

Determination of Surface Complexation Constant of Methylene Blue,NH4+, Na+ and K+ with SiO2 Surface
Received date: 2013-01-18
Online published: 2013-03-26
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51274104, 50874052) and the National Key Basic Research Program of China (973) (No. 2011CB933700).
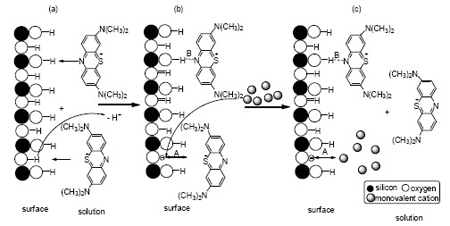
Understanding and reducing the environmental contaminations of persistent organic pollutants to soil and surface water is the central topic of environmental chemistry. In this study, the adsorption of Methylene Blue (MB), a typical model substance of organic dye, at the surface of silica, the main soil containing substance, may give insights for understanding the theoretical distribution of organic pollutants in the system of soil and surface water. The adsorption of MB and surface charge in SiO2 system with varying solution pH were characterized by electrokinetic phenomena and adsorption experiments. Testing results confirmed that the adsorption of MB at the silica surface belongs to the Langmuir type i.e. monolayer adsorption. Based on the experimental data, complexation constants of MB at the surface of SiO2 was calculated according to Constant Capacitance Model using computer software WinSGW to be: ≡Si2O-+MB+⇔≡Si2OMB (lg K=4.48) and ≡SiOH+MB+⇔≡SiOHMB+ (lg K=2.3). These results indicate that the adsorption of MB at the surface of silica includes two types i.e. electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding. In addition, the effect of monovalent cation (NH4+, Na+, K+) on the adsorption of MB at the surface of SiO2 was studied, the complexation constants of NH4+, Na+ or K+ with SiO2 surface were established respectively as: ≡Si2O-+M+⇔≡Si2OM [lg K=3.76, 2.73, 2.58 (M+=NH4+, Na+, K+)]. Furthermore, at higher concentration of , an additional surface reaction ≡SiOH+NH3+MB+⇔≡SiOHNH3MB+ (lg K=6.69) was established, which lead to the formation of a ternary surface complex ≡SiOHNH3MB+. These results suggest that mutual ion exchange reaction between adsorbed and solution monovalent ions can take place. The affinity of monovalent cations studied to the silica surface is in the order of MB+>NH4+>Na+>K+. This study has not only provided basic data for quantifying the adsorption of various monovalent cation at the surface of silica but also can hopefully provide theoretical basis for understanding the distribution of organic pollutants and ammonia in the system of contaminated soil and surface water.
Key words: SiO2; methylene blue; NH4+, Na+, K+; surface complexation constant
Qi Changlin , Ge Donglai , Zhu Xinxin , Sun Zhongxi . Determination of Surface Complexation Constant of Methylene Blue,NH4+, Na+ and K+ with SiO2 Surface[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(05) : 803 -809 . DOI: 10.6023/A13010095
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |