

Electrochemical Deposition of Graphene Supported PtCo Composite Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Methanol Oxidation
Received date: 2012-08-14
Online published: 2013-01-09
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20975056, 81102411, 21275082), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (Nos. ZR2011BZ004, ZR2011BQ005), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Japan-China Scientific Cooperation Program (No. 21111140014), State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science (No. SKLACLS1110) and the National Key Basic Research Development Program of China (973 special preliminary study plan, Grant no.: 2012CB722705).
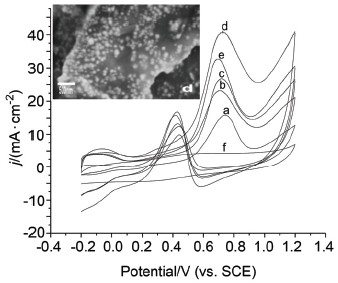
Direct methanol fuel cells are excellent power sources due to their high energy density, low pollutant emission and easy handling. However, commercial applications are limited by the high cost related to noble metal catalysts. Recent findings have proved that appropriate catalyst support, which improves the utilization of the noble metals in great depth, may be one breakthrough. Graphene nanosheet (GNS), a new two-dimensional carbon material with a single (or a few) atomic thickness, as the combination of its high surface area, high conductivity and unique graphitized basal plane structure, has recently attracted an enormous amount of interest from both theoretical and experimental scientists. It has been proved that catalysts supported on GNSs show improved activity than those supported on carbon black. Furthermore, alloying Pt with other metal is widely approved as a practical method to relieve the CO-poisoning of the catalyst, which can be ascribed to both a bi-functional mechanism and a ligand (electronic) effect. In this experiment, PtCo/graphene (GN) composite catalysts were synthesized on an indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate by the potentiostatic method. Catalyst samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX) and electrochemical methods. SEM results showed that the addition of graphene could enhance the dispersion of the catalytic particles and reduce the particle size, especially when the molar ratio of Pt and Co is 1:2.93, the particles had the smallest size and the best dispersion. Electrochemical tests demonstrated that graphene as the catalytic support could improve the CO-tolerance of the catalysts, which was determined by the outstanding electric conductivity and rich oxygen-containing species of graphene, resulting in good performance for electrocatalytic methanol oxidation. Furthermore, owing to the special electronic effect of Co, its addition also influenced the catalytic activity. It was found that when the molar ratio of Pt and Co was 1:2.93, the composite catalyst exhibited the most excellent catalytic performance for electrocatalytic methanol oxidation with the forward anodic peak current density of 662 A·gpt-1and the If/Ib of 2.34 which was nearly 1.8 times that of the traditional PtCo/C catalyst (If/Ib=1.32).
Shi Guoyu , Wang Zonghua , Xia Jianfei , Zhang Feifei , Xia Yanzhi , Li Yanhui . Electrochemical Deposition of Graphene Supported PtCo Composite Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Methanol Oxidation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(02) : 227 -233 . DOI: 10.6023/A12080553
[1] Li, Y. M.; Tang, L. H.; Li, J. H. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 846.
[2] Ye, W. C.; Kou, H. H.; Liu, Q. Z. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 4088.
[3] Zhang, H. M.; Zhou, W. Q.; Du, Y. K.; Yang, P.; Xu, J. K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 2529. (张红梅, 周卫强, 杜玉扣, 杨平, 徐景坤, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 2529.)
[4] Wang, Z. H.; Chen, T. W.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Qiao, H. Y.; Huang, A.-P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 392. (汪振辉, 陈体伟, 李晶, 王栋, 乔海燕, 黄爱平, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 392.)
[5] Zhou, Y. H.; Cen, S. Q.; Li, Z. L.; Niu, Z. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2007, 65, 2669. (周颖华, 岑树琼, 李则林, 牛振江, 化学学报, 2007, 65, 2669.)
[6] Sauda, T.; Ogiwara, N.; Takasu, Y.; Sugimoto, W. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 13390.
[7] Lee,Y. H.; Lee, G.; Shim, J. H.; Hwang, S.; Kwak, J.; Lee, K.; Song, H.; Park, J.-T. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4209.
[8] Wang, S. Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang S. P. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10505.
[9] Liu, S. H.; Yu, W. Y.; Chen, C. H.; Lo, A. Y.; Hwang, B. J.; Chien, S. H.; Liu, S. B. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1622.
[10] Liu, Z. L.; Su, F. B.; Zhang, X. H.; Tay, S. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3824.
[11] Xu, J. B.; Hua, K. F.; Sun, G. Z.; Wang, C. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 982.
[12] Sandoval Gonzalez, A.; Borja Arco, E.; Escalante, J. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1052.
[13] Wakisaka, M.; Mitsui, S.; Hirose, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23489.
[14] Prabhuram, J.; Zhao, T. S.; Tang, Z. K.; Chen, R.; Liang, Z. X. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5245.
[15] Wu, G.; Swaidan, R.; Li, D.; Li. N. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7622.
[16] Hernández-Fernández, P.; Nuño, R.; Fatás, E. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8267.
[17] Kakati, N.; Maiti, J.; Jee, S. H.; Lee, S. H.; Yoon, Y. S. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5617.
[18] Kim, C.; Kwon, H. H.; Song, I. K.; Sung, Y. E.; Chung, W. S.; Lee, H. I. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 404.
[19] Rozhkov, A. V.; Giavaras, G.; Bliokh, Y. P.; Freilikher, V.; Nori, F. Phys. Rev. 2011, 53, 77.
[20] Xu, C. W.; Su, Y. Z.; Tan, L. L.; Liu, Z. L. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 6322.
[21] Li, Y. J.; Gao, W;. Ci, L. J.; Wang, C. M. Carbon 2010, 48, 1129.
[22] Sharma, S.; Ganguly, A.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Miao, X.-P.; Li, M.-X. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19464.
[23] Wietechaa, M.; Zhu, J.; Gao, G.-H.; Wang, N. J. Power Sources 2012, 198, 34.
[24] Niu, L.; Li, Q. H.; Wei, F. H.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 271.
[25] Søgaard, M.; Odgaard, M.; Skou, E. M. Solid State Ionics 2001, 145, 31.
[26] Hamnett, A. Catal. Today 1997, 38, 445.
[27] Baldauf, M.; Preidel, W. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 162.
[28] Huang, Y. Y.; Zheng, S. Y.; Lin, X. Z.; Su, L. Q.; Guo, Y. L. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 63, 346.
[29] Ye, W. C.; Kou, H. H.; Liu, Q. Z. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 4096.
[30] Nicholson, R. S.; Shain, I. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 706.
[31] Wu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, B. Q. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 7.
[32] Wang, Z. B.; Yin, Z. P.; Shao, Y. Y. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 9.
[33] Laviron, E.; Roullier, L. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1980, 115, 65.
[34] Khan, A. S. A.; Ahmed, R.; Mirza, M. L. Turk. J. Chem. 2008, 32, 750.
[35] Wang, Z. H.; Xia, J. F.; Zhu, L. Y.; Zhang, F. F. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2012, 161, 133.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |