

Influence of O2 Annealed Electrode on Microcosmic Performances in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
Received date: 2013-02-18
Online published: 2013-07-19
Supported by
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CBA00700), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2011AA050527), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21003130, 21173228) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 20110490835, 2012T50581).
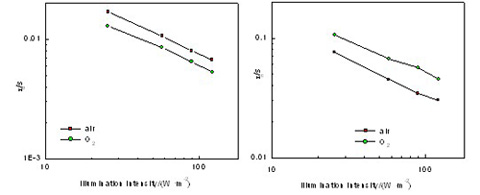
Over the last decade, different techniques had been employed to prepare nanoporous TiO2 electrode, aiming to improve the electron transport and depress electron recombination processes in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). Preparing TiO2 films by various atmospheres and annealing processes was an effective method to change their surface properties. Many results had been published recently regarding the effect of annealing atmospheres on cell performances, but there is no detailed study disclosing the working mechanism of O2 annealed electrode so far. In the present work, the influence of O2 anneal electrode on charge transport and recombination processes in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) was investigated. TiO2 films were prepared by a two-step annealing process. The 1st-step of annealing was performed in air or oxygen at 510℃ for 30 min which effectively removed the residual organics originated from the TiO2 precursor pastes. The 2nd-step of annealing was performed in nitrogen at 510℃ for 10 min which removed extra oxygen atoms resulted from the incorporation of oxygen atoms adsorbed onto photoanode surface during the 1st-step of annealing. Series resistance and fill factor (FF) of the cell can be improved by the 2nd-step. The surface properties of sintering films were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis (XPS). The microcosmic processes of recombination, transport and band edge movement were detected by intensity-modulated photocurrent spectroscopy (IMPS)/intensity-modulated photovoltage spectroscopy (IMVS). It was found that both open-circuit photovoltage (Voc) and short-circuit photocurrent (Jsc) were improved by O2 annealed electrode. O2 anneal could reduce the recombination centers of Ti3+ defects and the recombination between electron and was consequently depressed. Additionally, the electron transport process in TiO2 films was also improved due to the increase of dye absorption amount and more positive band shift by O2 anneal. Overall, O2 annealed electrode enhanced the light absorption efficiency, electron collection efficiency and injection efficiency, inducing the cell efficiency rose from 6.90% to 7.53%.
Kou Dongxing , Liu Weiqing , Hu Linhua , Chen Shuanghong , Huang Yang , Dai Songyuan . Influence of O2 Annealed Electrode on Microcosmic Performances in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(08) : 1149 -1153 . DOI: 10.6023/A13020196
[1] Oregan, B.; Gratzel, M. Nature 1991, 353, 737.
[2] Kou, D. X.; Liu, W. Q.; Hu, L. H.; Huang, Y.; Dai, S. Y.; Jiang, N. Q. Acta Phys. Sinica 2010, 59, 5857. (寇东星, 刘伟庆, 胡林华, 黄阳, 戴松元, 姜年权, 物理学报, 2010, 59, 5857.)
[3] Chen, C. Y.; Wang, M. K.; Li, J. Y.; Pootrakulchote, N.; Alibabaei, L.; Ngoc-le, C. H.; Decoppet, J. D.; Tsai, J. H.; Gratzel, C.; Wu, C. G.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Gratzel, M. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3103.
[4] Luo, Y. H.; Li, D. M.; Meng, Q. B. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4647.
[5] Yella, A.; Lee, H. W.; Tsao, H. N.; Yi, C. Y.; Chandiran, A. K.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Diau, E. W. G.; Yeh, C. Y.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Gratzel, M. Science 2011, 334, 629.
[6] Li, J.; Kong, F. T.; Zhang, C. N.; Liu, W. Q.; Dai, S. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 1357. (李洁, 孔凡太, 张昌能, 刘伟庆, 戴松元, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 1357.)
[7] Huang, X. W.; Deng, J. Y.; Xu, L.; Shen, P.; Zhao, B.; Tan, S. T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1604. (黄先威, 邓继勇, 许律, 沈平, 赵斌, 谭松庭, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1604.)
[8] Guo, L.; Pan, X.; Wang, M.; Kou, D. X.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C. N.; Dai, S. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 767. (郭磊, 潘旭, 王猛, 寇东星, 蔡墨朗, 张昌能, 戴松元, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 767.)
[9] Peter, L. M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2630.
[10] Zhu, K.; Schiff, E. A.; Park, N. G.; van de Lagemaat, J.; Frank, A. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 685.
[11] van de Lagemaat, J.; Frank, A. J. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 4292.
[12] Hagfeldt, A.; Gratzel, M. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 49.
[13] Hagfeldt, A.; Gratzel, M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 269.
[14] Zhu, K.; Kopidakis, N.; Neale, N. R.; van de Lagemaat, J.; Frank, A. J. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 25174.
[15] Nakamura, I.; Negishi, N.; Kutsuna, S.; Ihara, T.; Sugihara, S.; Takeuchi, E. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2000, 161, 205.
[16] Wu, N. L.; Lee, M. S.; Pon, Z. J.; Hsu, J. Z. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2004, 163, 277.
[17] Chen, C. M.; Hsu, Y. C.; Cherng, S. J. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 872.
[18] Lee, S.; Noh, J. H.; Bae, S. T.; Cho, I. S.; Kim, J. Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, J. K.; Jung, H. S.; Hong, K. S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7443.
[19] Lee, S.; Jun, Y.; Kim, K. J.; Kim, D. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 65, 193.
[20] Schlichthorl, G.; Huang, S. Y.; Sprague, J.; Frank, A. J. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 8141.
[21] Lin, H.; Liu, Y. Z.; Liu, C. J.; Li, X.; Shen, H. P.; Zhang, J.; Ma, T. L.; Li, J. B. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 653, 81.
[22] Edvinsson, T.; Pschirer, N.; Schoneboom, J.; Eickemeyer, F.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. Chem. Phys. 2009, 357, 124.
[23] O'Regan, B. C.; Durrant, J. R.; Sommeling, P. M.; Bakker, N. J. J. Phy. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14001.
[24] Gregg, B. A.; Chen, S. G.; Ferrere, S. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 3019.
[25] Fisher, A. C.; Peter, L. M.; Ponomarev, E. A.; Walker, A. B.; Wijayantha, K. G. U. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 949.
[26] Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Bisquert, J.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 87, 117.
[27] Park, J. H.; Kim, J. H.; Choi, C. J.; Kim, H.; Ahn, K. S. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2012, 567, 19.
[28] Zhu, K.; Neale, N. R.; Miedaner, A.; Frank, A. J. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 69.
[29] Li, C. H.; Luo, Y. H.; Guo, X. Z.; Li, D. M.; Mi, J. L.; So, L.; Hald, P.; Meng, Q. B.; Iversen, B. B. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 196, 504.
[30] Hu, L. H.; Dai, S. Y.; Wang, K. J. Acta Phys. Sinica 2005, 54, 1914. (胡林华, 戴松元, 王孔嘉, 物理学报, 2005, 54, 1914.)Hu, L. H.; Dai, S. Y.; Weng, J.; Xiao, S. F.; Sui, Y. F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S. H.; Kong, F. T.; Pan, X.; Liang, L. Y.; Wang, K. J. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 358.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |