthar, N.; Shuaib, A.; Haik, Y. Neuromolecular Med. 2022, 24, 339.
|
|
| [28] |
D'Atri, V.; Imiołek, M.; Quinn, C.; Finny, A.; Lauber, M.; Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1722, 464862.
|
| [29] |
Chen, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Du, L. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2021, 9, 811971.
|
| [30] |
Böing, A. N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A. E.; Coumans, F. A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23430.
|
| [31] |
An, M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Lubman, D. M. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3599.
|
| [32] |
Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Norman, M.; Lazarovits, R.; Trieu, W.; Lee, J. H.; Church, G. M.; Walt, D. R. Elife 2021, 10, 70725.
|
| [33] |
Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, T.; Cui, Y. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12145.
|
| [34] |
Coumans, F. A. W.; Brisson, A. R.; Buzas, E. I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E. E. E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A. F.; Lacroix, R.; Lee, Y.; van Leeuwen, T. G.; Mackman, N.; Mäger, I.; Nolan, J. P.; van der Pol, E.; Pegtel, D. M.; Sahoo, S.; Siljander, P. R. M.; Sturk, G.; de Wever, O.; Nieuwland, R. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1632.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309417 pmid: 28495994 |
| [35] |
Jia, Y.; Yu, L.; Ma, T.; Xu, W.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y.; Shi, H. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6548.
|
| [36] |
Liangsupree, T.; Multia, E.; Riekkola, M. L. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1636, 461773.
|
| [37] |
Shin, H.; Han, C.; Labuz, J. M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Gho, Y. S.; Takayama, S.; Park, J. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13103.
|
| [38] |
Kim, J.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0129760.
|
| [39] |
Kırbaş, O. K.; Bozkurt, B. T.; Asutay, A. B.; Mat, B.; Ozdemir, B.; Öztürkoğlu, D.; Ölmez, H.; İşlek, Z.; Şahin, F.; Taşlı, P. N. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19159.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55477-0 pmid: 31844310 |
| [40] |
Ansari, F. J.; Tafti, H. A.; Amanzadeh, A.; Rabbani, S.; Shokrgozar, M. A.; Heidari, R.; Behroozi, J.; Eyni, H.; Uversky, V. N.; Ghanbari, H. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2024, 38, 101668.
|
| [41] |
Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, S.; Yang, C.; Guan, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Gao, T.; Zhao, J.; Fan, N.; Song, Y.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Guan, F.; Tan, Z. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12499.
|
| [42] |
Zhang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.; Du, S.; Li, P. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6917.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S264498 pmid: 33061359 |
| [43] |
Sharma, P.; Ludwig, S.; Muller, L.; Hong, C. S.; Kirkwood, J. M.; Ferrone, S.; Whiteside, T. L. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1435138.
|
| [44] |
Altıntaş, Ö.; Saylan, Y. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 16029.
|
| [45] |
Theel, E. K.; Schwaminger, S. P. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9004.
|
| [46] |
Liu, H. Y.; Kumar, R.; Zhong, C.; Gorji, S.; Paniushkina, L.; Masood, R.; Wittel, U. A.; Fuchs, H.; Nazarenko, I.; Hirtz, M. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008493.
|
| [47] |
Lo, T.-W.; Zhu, Z.; Purcell, E.; Watza, D.; Wang, J.; Kang, Y.-T.; Jolly, S.; Nagrath, D.; Nagrath, S. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1762.
|
| [48] |
Zhang, P.; Zhou, X.; He, M.; Shang, Y.; Tetlow, A. L.; Godwin, A. K.; Zeng, Y. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 438.
doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0356-9 pmid: 31123323 |
| [49] |
Ramnauth, N.; Neubarth, E.; Makler-Disatham, A.; Sher, M.; Soini, S.; Merk, V.; Asghar, W.; Sensors 2023, 23, 8292.
|
| [50] |
Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Rufo, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Kim, Y.; Wu, M.; Abemayor, E.; Tu, M.; Chia, D.; Spruce, R.; Batis, N.; Mehanna, H.; Wong, D. T. W.; Huang, T. J. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 50.
|
| [51] |
Shi, L.; Kuhnell, D.; Borra, V. J.; Langevin, S. M.; Nakamura, T.; Esfandiari, L. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3726.
|
| [52] |
Le, M. N.; Fan, Z. H. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 022005.
|
| [53] |
Ozcelik, A.; Cevik, O. Biocell 2023, 47, 959.
|
| [54] |
Saito, S. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 17.
|
| [55] |
Tan, W.; Donovan, M. J.; Jiang, J. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2842.
|
| [56] |
Zhang, K. X.; Yue, Y. L.; Wu, S. X.; Liu, W.; Shi, J. J.; Zhang, Z. Z. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1245.
|
| [57] |
Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3817.
|
| [58] |
Tang, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Q.; Cui, Z.; Liang, A.; Ke, B.; Yang, D.; Yao, C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2023, 120, e2303822120.
|
| [59] |
Oeyen, E.; Van Mol, K.; Baggerman, G.; Willems, H.; Boonen, K.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, A.; Schildermans, K.; Cho, W. C.; Mertens, I. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1490143.
|
| [60] |
Hu, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Tong, L.; Dong, M.; Xu, T.; Li, Z. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12470.
|
| [61] |
Wu, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Qing, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, X.; Xie, Z.; Niu, L.; Guo, X.; Cai, T.; Guo, X.; Yang, F. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 234.
|
| [62] |
Oh, S.; Kang, D.; Ahn, S. M.; Simpson, R. J.; Lee, B. H.; Moon, M. H. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1082.
|
| [63] |
Liu, C.; Tian, F.; Deng, J.; Sun, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 679. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘超, 田飞, 邓瑾琦, 孙佳姝, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 679.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120610 |
|
| [64] |
Liu, C.; Zhao, J. X.; Tian, F.; Cai, L. L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Q.; Chang, J. Q.; Wan, F. N.; Yang, Y. J.; Dai, B.; Cong, Y. L.; Ding, B. Q.; Sun, J. S.; Tan, W. H. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 183.
|
| [65] |
Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4996.
|
| [66] |
Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Tian, F.; Feng, Q.; Qin, L.; Bai, L.; Fu, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2292.
|
| [67] |
Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33935.
|
| [68] |
Li, Q.; Plao, X. K.; Wang, F. C.; Li, X. J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L. Q.; Liu, D. B. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13633.
|
| [69] |
Zhang, P.; Dong, B.; Zeng, E.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, D. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11273.
|
| [70] |
Di, H.; Zeng, E.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, D. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12752.
|
| [71] |
Li, Q.; Zhang, Z. W.; Wang, F. C.; Wang, X.; Zhan, S. S.; Yang, X. Q.; Xu, C.; Liu, D. B. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf4568.
|
| [1] | Zhao Li-Dong, Zuo Peng, Yin Bin-Cheng, Hong Chenglin, Ye Bang-Ce. A Cell Membrane-Anchored DNA Tetrahedral Sensor for Real-time Monitoring of Exosome Secretion [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(10): 1076-1081. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||