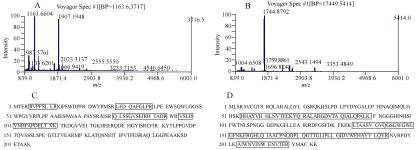
In order to better understand the molecular mechanisms of Benzo(a)pyrene [B(a)P] mediated toxicity on airway epithelial cells, comparative proteomics involving two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry (MS) was performed on total proteins extracts from B(a)P-A549 and its control cell line DMSO-A549. Then the expression of heat shock protein 27 (HSP 27) and Mn superoxide dismutase (Mn SOD), two of the identified differential expressed protein, was analyzed using western blot. After 0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L B(a)P treatment, the Mn SOD expression levels were detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot analysis, the total antioxidant capacity, total activity of SOD, catalase activity (CAT) and glutathione reductase activity (Gr) were determined also. In this study, 23 differentially expressed proteins was identified. Western blot confirm that B(a)P decreased heat shock protein 27 and Mn SOD expression levels in A549 cells. and the expression levels of this two genes were increased to the control level after detoxification. After 0.1, 1, 10 μmol/L B(a)P treatment on A549 cells, the expression level of Mn SOD and SOD activity were significantly induced after 0.1 μmol/L B(a)P exposure and then reduced after 1 μmol/L and 10 μmol/L B(a)P exposure. With the increased concentration of B(a)P, the catalase activity, the total antioxidant capacity and the glutathione reductase activity increased. Our results indicate that HSP 27 and Mn SOD may be related to the B(a)P mediated toxicity in airway epithelial cells. CAT and Gr may play an important role to antioxidant injury induced by B(a)P.
MIN Ling-Feng
,
HE Shu-Ya
,
CHEN Qiong
,
XIE Ming-Xuan
,
PENG Hong-Bing
,
CAO Lan-Yu
,
WANG Huai-Shi
,
ZHU Xiao-Yan
. Using Proteomic Analysis to Screen for Differentially Expressed Proteins in Airway Epithelial Cells Toxicity Mediated by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011
, 69(21)
: 2609
-2617
.
DOI: 10.6023/A1012161J


