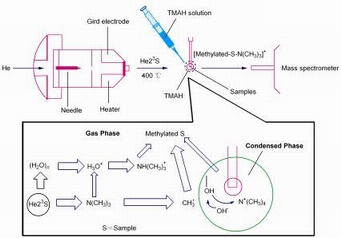
Direct analysis in real time ion source (DART) has been applied to the rapid analysis of solid, liquid and gaseous samples. The compounds with either high volatility or high proton affinity are favorable for DART analysis. However, a lot of natural products such as ginsenosides and ginseng oligosaccharides are difficult to be directly ionized by DART due to their low volatility and proton affinity. Derivatization is very necessary in the analysis of the compounds with low volatility and proton affinity. Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) is a frequently used methylation reagent which can be applied to improve the volatility of low volatile compound in GC-MS. In the current work, TMAH was introduced to assist the ionization of ginsenoside and ginseng oligosaccharide in DART. Small amount of ginsenoside standard or ginseng oligosaccharide powder was collected on the end of melting point tubes respectively. Then 5 μL of liquid from a solution containing 25% solution of TMAH dissolved in MeOH was applied to elute the surface of each melting point tube. Finally, all the end of melting point tubes containing sample powder and TMAH were put on a stainless holder for DART analysis. The solvents were flash evaporated in the DART source at 400 ℃ and the signals of methylated analytes were detected. The mechanism of methylation and ionization in DART was elucidated from the aspects of condensed and gas phase. On the one hand, the methylation enhanced volatility of analytes, on the other hand, a N(CH3)3H+ ion was generated to assist the ionization of methylated analytes. Incomplete and complete methylation is the major reaction of ginsenoside, but hypermethylation occurred in ginseng oligosaccharide with the increase of number of hydroxyls. The results showed that the synergy of methylation reaction both in condensed phase and gas phase is the fundamental reason of the generation of methylated ions. The methylation in condensed phase is governed by necleophilic reaction, and radical reaction is the major reaction in gas phase.
Yu Qing
,
Yu Binbin
,
Yue Hao
,
Jiao Lili
,
Liu Shuying
. Study of Mechanism of Ionization Assisted by Methylation in Direct Analysis in Real Time Ion Source[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012
, 70(15)
: 1650
-1654
.
DOI: 10.6023/A12050214
[1] Cody, R. B.; Laramee, J. A.; Durst, H. D. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2297.
[2] Jones, R. W.; Cody, R. B.; McClelland, J. F. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 915.
[3] Cody, R. B. Anal. Chem. 2008, 81, 1101.
[4] Haefliger, O. P.; Jeckelmann, N. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1361.
[5] Harris, G. A.; Galhena, A. S.; Fernaandez, F. M. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4508.
[6] Eberherr, W.; Buchberger, W.; Hertsens, R.; Klampfl, C. W. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5792.
[7] Petucci, C.; Diffendal, J.; Kaufman, D.; Mekonnen, B.; Terefenko, G.; Musselman, B. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5064.
[8] Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1496.
[9] Kubec, R.; Cody, R. B.; Dane, A. J.; Musah, R. A.; Schraml, J.; Vattekkatte, A.; Block, E. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1121.
[10] Fernández, F. M.; Cody, R. B.; Green, M. D.; Hampton, C. Y.; McGready, R.; Sengaloundeth, S.; White, N. J.; Newton, P. N. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 702.
[11] Curtis, M. E.; Jones, P. R.; Sparkman, O. D.; Cody, R. B. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 2082.
[12] Song, F.-R.; Yan, C.-Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Liu, S.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 1103. (宋凤瑞, 闫存玉, 刘宁, 刘志强, 刘淑莹, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 1103.)
[13] Liu, R. N.; Yue, H.; Krechmer, J.; Jiao, L.; Liu, C. C.; Musselman, B.; Liu, S.-Y. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22 (Supplement 1), 88.
[14] Fabbri, D.; Helleur, R. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1999, 49, 277.


