

Synthesis of Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 Nanocomposites and Investigation into Their Catalysis Properties
Received date: 2012-11-07
Online published: 2013-01-21
Supported by
Project supported by the Cultural Heritage Conversation Science and Technology Research Foundation (No. 20090106) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201001007).
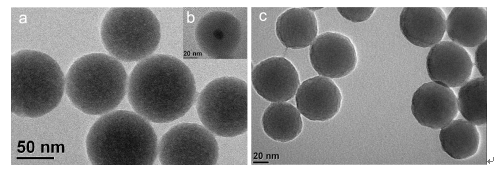
The design and synthesis of functional nanocomposites are very important since these materials have been widely used in different fields such as catalytic chemical reaction, the fabrication of chemical sensors or biosensor as well as the design of the nanodrug delivery systems. Herein, a new method for preparing the Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites by the reverse microemulsion route was developed. The magnetic fluid, which was consisted of the chitosan and Fe3O4 nanoparticles, was firstly prepared based on the strong supra-molecules interaction between chitosan and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Then, due to the better and stronger affinity of the silica to chitosan, the chitosan modified magnetic fluids was successfully doped into the silica nanoparticles while the silica nanoparticles was being formed in the reverse microemulsion system. In this case, the magnetic chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 nanocomposites was successfully synthesized. Thereafter, the magnetic nanocomposites were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), magnetization curve, SEM energy spectrum, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and zeta potential of the nanoparticles surface techniques, respectively. Our results showed that the as-prepared Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites were spherical shape with core-shell structure apparently and their size is about 60 nm. More importantly, it was also found that there were lots of nanochannels inside the as-prepared Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites due to the porous hydrogel structural property of the chitosan. At the same time, the nanochannel behavior of the nanocomposites was further investigated by using the Luminol-H2O2 chemiluminescence reaction based on the catalytic effect of magnetic Fe3O4 particles towards the chemiluminescence reaction. The chemiluminescence investigating results showed that the 60 nm Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites offered a lot of nanochannels, which allowed both the luminol and H2O2 to be diffused into the inner part of the nanocomposites to react with Fe3O4 particles in the core part of the nanocomposites and produce the catalytic chemiluminescence signals. This behavior of the as-prepared magnetic nanocomposites may pave way to design the chemiluminescence-based sensor or biosensor.
Key words: nanocomposites; Fe3O4 nanoparticles; chemiluminescence; nanochannel
Wei Wei , Zhang Quan , Zheng Xingwang . Synthesis of Chitosan/Fe3O4/SiO2 Nanocomposites and Investigation into Their Catalysis Properties[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(03) : 387 -391 . DOI: 10.6023/A12110888
[1] Jeong, J. Y.; Cho, M. Y.; Lim, Y. T.; Song, N. W.; Chung, B. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5296.
[2] Liu, J. P.; Zhang, L. L.; Wang, C.; Xu, H. Y.; Zhao, X. J. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 954.
[3] Shan, Y.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2916.
[4] Wu, W. T.; Shen, J.; Gai, Z.; Hong, K. L.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. Q. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9876.
[5] Lu, A. H.; Salabas, E. L.; Schüth, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222.
[6] Selvan, S. T.; Patra, P. K.; Chung, Y. A.; Ying, J. Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2448.
[7] Du, X. Y.; He, J.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L. J.; An, S. S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2717.
[8] Ma, M.; Chen, H. R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Cui, X. Z.; Shi, J. L. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 989.
[9] Insin, N.; Tracy, J. B.; Lee, H.; Zimmer, J. P.; Westervelt, R. M.; Bawendi, M. G. ACS nano 2008, 2(2), 197.
[10] Zou, X.; Huang, H.; Gao, Y.; Su, X. G. Analyst 2012, 137, 648.
[11] Zhi, J.; Wang, Y. J.; Lu, Y. C.; Ma, J. Y.; Luo, G. S. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1552.
[12] Jiang, C. Z.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X. M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H. Q.; Song, D. Q. Talanta 2012, 89, 38.
[13] Fu, R.; Jin, X. M.; Liang, J. L.; Zheng, W. S.; Zhuang, J. Q.; Yang, W. S. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15352.
[14] Wang, R.; Han, H. Z.; Zheng, X. W.; Li, Y. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68(17), 1726. (汪绒, 韩海洲, 郑行望, 李玉虎, 化学学报, 2010, 68(17), 1726.)
[15] Triantis, T. M.; Papadopoulos, K.; Yannakopoulou, E.; Dimotikali, D.; Hrbá?, J.; Zbo?il, R. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 483.
[16] Wei, H.; Wang, E. K. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2250.
[17] Zhang, L. N.; Guo, Z. H.; Zheng, X. W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69(20), 2486. (张李娜, 郭志慧, 郑行望, 化学学报, 2011, 69(20), 2486.)
[18] He, X. X.; Shi, B. H.; Wang, K. M.; Chen, M.; Tan, W. H. J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 37(4), 62. (何晓晓, 石碧华, 王柯敏, 陈冕, 谭蔚泓, 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(4), 62.)
[19] Xia, H. B.; Foo, P.; Yi, J. B. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2442.
[20] Zhang, W. J.; Zhang, Y. X.; Shi, X. H.; Liang, C.; Xian, Y. Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16177.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |