Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (2): 223-230.DOI: 10.6023/A25090310 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
高林a,†, 江东彬a,†, 徐源b, 姚青a, 刘冯立a, 孙伟海a, 杜振波a, 孙留学a,c, 吴季怀a,*( ), 兰章a,*(
), 兰章a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-09-12
发布日期:2025-11-27
基金资助:
Lin Gaoa, Dongbin Jianga, Yuan Xub, Qing Yaoa, Fengli Liua, Weihai Suna, Zhenbo Dua, Liuxue Suna,c, Jihuai Wua,*( ), Zhang Lana,*(
), Zhang Lana,*( )
)
Received:2025-09-12
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
*E-mail: jhwu@hqu.edu.cn;lanzhang@hqu.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:Share
Lin Gao, Dongbin Jiang, Yuan Xu, Qing Yao, Fengli Liu, Weihai Sun, Zhenbo Du, Liuxue Sun, Jihuai Wu, Zhang Lan. Interface Modification and Dipole Realization for Efficient Carbon-based CsPbI2Br Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(2): 223-230.
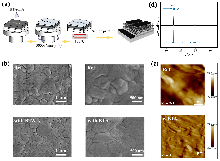

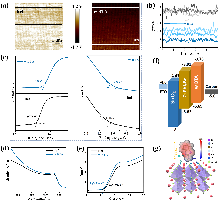

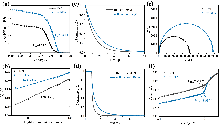
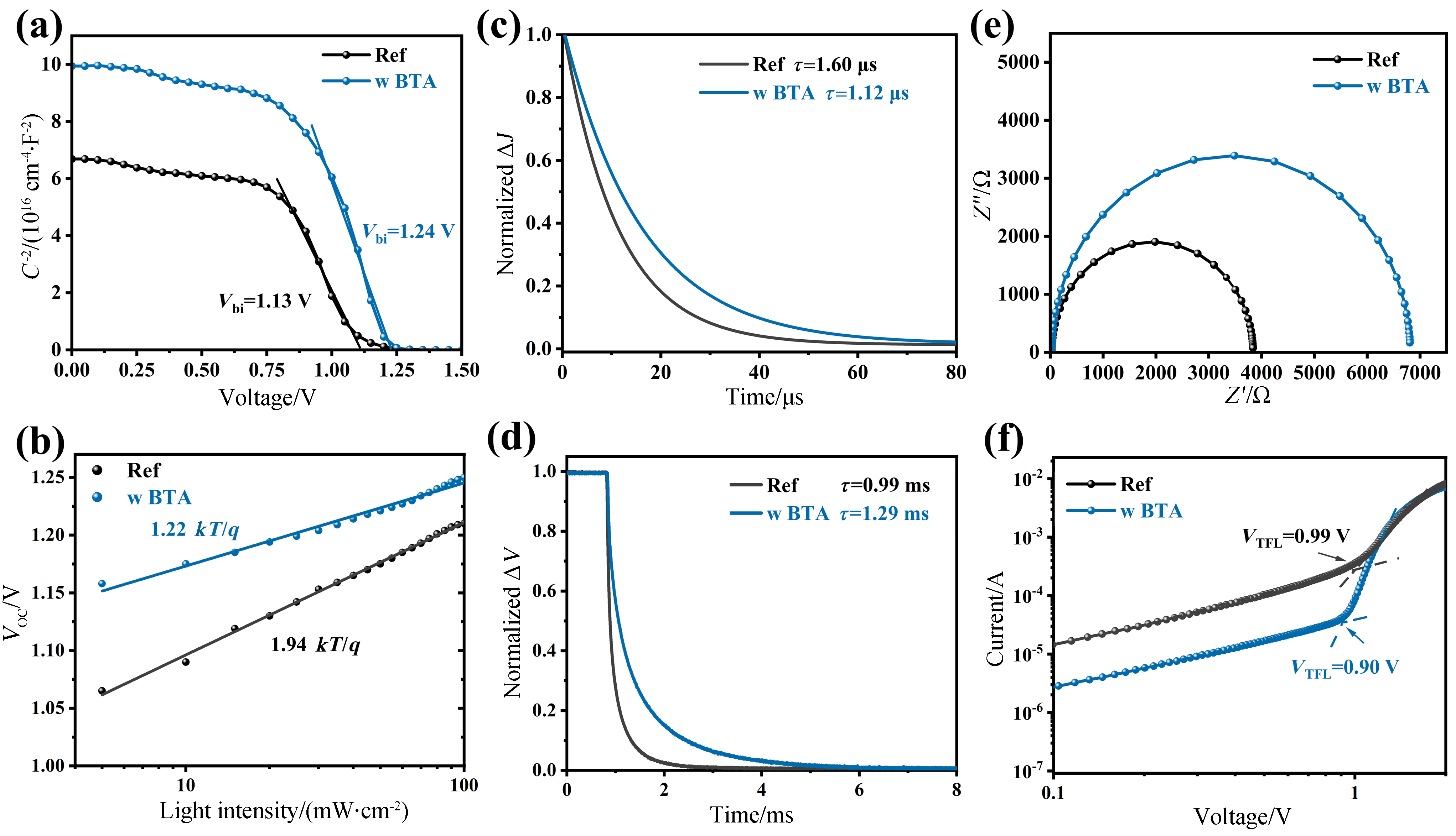
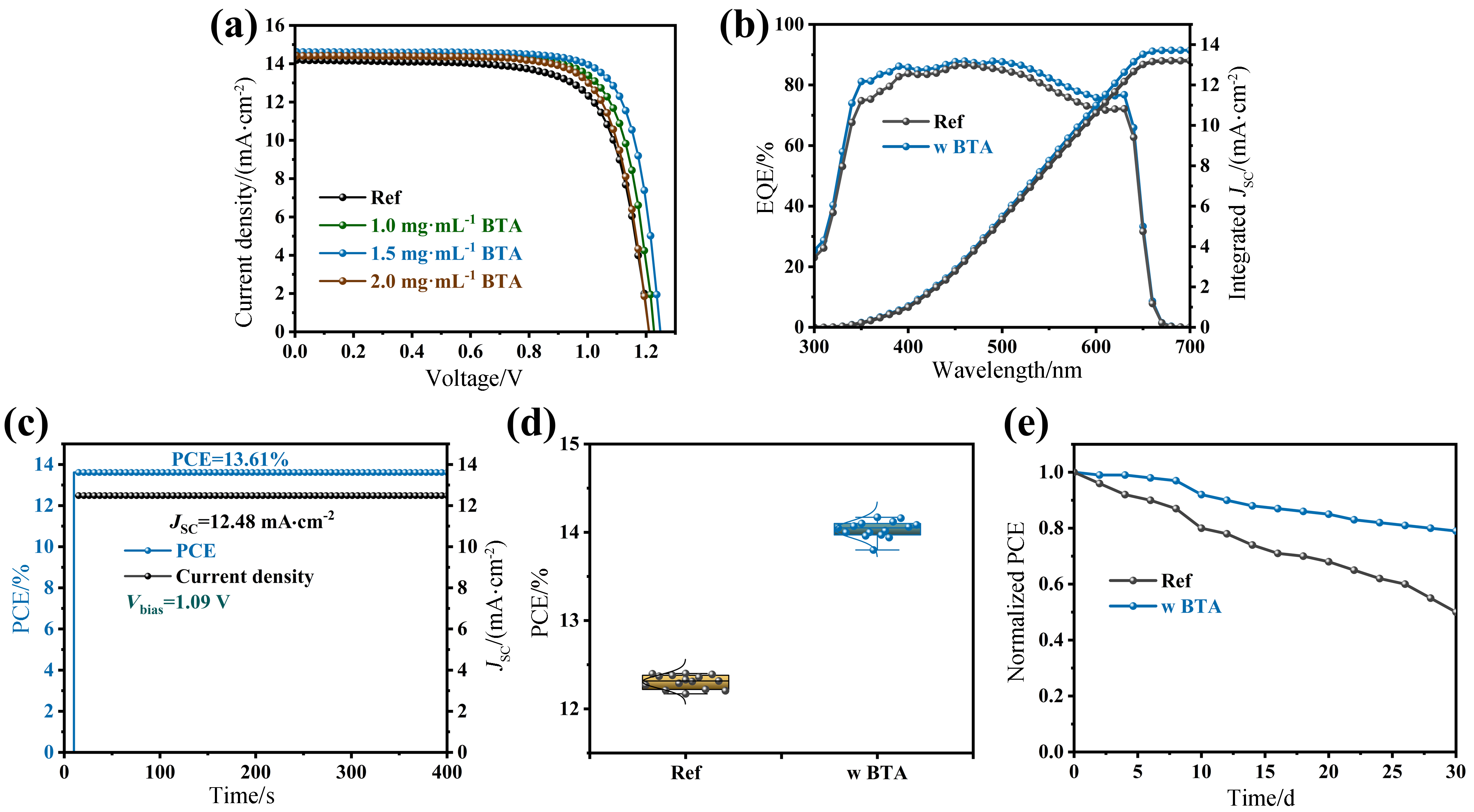
| [1] |
doi: 10.6023/A24040134 |
|
(陈宇波, 郑德旭, 王楠, 刘吉双, 于凤阳, 吴飒建, 刘生忠, 李智鹏, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 987.)
doi: 10.6023/A24040134 |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1039/D4EE05462H |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1039/C9CS00711C |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00424 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00236 pmid: 28540366 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v34.1 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.7 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41578-022-00503-3 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v13.33 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/nn5036476 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.43 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.13 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2021.01.030 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104180 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134611 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v28.45 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v14.50 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.1c01060 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c15880 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.32 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v37.3 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.161053 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v14.34 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.01.001 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/nature14133 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v15.11 |
| [31] |
|
|
(王云飞, 刘建华, 于美, 钟锦岩, 周琪森, 邱俊明, 张晓亮, 物理化学学报, 2021, 37, 2006030.)
|
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v42.16 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.10.035 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1039/C9TC05679C |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.11.068 |
| [36] |
|
|
(宋健, 苏星宙, 姚倩楠, 杨雪昆, 赵宇龙, 强颖怀, 任春光, 无机化学学报, 2023, 39, 327.)
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.03.029 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.4 |
|
(殷逍遥, 朱文昊, 施谱垚, 李宗盛, 王艺超, 朱能敏, 汪杨, 孙伟海, 无机化学学报, 2025, 41, 469.)
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2024.03.026 |
| [40] |
|
|
(董鹏宇, 姜月, 杨正池, 刘立城, 李固, 文鑫洋, 王祯, 施信波, 周国富, 刘俊明, 高进伟, 物理化学学报, 2025, 41, 2407025.)
|
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c04316 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.19 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v14.10 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.02.011 |
| [1] | Wenhao Zhu, Yujie Wang, Hao Li, Yang Wang, Songzhi Zheng, Zeyuan Wang, Shaotian Chen, Weihai Sun, Xiaomin Zhao. Interface Engineering Using Polyacrylic Acid Sodium for the Fabrication of Highly Efficient and Stable All-Inorganic CsPbBr3 Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(6): 616-623. |
| [2] | Yajing Peng, Yuxin Zhao, Jinhui Yang, Xinxin Zhang, Jialing Cheng. Study on the Influence of Component and Concentration of CsPbBrxI3-x All-inorganic Perovskite Quantum Dots on Electronic Structure and Fluorescence Properties [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(8): 879-886. |
| [3] | Chengyu Fu, Xingyu Zhou, Peng Yang. Surface Functionalization Based on Protein Amyloid-like Aggregation★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1566-1576. |
| [4] | Zhenyu Guo, Huanping Zhou. Research Progress of Composition and Structure Design in Perovskites for High Performance Light-emitting Diodes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(3): 223-237. |
| [5] | Yang Ying, Lin Feiyu, Zhu Congtan, Chen Tian, Ma Shupeng, Luo Yuan, Zhu Liu, Guo Xueyi. Research Progress in the Stability of Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(3): 217-231. |
| [6] | Pei Juan, Hao Yanzhong, Lv Haijun, Sun Bao, Li Yingpin, Wang Shangxin. Improving the Photovoltaic Performance of TiO2/P3HT Hybrid Solar Cell by Interfacial Modification [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014, 72(12): 1245-1250. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||