Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1498-1506.DOI: 10.6023/A25070260 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
王嘉玮a, 张宁a, 范晓强a,*( ), 孔莲a,*(
), 孔莲a,*( ), 赵震a,b,*(
), 赵震a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-07-18
发布日期:2025-10-14
基金资助:
Jiawei Wanga, Ning Zhanga, Xiaoqiang Fana,*( ), Lian Konga,*(
), Lian Konga,*( ), Zhen Zhaoa,b,*(
), Zhen Zhaoa,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-07-18
Published:2025-10-14
Contact:
* E-mail: fanxiaoqiang1986@126.com;konglian0907@163.com;zhenzhao@cup.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Jiawei Wang, Ning Zhang, Xiaoqiang Fan, Lian Kong, Zhen Zhao. Study on the Influence of Fe Promoter on Propane Dehydrogenation Performance of PtFe/Silicalite-1 Catalyst[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1498-1506.
| Sample | Smica/(m2•g⁻1) | SBETb/(m2•g⁻1) | davec/nm | dBJHd/nm | Vmice/(cm3•g⁻1) | Vt f/(cm3•g⁻1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt0.1Fe/S-1 | 221.5 | 434.5 | 2.4 | 4.4 | 0.11 | 0.26 |
| Pt0.5Fe/S-1 | 208.4 | 423.5 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 0.11 | 0.25 |
| Pt0.7Fe/S-1 | 206.0 | 407.3 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 0.11 | 0.24 |
| Pt1.0Fe/S-1 | 251.5 | 376.3 | 2.3 | 4.4 | 0.13 | 0.22 |
| Pt1.5Fe/S-1 | 260.3 | 392.5 | 2.3 | 4.5 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| Pt2.0Fe/S-1 | 248.4 | 366.9 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
| Sample | Smica/(m2•g⁻1) | SBETb/(m2•g⁻1) | davec/nm | dBJHd/nm | Vmice/(cm3•g⁻1) | Vt f/(cm3•g⁻1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt0.1Fe/S-1 | 221.5 | 434.5 | 2.4 | 4.4 | 0.11 | 0.26 |
| Pt0.5Fe/S-1 | 208.4 | 423.5 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 0.11 | 0.25 |
| Pt0.7Fe/S-1 | 206.0 | 407.3 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 0.11 | 0.24 |
| Pt1.0Fe/S-1 | 251.5 | 376.3 | 2.3 | 4.4 | 0.13 | 0.22 |
| Pt1.5Fe/S-1 | 260.3 | 392.5 | 2.3 | 4.5 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| Pt2.0Fe/S-1 | 248.4 | 366.9 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
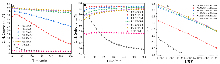

| Sample | Propane conversion/% | Propylene selectivity/% | kd/h⁻1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |||
| Pt0.1Fe/S-1 Pt0.5Fe/S-1 Pt0.7Fe/S-1 Pt1.0Fe/S-1 Pt1.5Fe/S-1 Pt2.0Fe/S-1 1.0Fe/S-1 | 20.9 48.5 55.7 59.8 59.0 59.9 3.5 | 2.9 12.6 35.1 52.9 55.3 56.2 3.0 | 92.6 93.6 93.7 89.1 89.4 85.6 73.2 | 59.2 94.3 96.9 96.4 95.1 94.7 73.0 | 0.363 0.313 0.141 0.046 0.025 0.025 0.027 | |
| Sample | Propane conversion/% | Propylene selectivity/% | kd/h⁻1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |||
| Pt0.1Fe/S-1 Pt0.5Fe/S-1 Pt0.7Fe/S-1 Pt1.0Fe/S-1 Pt1.5Fe/S-1 Pt2.0Fe/S-1 1.0Fe/S-1 | 20.9 48.5 55.7 59.8 59.0 59.9 3.5 | 2.9 12.6 35.1 52.9 55.3 56.2 3.0 | 92.6 93.6 93.7 89.1 89.4 85.6 73.2 | 59.2 94.3 96.9 96.4 95.1 94.7 73.0 | 0.363 0.313 0.141 0.046 0.025 0.025 0.027 | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117914 |
| [3] |
|
|
(王文欣, 单译欧, 宋佳欣, 范晓强, 于学华, 孔莲, 肖霞, 解则安, 赵震, 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46, 130.)
|
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1021/cr5002436 pmid: 25163050 |
| [5] |
|
|
(柳海涛, 李会泉, 杨玮娇, 王兴瑞, 张懿, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 1749.)
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.44 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2020.02.019 |
| [8] |
|
|
(代怡, 王凯杰, 张耀远, 吴芹, 史大昕, 陈康成, 杨彦鹏, 黎汉生, 低碳化学与化工, 2025, 50, 106.)
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
(洪学思, 吴省, 宋磊, 缪长喜, 杨为民, 化工进展, 2024, 43, 5517.)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2024-0476 |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00983K |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00928 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.6023/A22100420 |
|
(张红丹, 兰欣雨, 程鹏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 100.)
doi: 10.6023/A22100420 |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1126/science.adk5195 pmid: 38422151 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09168-8 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2022.03.029 |
| [16] |
|
|
(邱易, 敬方梨, 罗仕忠, 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2020, 45, 8.)
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
(沈姗姗, 刘晓晖, 郭勇, 物理化学学报, 2023, 39, 85.)
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
(季东, 苏怡, 刘涛, 分子催化, 2007, 4, 371.)
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
(李佩, 郑跃楠, 刘占凯, 陆安慧, 物理化学学报, 2025, 41, 97.)
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
(王新, 许友好, 石油学报(石油加工), 2025, 41, 1034.)
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118467 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c13351 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1039/D2RA05107A |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c05478 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c07792 |
| [27] |
|
|
(刘奕萱, 胡慧敏, 范晓强, 于学华, 孔莲, 肖霞, 解则安, 赵震, 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46, 78.)
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1021/jp802955s |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05520 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1039/C7TA01791J |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c00649 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v12.4 |
| [35] |
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||