Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (5): 527-540.DOI: 10.6023/A24010038 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
张华林a,b,c, 赵梦飞a,b,c, 江晓亮b, 田少静b, 滕泽栋a,e, 李庭刚a,b,c,d,e,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-01-29
发布日期:2024-04-02
作者简介: |
张华林, 2022年江西理工大学与中国科学院赣江创新研究院联合培养在读博士研究生, 主要从事方向为生态修复与改良. |
 |
赵梦飞, 2021年江西理工大学与中国科学院赣江创新研究院联合培养在读博士研究生, 主要从事方向为稀土生物浸出. |
 |
江晓亮, 中国科学院赣江创新研究院助理研究员, 主要从事矿山土壤改良、土壤重金属生态修复、重金属超富集植物与根际微生物互作机制研究. |
 |
田少静, 2022年中国科学院赣江创新研究院在读博士研究生, 主要从事环境功能材料设计与研发及其应用于稀土矿区的生态修复. |
 |
滕泽栋, 中国科学院过程工程研究所副研究员, 主要从事污染生态环境跨介质修复、环境生物技术强化减污降碳、环境功能材料设计与开发等方面的基础和应用研究. |
 |
李庭刚, 博士, 研究员, 博士生导师, 中国科学院过程所“百人计划”、江西省“千人计划”入选者. 2008年获中国科学院生态环境研究中心博士学位, 2006~2008年在新加坡南洋理工大学进行博士联合培养, 2010~2019年在新加坡国立大学做博士后、特聘研究员, 2019年至今在中国科学院过程工程研究所工作, 环境生物技术课题组组长. 中国科学院赣江创新研究院双聘. 长期从事环境生物过程转化机理与能源资源化技术研究, 主要涉及土壤-地下水修复、高盐有机废水处理与资源化、稀土生物冶金、生物新能源制造、环境污染物定向生物转化与功能材料应用基础研究. 主持国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划项目课题、地方科技重大专项以及企业委托等科研项目. 近年来在Science子刊Science Advances, Biotechnology for Biofuels, Environmental Science & Technology, Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Water Research, Bioresource Technology, Journal of Biotechnology, Renewable Energy等主流期刊上发表论文40余篇, 申请和授权发明专利20余项. 担任巴塞尔公约亚太区中心化学品和废物环境管理智库专家, 中国自然资源学会废弃物资源化专业委员会委员, Clean Energy Science and Technology等期刊编委, Membrane期刊客座编辑, 荣获2021年中国产学研促进会科技合作创新奖, 2022年中国发明协会发明创业成果奖二等奖. |
基金资助:
Hualin Zhanga,b,c, Mengfei Zhaoa,b,c, Xiaoliang Jiangb, Shaojing Tianb, Zedong Tenga,e, Tinggang Lia,b,c,d,e( )
)
Received:2024-01-29
Published:2024-04-02
Contact:
*E-mail: tgli@ipe.ac.cn
Supported by:Share
Hualin Zhang, Mengfei Zhao, Xiaoliang Jiang, Shaojing Tian, Zedong Teng, Tinggang Li. Research Progress of Coal Gangue Modification Method and Its Resource and Environment Utilisation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 527-540.
| 来源 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | R2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 掘进矸石 | 53.10 | 18.40 | 8.10 | 4.50 | 1.50 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| 洗选矸石 | 50.50 | 37.90 | 4.15 | 1.80 | 1.07 | 1.60 | 0.65 |
| 普通煤矸石 | 41.10 | 22.90 | 2.40 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 0.86 | 2.00 |
| 六安市煤炭开采 | 37.80 | 21.20 | 2.50 | 2.60 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 1.40 |
| 内蒙古准格尔 | 36.90 | 38.98 | 0.33 | — | 0.03 | 1.01 | 0.17 |
| 于贵州盘县某矿区 | 37.30 | 17.35 | 18.19 | 6.85 | 1.15 | 4.19 | — |
| 普通煤矸石 | 38.18 | 18.48 | 12.97 | 2.86 | 2.63 | 4.51 | 0.02 |
| 高铝煤矸石 | 42.17 | 48.41 | 0.07 | 3.77 | 0.94 | 1.35 | — |
| 普通煤矸石 | 41.47 | 15.95 | 3.53 | 1.23 | 1.79 | — | 1.71 |
| 来源 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | R2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 掘进矸石 | 53.10 | 18.40 | 8.10 | 4.50 | 1.50 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| 洗选矸石 | 50.50 | 37.90 | 4.15 | 1.80 | 1.07 | 1.60 | 0.65 |
| 普通煤矸石 | 41.10 | 22.90 | 2.40 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 0.86 | 2.00 |
| 六安市煤炭开采 | 37.80 | 21.20 | 2.50 | 2.60 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 1.40 |
| 内蒙古准格尔 | 36.90 | 38.98 | 0.33 | — | 0.03 | 1.01 | 0.17 |
| 于贵州盘县某矿区 | 37.30 | 17.35 | 18.19 | 6.85 | 1.15 | 4.19 | — |
| 普通煤矸石 | 38.18 | 18.48 | 12.97 | 2.86 | 2.63 | 4.51 | 0.02 |
| 高铝煤矸石 | 42.17 | 48.41 | 0.07 | 3.77 | 0.94 | 1.35 | — |
| 普通煤矸石 | 41.47 | 15.95 | 3.53 | 1.23 | 1.79 | — | 1.71 |
| 来源 | 表观密度/ (kg·m-3) | 堆积密度/ (kg·m-3) | 含水量/% | 破碎率/% | 孔隙率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽宁 | 2276~2653 | 1220~1550 | 3.15~9.8 | 9.9~25.2 | 22.0~52.8 |
| 江苏 | 2620~2712 | 1430~1612 | 1.7~3.9 | 16.8~24.4 | — |
| 山西 | 2083~2689 | 1130~1201 | 4.7~11.4 | 18.1~19.0 | — |
| 河南 | 2510~2540 | 1264~1320 | 1.7~3.9 | 17.9~19.1 | 47.5~51.5 |
| 来源 | 表观密度/ (kg·m-3) | 堆积密度/ (kg·m-3) | 含水量/% | 破碎率/% | 孔隙率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽宁 | 2276~2653 | 1220~1550 | 3.15~9.8 | 9.9~25.2 | 22.0~52.8 |
| 江苏 | 2620~2712 | 1430~1612 | 1.7~3.9 | 16.8~24.4 | — |
| 山西 | 2083~2689 | 1130~1201 | 4.7~11.4 | 18.1~19.0 | — |
| 河南 | 2510~2540 | 1264~1320 | 1.7~3.9 | 17.9~19.1 | 47.5~51.5 |
| 物理改性方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉碎、磨细 | 提高比表面积,增强煤 矸石的反应性和结合性 | 过度磨细可能导致能源消耗增加和处理成本上升 | [ |
| 筛分 | 提高物料的均一性和使用灵活性 | 无法去除所有杂质, 分离效率较低 | [ |
| 浮选和重力分离 | 可以提高煤矸石中有价值成分的浓度 | 需要大量的水和化学试剂,增加处理成本和环境风险 | [ |
| 磁选 | 移除铁磁性矿物, 提纯 效果好 | 对非磁性杂质的去除效果有限 | [ |
| 静电分离 | 有效于分离电性不同的矿物颗粒 | 对湿度和其他环境因素敏感, 可能影响分离效果 | [ |
| 造粒成型 | 提升煤矸石的物理稳定性和易处理性 | 需要额外的粘结剂或加工步骤 | [ |
| 洗涤 | 可以去除表面灰尘和泥土, 提高煤矸石的纯度 | 大量废水产生, 需要额外的水处理步骤 | [ |
| 物理改性方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 粉碎、磨细 | 提高比表面积,增强煤 矸石的反应性和结合性 | 过度磨细可能导致能源消耗增加和处理成本上升 | [ |
| 筛分 | 提高物料的均一性和使用灵活性 | 无法去除所有杂质, 分离效率较低 | [ |
| 浮选和重力分离 | 可以提高煤矸石中有价值成分的浓度 | 需要大量的水和化学试剂,增加处理成本和环境风险 | [ |
| 磁选 | 移除铁磁性矿物, 提纯 效果好 | 对非磁性杂质的去除效果有限 | [ |
| 静电分离 | 有效于分离电性不同的矿物颗粒 | 对湿度和其他环境因素敏感, 可能影响分离效果 | [ |
| 造粒成型 | 提升煤矸石的物理稳定性和易处理性 | 需要额外的粘结剂或加工步骤 | [ |
| 洗涤 | 可以去除表面灰尘和泥土, 提高煤矸石的纯度 | 大量废水产生, 需要额外的水处理步骤 | [ |
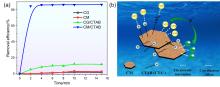

| 改性方法 | 运用 | 效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 焙烧、酸化 | 含对羟基苯磺酸废水吸附 | 去除率达到85.34% | [ |
| HCl、KOH改性 | 含U(VI)废水净化 | 吸附量为140 mg/g | [ |
| 碱溶、焙烧 | Al、Si的提取 | 提取率78.9%和69.2% | [ |
| 5%硬脂酸、70 ℃反应2 h | 聚氯乙烯热稳定性探究 | 10%添加后其冲击强度为9.05 kJ/m2 | [ |
| NaOH、焙烧 | 含镉土壤 | Cd2+减少了14.2%~29.8% | [ |
| 焙烧后HCl处理, 再混合FeCo2O4、柠檬酸焙烧 | 工业固体废物腐殖酸降解 | 腐殖酸(20 mg/L)的降解效率接近85% | [ |
| NaOH/NasSiO3处理、焙烧、微波活化 | 生产多孔陶瓷材料 | 抗压强度提高1倍 | [ |
| KOH、焙烧, 焙烧后聚乙烯亚胺-乙醇 溶液80 ℃反应12 h | CO2吸附 | 15%聚乙烯亚胺负载量对CO2吸附量为 1.59 mmol/g, 吸附效能提升37.1% | [ |
| 焙烧、水热后与双十二烷基二甲基溴化铵反应 | 含腐殖酸溶液 | 腐殖酸去除率88.71% | [ |
| 焙烧、ZnCl2-FeCl3改性 | 光催化剂制备及其降解五氯酚 | 降解率达到100%, 具有光催化降解效果, 可重复使用 | [ |
| 改性方法 | 运用 | 效果 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 焙烧、酸化 | 含对羟基苯磺酸废水吸附 | 去除率达到85.34% | [ |
| HCl、KOH改性 | 含U(VI)废水净化 | 吸附量为140 mg/g | [ |
| 碱溶、焙烧 | Al、Si的提取 | 提取率78.9%和69.2% | [ |
| 5%硬脂酸、70 ℃反应2 h | 聚氯乙烯热稳定性探究 | 10%添加后其冲击强度为9.05 kJ/m2 | [ |
| NaOH、焙烧 | 含镉土壤 | Cd2+减少了14.2%~29.8% | [ |
| 焙烧后HCl处理, 再混合FeCo2O4、柠檬酸焙烧 | 工业固体废物腐殖酸降解 | 腐殖酸(20 mg/L)的降解效率接近85% | [ |
| NaOH/NasSiO3处理、焙烧、微波活化 | 生产多孔陶瓷材料 | 抗压强度提高1倍 | [ |
| KOH、焙烧, 焙烧后聚乙烯亚胺-乙醇 溶液80 ℃反应12 h | CO2吸附 | 15%聚乙烯亚胺负载量对CO2吸附量为 1.59 mmol/g, 吸附效能提升37.1% | [ |
| 焙烧、水热后与双十二烷基二甲基溴化铵反应 | 含腐殖酸溶液 | 腐殖酸去除率88.71% | [ |
| 焙烧、ZnCl2-FeCl3改性 | 光催化剂制备及其降解五氯酚 | 降解率达到100%, 具有光催化降解效果, 可重复使用 | [ |
| 改性方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 酸碱改性 | 去除表面杂质, 提高纯度; 改变表面性质, 增强活性 | 产生废水、废气, 污染环境, 引入新的有害物质 |
| 有机改性 | 改性亲水/疏水性, 提高应用性能 | 成本高, 可能影响其他性质 |
| 热活化改性 | 提高孔隙结构、比表面积, 增强吸附能力和化学活性 | 高温处理可能导致内部结构破坏, 影响性能; 成本较高 |
| 生物改性 | 环境友好, 成本低廉 | 受操作条件影响大, 周期一般较长 |
| 复合改性 | 结合多种改性方法的优点, 综合性能好, 能满足不同需求 | 制备复杂, 成本高, 需要平衡各种改性方法的影响 |
| 改性方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 酸碱改性 | 去除表面杂质, 提高纯度; 改变表面性质, 增强活性 | 产生废水、废气, 污染环境, 引入新的有害物质 |
| 有机改性 | 改性亲水/疏水性, 提高应用性能 | 成本高, 可能影响其他性质 |
| 热活化改性 | 提高孔隙结构、比表面积, 增强吸附能力和化学活性 | 高温处理可能导致内部结构破坏, 影响性能; 成本较高 |
| 生物改性 | 环境友好, 成本低廉 | 受操作条件影响大, 周期一般较长 |
| 复合改性 | 结合多种改性方法的优点, 综合性能好, 能满足不同需求 | 制备复杂, 成本高, 需要平衡各种改性方法的影响 |
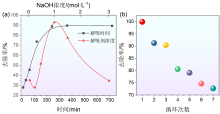
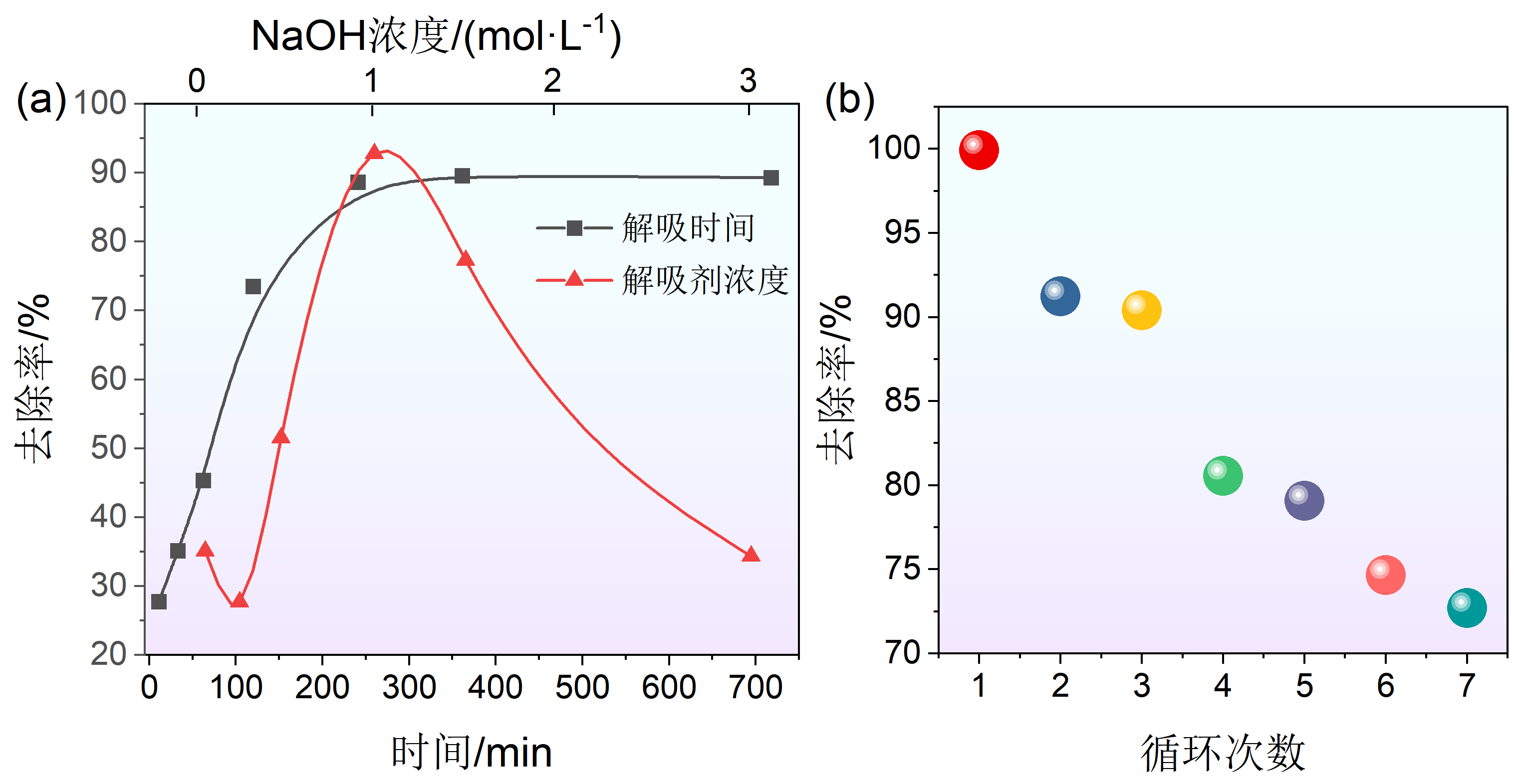
| 利用途径 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 废水处理 | 有效去除水中的重金属有机物等; 成本低廉, 实现废弃物资源化; 可以再生, 减少资源消耗 | 需要对煤矸石预处理; 吸附能力有限, 需要定期更换; 可能造成二次污染 |
| 土壤修复 | 提高土壤透气性和水保持能力; 促进作物生长, 提高产量 | 土壤改良剂受原料性质影响较大, 不同的土壤类型所需的改良剂不同; 需要评估长期效应和环境风险 |
| 建筑材料 | 降低建材成本; 提高材料的绝热性和耐火性 | 强度、耐久性等可能不如传统材料; 生产过程中可能需要额外的能源和成本 |
| 能源回收 | 减少化石能源依赖, 缓解环境压力 | 技术、设备成本要求高; 回收过程可能产生对环境不利的物质, 需要严格控制排放 |
| 肥料生产 | 提高土壤治理和作物产量, 减少化学肥料的使用 | 对原料要求高, 可能需要对煤矸石进行无害化处理, 生产使用过程需要严格控制质量 |
| 电池原料 | 高硅含量且成本较低 | 对硅提纯技术要求高; 技术研发和产业化过程存在壁垒 |
| 利用途径 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 废水处理 | 有效去除水中的重金属有机物等; 成本低廉, 实现废弃物资源化; 可以再生, 减少资源消耗 | 需要对煤矸石预处理; 吸附能力有限, 需要定期更换; 可能造成二次污染 |
| 土壤修复 | 提高土壤透气性和水保持能力; 促进作物生长, 提高产量 | 土壤改良剂受原料性质影响较大, 不同的土壤类型所需的改良剂不同; 需要评估长期效应和环境风险 |
| 建筑材料 | 降低建材成本; 提高材料的绝热性和耐火性 | 强度、耐久性等可能不如传统材料; 生产过程中可能需要额外的能源和成本 |
| 能源回收 | 减少化石能源依赖, 缓解环境压力 | 技术、设备成本要求高; 回收过程可能产生对环境不利的物质, 需要严格控制排放 |
| 肥料生产 | 提高土壤治理和作物产量, 减少化学肥料的使用 | 对原料要求高, 可能需要对煤矸石进行无害化处理, 生产使用过程需要严格控制质量 |
| 电池原料 | 高硅含量且成本较低 | 对硅提纯技术要求高; 技术研发和产业化过程存在壁垒 |
| [1] |
Li, J. J.; Wang, J. M. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 239, 117946.
|
| [2] |
Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Q. L. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 25221.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02319 pmid: 37483240 |
| [3] |
Jiao, Y. W.; Qiao, J. Q.; Jia, R. J.; Wei, P. Y.; Li, Y. Q.; Guo, J. K. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133965.
|
| [4] |
Ashfaq, M.; Heeralal, M.; Moghal, A. A. B. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2020, 5, 1.
|
| [5] |
Chilikwazi, B.; Onyari, J. M.; Wanjohi, J. M. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2053.
|
| [6] |
Wang, C.; Feng, K.; Wang, L. P.; Yu, Q. R.; Du, F. L.; Guo, X. L. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage. 2023, 25, 1622.
|
| [7] |
Guan, H. B.; Yu, J. T.; Umuhuza, K. A. S.; Sun, Q. W. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16369.
|
| [8] |
Kong, D. S.; Zhou, Z. H.; Song, S. J.; Jiang, R. L. Materials 2023, 16, 499.
|
| [9] |
Liu, L. H.; Liu, Q. F.; Li, Y. K.; Cao, H. Y.; Kang, X. J. Clays Clay Miner. 2022, 70, 695.
|
| [10] |
Yan, S. Y.; Zhang, F. Y.; Liu, J. J.; Ren, B.; He, P. G.; Jia, D. C.; Yang, J. L. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 227, 483.
|
| [11] |
Li, X. Y.; Liu, L.; Bai, C. Y.; Yang, K.; Zheng, T.; Lu, S.; Li, H. Q.; Qiao, Y. J.; Colombo, P. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 1473.
|
| [12] |
Lv, B.; Zhao, Z. Y.; Deng, X. W.; Fang, C. J.; Dong, B. B.; Zhang, B. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage. 2022, 24, 1579.
|
| [13] |
Zhao, R. B.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y. G.; Liu, Z. L.; Du, C. F. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122432.
|
| [14] |
Liu, F. Q.; Xie, M. Z.; Yu, G. Q.; Ke, C. Y.; Zhao, H. L. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10318.
|
| [15] |
Zhou, J. M.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Bu, N. J.; Hu, P. F.; Gao, J. M.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J. B. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122698.
|
| [16] |
Peng, L. G.; Wang, R.; Cheng, H. Q.; Zhang, L. Q.; He, Y. G.; Yin, C. H.; Zhang, X. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 1.
|
| [17] |
Xu, P. J.; Zhu, Y. F.; Cao, Y. D.; Cao, Z.; Xin, X. M. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 3137 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐培杰, 朱毅菲, 曹永丹, 曹钊, 辛学铭, 环境工程学报, 2023, 17, 3137.)
|
|
| [18] |
Zhang, H. L.; Teng, Z. D.; Jiang, X. L.; Li, T. G. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 1 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张华林, 滕泽栋, 江晓亮, 李庭刚, 环境化学, 2024, 43, 1.)
|
|
| [19] |
Gao, S.; Zhang, X. M.; Guo, L. H. Materials 2021, 14, 6803.
|
| [20] |
Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A. V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 190, 80.
doi: S0301-4797(16)31038-6 pmid: 28039822 |
| [21] |
Guo, Y. X.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Cheng, F. Q. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 2443 (in Chinese).
|
|
(郭彦霞, 张圆圆, 程芳琴, 化工学报, 2014, 65, 2443.)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.07.006 |
|
| [22] |
Gu, W. Z.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z. C.; He, Z. W. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0281513.
|
| [23] |
Song, S.; Li, S. G.; Zhang, T. J.; Pan, H. Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, L. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0262235.
|
| [24] |
Yang, D. L.; Tang, J. J.; Hu, N. N.; Xia, Y. T.; Yu, Y. T.; Huang, Q. Q. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 107.
|
| [25] |
Zhou, M.; Lai, W. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0279955.
|
| [26] |
Valeev, D.; Kunilova, I.; Alpatov, A.; Varnavskaya, A.; Ju, D. Minerals-Basel 2019, 9, 320.
|
| [27] |
Xu, X. Q.; Guo, Z. Q.; Zhu, D. Q.; Pan, J.; Yang, C. C.; Li, S. W. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 183, 59.
|
| [28] |
Chen, J.; Honaker, R. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 131, 317.
|
| [29] |
Mohanta, S. K.; Rout, B.; Dwari, R. K.; Reddy, P. S. R.; Mishra, B. K. Powder Technol. 2016, 294, 292.
|
| [30] |
Dai, L.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 3, 1.
|
| [31] |
Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. J.; Zhang, J. X.; Jiang, H. Q.; Wang, Y. B.; Yang, K.; Tian, X. G.; Yuan, L. F. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 5798.
|
| [32] |
Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A. V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 190, 80.
doi: S0301-4797(16)31038-6 pmid: 28039822 |
| [33] |
Na, F. X. M.S. Thesis, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang, 2023 (in Chinese).
|
|
(那芳溪, 硕士论文, 沈阳工业大学, 沈阳, 2023.)
|
|
| [34] |
Yang, N.; Ma, J. Z.; Shi, J. B.; Guo, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 207 (in Chinese).
|
|
(杨娜, 马建中, 石佳博, 郭旭, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 207.)
|
|
| [35] |
Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Su, Y. G.; Du, C. F. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 211, 106208.
|
| [36] |
Yang, C. Y.; Liu, L. J.; Shang, Z. B.; Li, D. L.; Zhong, R. F. Chem. Res. 2020, 31, 400 (in Chinese).
|
|
(杨长钰, 刘兰靖, 尚中博, 李德亮, 种瑞峰, 化学研究, 2020, 31, 400.)
|
|
| [37] |
Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wei, J. X.; Su, Y. B.; Gao, P. Q. Sci. Technol. Chem. Ind. 2022, 30, 1 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张岩, 马强, 魏建雄, 苏昱博, 高平强, 化工科技, 2022, 30, 1.)
|
|
| [38] |
Su, Z. N.; Li, X. H.; Zhang, Q. J. Cleaner Prod. 2022, 363, 132408.
|
| [39] |
Wei, R. L.; Yue, Z. H.; Liu, D. H.; Li, Z. W.; Wang, Y. J. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2023, 52, 2317 (in Chinese).
|
|
(魏瑞丽, 岳志涵, 刘德华, 李泽文, 王宇杰, 当代化工, 2023, 52, 2317.)
|
|
| [40] |
Song, Y. H.; Liu, Y. L.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. R.; Cao, Y. X. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3879 (in Chinese).
|
|
(宋永伟, 刘也琳, 王蕊, 王鹤茹, 曹艳晓, 中国环境科学, 2020, 40, 3879.)
|
|
| [41] |
Sheng, D. H.; Li, X. J.; Zhang, J. N.; Dong, L. M.; Du, X. Soil Fert. Sci. China 2023, 2023, 241 (in Chinese).
|
|
(盛定红, 李小军, 张景宁, 董丽敏, 杜鑫, 中国土壤与肥料, 2023, 2023, 241.)
|
|
| [42] |
Chen, J.; Guan, X.; Zhu, M. Y.; Gao, J. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1.
|
| [43] |
Zhang, W. Q.; Dong, X. W.; Huang, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, M.; Chai, J. Energies 2020, 13, 2504.
|
| [44] |
Shao, S.; Ma, B. Z.; Wang, C. Y.; Chen, Y. Q. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 564.
|
| [45] |
Gao, Y.; Huang, J. D.; Li, M.; Dai, Z. R.; Jiang, R. L.; Zhang, J. X. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8421.
|
| [46] |
Han, L. A.; Ren, W. G.; Wang, B.; He, X. X.; Ma, L. J.; Huo, Q. H.; Wang, J. C.; Bao, W. R.; Chang, L. P. Fuel 2019, 253, 1184.
|
| [47] |
Xu, F. Q.; He, X. F.; Hou, Z. Y.; Yang, X. Y.; Cao, X. X. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2022, 28, 553.
|
| [48] |
Zhao, H. H.; Li, P. Y.; He, X. D. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133347.
|
| [49] |
Zhao, B. H.; Zhu, Y. H.; Wang, C. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 110736.
|
| [50] |
Li, X. Y.; Qiao, Y. J.; Shao, J. H.; Bai, C. Y.; Li, H. Q.; Lu, S.; Zhang, X. H.; Yang, K.; Colombo, P. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 33914.
|
| [51] |
Quan, C.; Wang, F. D.; Guo, A. J.; Yang, T. H.; Li, R. D. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, DOI:10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0436 (in Chinese).
|
|
(全翠, 王福栋, 郭爱军, 杨天华, 李润东, 煤炭学报, 2023, DOI:10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0436.)
|
|
| [52] |
Zhu, Y. H.; Zhao, B. H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Yang, H. S. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2023, 42, 5531 (in Chinese).
|
|
(朱义浩, 赵白航, 王淳, 张雨晴, 杨海山, 化工进展, 2023, 42, 5531.)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-2157 |
|
| [53] |
Xie, J.; Xia, R. N.; Du, H. X.; Zhao, S. C.; Xu, H. New Chem. Mater. 2019, 47, 165 (in Chinese).
|
|
(谢娟, 夏润南, 杜红霞, 赵树春, 许红, 化工新型材料, 2019, 47, 165.)
|
|
| [54] |
Wang, J. L.; Guo, X. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279.
|
| [55] |
Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. X.; Wang, J. X.; Liu, X. S. Chem. Bull. 2022, 85, 1090 (in Chinese).
|
|
(赵昱, 刘喆, 刘佳欣, 王佳璇, 刘兴社, 化学通报, 2022, 85, 1090.)
|
|
| [56] |
Xiang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, J. M.; Chen, Y. P. Leather Manufacture and Environmental Technology 2023, 4, 123 (in Chinese).
|
|
(向艳, 侯艳, 周建民, 陈亚平, 皮革制作与环保科技, 2023, 4, 123.)
|
|
| [57] |
Liu, D. K.; Ban, M. H.; Peng, X.; Bai, B.; Xu, F. Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 2023, 39, 285 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘登科, 班渺寒, 彭旭, 白斌, 徐飞, 离子交换与吸附, 2023, 39, 285.)
|
|
| [58] |
Zhang, W.; Qi, X.; Miao, Y. W.; Lv, F. K.; Chen, Z. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources 2023, 43, 120 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张伟, 亓欣, 苗英威, 吕发奎, 陈政, 矿产保护与利用, 2023, 43, 120.)
|
|
| [59] |
Jia, Y. S.; Liu, H. W.; Han, S. X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Z. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11879.
|
| [60] |
Zhao, W. T.; Feng, K.; Zhang, H.; Han, L.; He, Q. D.; Huang, F.; Yu, W. M.; Guo, F.; Wang, W. B. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138287.
|
| [61] |
Xiang, M. T.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Y.; Lei, K. G.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D. F.; Fang, X. Q.; Cao, Y. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911.
|
| [62] |
Liu, F. Y.; Song, H. P.; Wu, H. B.; Feng, Z. J.; Cai, C. J.; Zhang, J. J.; Zhou, J. J. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources 2023, 43, 14 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘帆俞, 宋慧平, 吴海滨, 冯政君, 柴春镜, 张俊杰, 周建军, 矿产保护与利用, 2023, 43, 14.)
|
|
| [63] |
Chen, M.; Zhou, Y. Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X. Y.; Yuan, L. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139380.
|
| [64] |
Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J. M.; Chen, X. Y.; Yuan, L. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150199.
|
| [65] |
Liu, C. X.; Ma, S. H.; Wang, X. H.; Qu, Y. J.; Du, H. Biodegradation 2023, 34, 125.
|
| [66] |
Nan, Y. C.; Yang, Y. G.; Wang, Z. Q.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Q. M. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1253 (in Chinese).
|
|
(南益聪, 杨永刚, 王泽青, 周杨, 苏巧梅, 应用生态学报, 2023, 34, 1253.)
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202305.028 |
|
| [67] |
Wu, H. K.; Kang, S.; Zhang, H. Q.; Sun, Q. M.; Shen, R. X.; Shu, Z. L. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133833.
|
| [68] |
Zhang, T.; Wen, Q. X.; Gao, S. S.; Teng, J. P. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132646.
|
| [69] |
Liu, S.; Jin, J.; Yu, H. Y.; Cao, Y. C.; Du, Y. F.; Sun, X. L.; Qian, G. P. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130287.
|
| [70] |
Zhang, B.; Yan, B. Q.; Li, Y. T. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130218.
|
| [71] |
Zhao, H.; Wang, S. F.; Wang, R.; Shen, L. H.; Wang, Q. H. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 378, 131062.
|
| [72] |
Gao, S. S.; Zhao, G. H.; Guo, L. H.; Zhou, L. Q.; Yuan, K. K. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121212.
|
| [73] |
Yuan, C. Y.; Wang, H. Coal Process. Compr. Util. 2020, 2020, 71 (in Chinese).
|
|
(袁春玉, 王浩. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2020, 2020, 71.)
|
|
| [74] |
Guan, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, J. X.; Zhang, P. X.; Long, H. Concrete 2023, 2023, 103 (in Chinese).
|
|
(关虓, 高洁, 陈霁溪, 张鹏鑫, 龙行, 混凝土, 2023, 2023, 103.)
|
|
| [75] |
Chen, F. W.; Sang, S. B.; Ma, Y. Z.; Li, Y. W. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2023, 3, 1.
|
| [76] |
Gao, Y. Sichuan Build Mater. 2023, 49, 193 (in Chinese).
|
|
(高阳, 四川建材, 2023, 49, 193.)
|
|
| [77] |
Qin, Q. Z.; Deng, J. S.; Geng, H. H.; Bai, Z. Y.; Gui, X. H.; Ma, Z. T.; Miao, Z. Y. J. Cleaner Prod. 2022, 340, 130765.
|
| [78] |
Guo, Y. X.; Lv, H. B.; Yang, X.; Cheng, F. Q. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 177.
|
| [79] |
Zhang, L.; Chen, H. C.; Pan, J. H.; Wen, Z. P.; Shi, S. L.; Long, X.; Zhou, C. C. Minerals 2022, 12, 1371.
|
| [80] |
Zhang, L. Y.; Xiao, J.; Yao, Z.; Yuan, J.; Ye, S. C.; Zhong, Q. F. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136064.
|
| [81] |
Xiao, J.; Li, F. C.; Zhong, Q. F.; Bao, H. G.; Wang, B. J.; Huang, J. D.; Zhang, Y. B. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 118.
|
| [82] |
Qin, Q. Z.; Geng, H. H.; Deng, J. S.; Su, X. B.; Chen, M.; Park, C. B. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147036.
|
| [83] |
Zhou, Q.; Zhang, R. X.; Meng, J. X.; Shen, Z. L.; Yang, T. H.; Xing, W. L. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 109, 101292.
|
| [84] |
Du, S. L.; Dong, Y. C.; Guo, F. Q.; Tian, B. L.; Mao, S. B.; Qian, L.; Xin, C. Y. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 14138.
|
| [85] |
Jiang, X. Y.; Yang, S. Q.; Zhou, B. Z.; Song, W. X.; Cai, J. W.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, Q. C.; Yang, K. Fire Mater. 2022, 46, 549.
|
| [86] |
Ashfaq, M.; Heera Lai, M.; Moghal, A. A. B. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, Vol. 144, Eds.: Hazarika, H.; Madabhushi, G. S. P.; Yasuhara, K.; Bergado, D. T., Springer, Singapore, 2021, pp. 203-218.
|
| [87] |
Xu, Y. H.; Wu, H. J.; Dong, Z. F.; Wang, Q. Q.; Chen, Y. Y. Environ. Dev. Sustainable 2023, 1.
|
| [88] |
Quan, C.; Chu, H.; Zhou, Y. Y.; Su, S.; Su, R. R.; Gao, N. B. Fuel 2022, 322, 124184.
|
| [89] |
Yi, D. W.; Du, H. L.; Li, Y. F.; Gao, Y. M.; Liu, S. F.; Xu, B. Y.; Huang, H. Q.; Kang, L. Coatings 2023, 13, 1886.
|
| [90] |
Ai, J. J.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Yin, Y. K.; Wu, Z. J.; Zhang, J. B. Fuel 2023, 341, 127692.
|
| [91] |
Liu, X.; Liu, W. K.; Zhang, H. B.; Niu, H. P. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1305.
|
| [92] |
Zheng, W. K.; Li, Y. C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y. X.; Li, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 42753.
|
| [93] |
Geng, J. J. M.S. Thesis, Nanchang Hangkong University, 2014 (in Chinese).
|
|
(耿军军, 硕士论文, 南昌航空大学, 南昌, 2014.)
|
|
| [94] |
Qiu, J. S.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, R. Y.; Gao, Y.; Guan, X. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128071.
|
| [95] |
Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, W.; Lan, D. W.; Hao, G. Y.; Yi, X. Y.; Yang, Z. X.; Hu, J. L.; He, W. X.; Liu, Y. Y.; Ma, L. T.; Cui, J. L.; Sun, J. C. Solid State Ionics 2021, 371, 115772.
|
| [96] |
Wang, B.; Ma, Y. N.; Lee, X. Q.; Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X. Y.; Li, L.; Chen, M. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143664.
|
| [97] |
Zhang, Y.; Wei, J. X.; Zhang, X. Y.; Gao, P. Q. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2023, 31, 1.
|
| [1] | Huang Xiao-yue, Wang Wei, Ling Lan, Zhang Wei-xian. Heavy Metal-nZVI Reactions: the Core-shell Structure and Applications for Heavy Metal Treatment [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 529-537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||