Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1551-1560.DOI: 10.6023/A25070252 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
刘文素, 江莎*( ), 王渝童, 谢林林, 张登翔, 谭力伟, 汪永杰
), 王渝童, 谢林林, 张登翔, 谭力伟, 汪永杰
投稿日期:2025-07-11
发布日期:2025-09-28
基金资助:
Wensu Liu, Sha Jiang*( ), Yutong Wang, Linlin Xie, Dengxiang Zhang, Liwei Tan, Yongjie Wang
), Yutong Wang, Linlin Xie, Dengxiang Zhang, Liwei Tan, Yongjie Wang
Received:2025-07-11
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
* E-mail: jiangsha@cqupt.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Wensu Liu, Sha Jiang, Yutong Wang, Linlin Xie, Dengxiang Zhang, Liwei Tan, Yongjie Wang. CaF2 Nanoprobes with Mn2+ Ions/Dimers Exhibiting Differential Thermal Responses for Multimodal Optical Thermometry[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1551-1560.
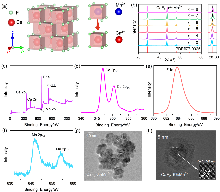

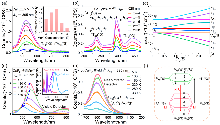

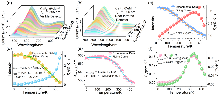

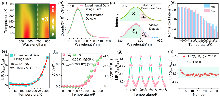

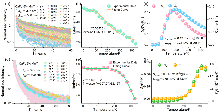
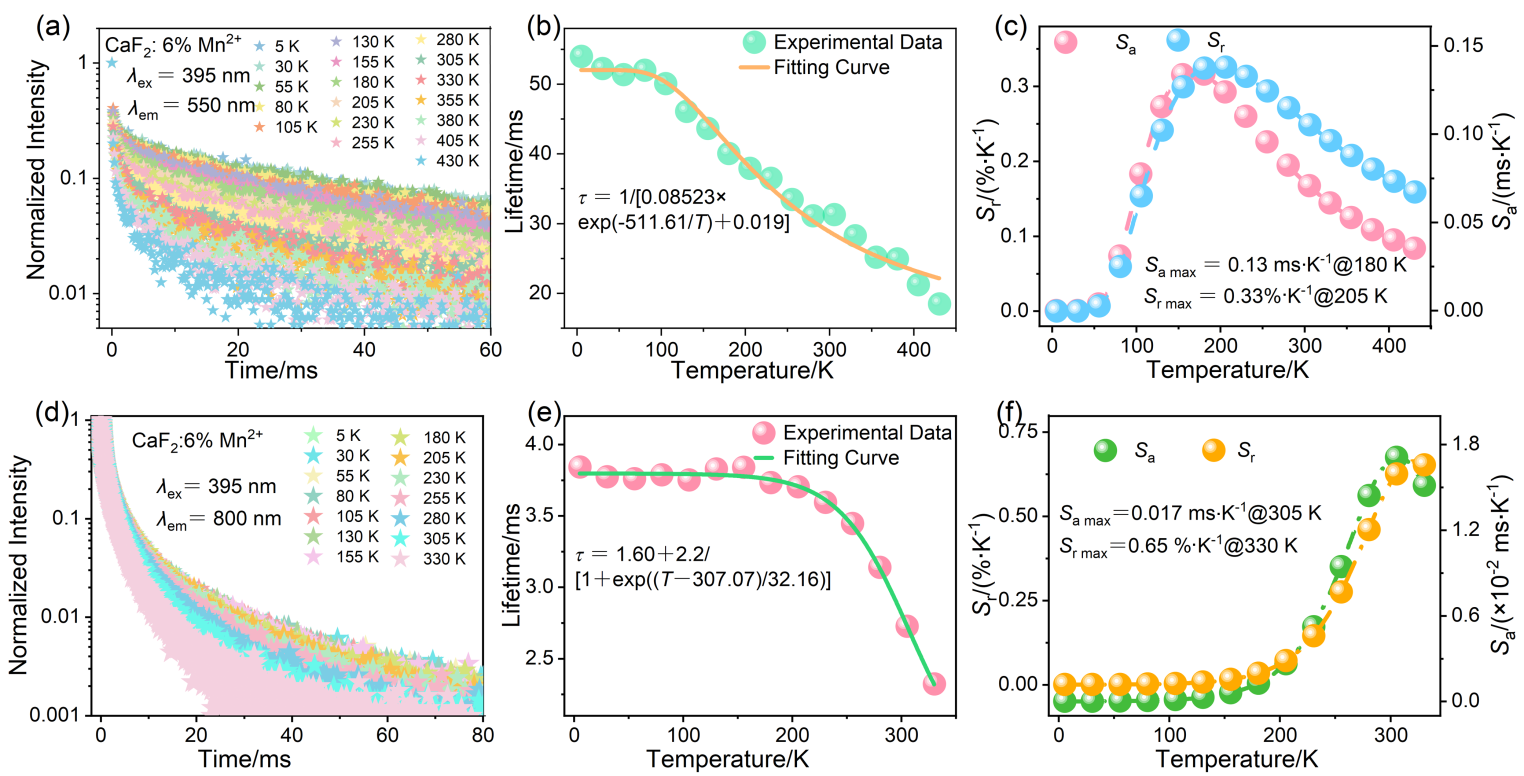
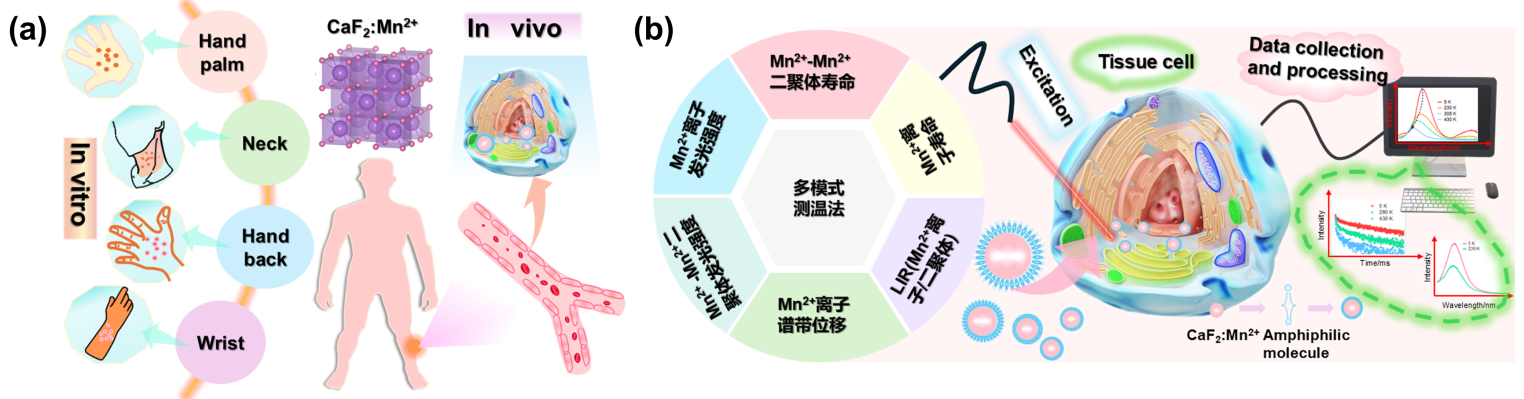
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.216196 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c05370 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1002/lpor.v19.4 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46727-5 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2023.10.010 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v35.36 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.6023/A17070341 |
|
(秦天依, 曾毅, 陈金平, 于天君, 李嫕, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1164.)
doi: 10.6023/A17070341 |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.6023/A23040108 |
|
(马天骄, 李瑾, 马晓东, 姜学松, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 749.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040108 |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.6023/A23050242 |
|
(温哥华, 温都日娜, 陈秀梅, 麻秀芳, 翁果果, 韦依凡, 鲍松松, 谢小吉, 胡淑贤, 郑丽敏, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1311.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050242 |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0957-y |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1039/D3QI01864D |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.06.385 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2023.415298 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2006.05.011 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2025.121185 |
| [16] |
pmid: 26682406 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00806 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120143 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00690 pmid: 36102851 |
| [20] |
|
|
(周全新, 夏志国, 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50, 3103.)
|
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1002/adom.v12.36 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118241 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2015.05.014 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2011.12.015 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/0022-2313(81)90027-2 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s40843-018-9288-4 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1002/adom.v7.24 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1039/D4TC00890A |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c00548 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29881-6 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1002/adom.v11.5 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1002/advs.v2.7 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c03935 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v21.17 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000835 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b03886 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120300 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5c00728 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02118 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1002/advs.v11.7 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00644 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1021/jp502825p |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||