

A Benzoxazole-Based Fluorescent Probe for Visual Detection of Hg2+
Received date: 2013-07-29
Online published: 2013-09-10
Supported by
Project supported by the Youth Program of Educational Commission of Hubei Province (No. Q20134402), the Hubei Polytechnic University Innovation Program (No. 12xjz21C) and the Open Foundation of Hubei Key Laboratory of Mine Environmental Pollution Control & Remediation (No. 2012103).
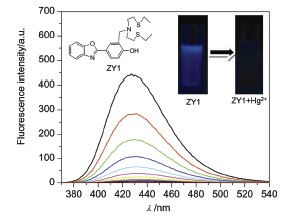
A benzoxazole-based fluorescent probe 4-(benzo[d]oxazol-2-yl)-2-((bis(2-(ethylthio)ethyl)amino)methyl)phenol (ZY1) was designed and synthesized, and characterized by mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and X-ray single crystal diffraction, etc. ZY1 was prepared by Mannich reaction, and its pale yellow crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction studies were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethyl acetate solution at room temperature over a period of a few days. The results showed that ZY1 exhibited good sensitivity and selectivity to Hg2+. The fluorescence of ZY1 was quenched dramatically in the presence of Hg2+, and it remained nearly constant in the range of pH 3.0~9.0. Other metal ions, such as K+, Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, induced negligible fluorescence quenching for ZY1 under the same conditions. When the concentration of Hg2+ was increased from 0 to 30 μmol/L, the fluorescence of ZY1 (10 μmol/L) quenched gradually. Binding analysis using the method of continuous variations (Job's plot) established that the stoichiometry of ZY1-Hg2+ complex was estimated to be 1:1. The fluorescence intensity varied almost linearly vs. the concentration of Hg2+ (0.5~4.8 μmol/L), and the detection limit of Hg2+ was estimated to be 0.08 μmol/L. Moreover, ZY1 was used for the visual detection of Hg2+ and applied to image intracelluar Hg2+ in living HeLa cells, indicating that it could be a useful tool in bioanalytical applications.
Key words: benzoxazole; mercuric ion; fluorescent probe; visual detection; fluorescent imaging
Zhang Yong , Li Wei , Wang Qiang , Zhang Ruoxuan , Xiong Qijie , Shen Xiang , Guo Jing , Chen Xuemei . A Benzoxazole-Based Fluorescent Probe for Visual Detection of Hg2+[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(11) : 1496 -1499 . DOI: 10.6023/A13070796
[1] Clarkson, T. W.; Magos, L.; Myers, G. J. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1731.
[2] Nolan, E. M.; Lippard, S. J. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3443.
[3] Du, M.-H.; Han, Z.-X.; Wu, X.-Y.; Liang, G.-X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.-Q. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2012, 29, 3170. (杜明辉, 韩志湘, 吴向阳, 梁国熙, 赵婷, 张浩琪, 光谱实验室, 2012, 29, 3170.)
[4] Wu, X.-L.; Lai, J.-P.; Zhao, Y.-B. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2012, 33, 695. (吴小丽, 赖金平, 赵一兵, 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33, 695.)
[5] Huang, W.-J.; Wu, W.-H.; Liang, J.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 873. (黄文君, 吴文辉, 梁嘉香, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 873.)
[6] Chi, X.-B.; Liu, Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1545. (迟兴宝, 刘洋, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 1545.)
[7] Lü, S.-Y.; Ye, T.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.-J.; Wei, G.-F.; Lü, J.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 831. (吕诗言, 叶泰, 姜欣, 王晶晶, 魏国芬, 吕鉴泉, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 831.)
[8] Nolan, E. M.; Lippard, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5910.
[9] Yang, Y.-M.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, W.; Li, F.-Y. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 192.
[10] Meng, Q.-H.; Cheng, S.; Lan, M.-B.; Wei, G. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 249
[11] Liu, J.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Guo, W. Analyst 2013, 138, 2654.
[12] Priyanka, S.; Rashid, A.; Syed, S. R.; Mohammad, S.; Satyakam, P.; Arvind, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 3688.
[13] Lin, Q.; Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wei, T.-B. Prog. Chem. 2013, 25, 1177. (林奇, 陈佩, 刘娟, 符永鹏, 张有明, 魏太保, 化学进展, 2013, 25, 1177.)
[14] Wang, X.-M.; Wang, J.-G.; Xu, W.-C. Dyestuffs Coloration, 2005, 42, 8. (王雪梅, 王景国, 胥维昌, 染料与染色, 2005, 42, 8.)
[15] Pan, J.-X.; Wang, C.-J.; Gao, Z.-H.; Yao, X.-K.; Wang, R.-J. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 1990, 11, 31. (潘家杏, 王超杰, 高振衡, 姚心侃, 王如骥, 高等学校化学学报, 1990, 11, 31.)
[16] Fan, J.-L.; Guo, K.-X.; Peng, X.-J.; Du, J.-J.; Wang, J.-Y.; Sun, S.-G.; Li, H.-L. Sens. Actuators, B: Chem. 2009, 142, 191.
[17] Taki, M.; Akaoka, K.; Iyoshi, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 13075.
[18] Du, J.-J.; Fan, J.-L.; Peng, X.-J.; Sun, P.-P.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, H.-L.; Sun, S.-G. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 476.
[19] Chen, X.-Q.; Nam, S.-W.; Jou, M. J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, S.; Yoon, J. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5235.
[20] Chen, M.-L.; Lv, X.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, W. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 2345.
[21] Chen, W.-H.; Xing, Y.; Pang, Y. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1362.
[22] Kwon, J. E.; Lee, S.; You, Y.; Baek, K. H.; Ohkubo, K.; Cho, J.; Fukuzumi, S.; Shin, I.; Park, S. Y.; Nam, W. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 8760.
[23] Shortreed, M.; Kopelman, R.; Kuhn, M.; Hoyland, B. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1414.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |