

Rapid Analysis of Adulterated Chinese Liquor by Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Received date: 2013-07-14
Online published: 2013-10-02
Supported by
Project supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 21225522), Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21265001), Jiangxi Science & Technology Pillar Program (No. 2010BNB00900, 20113BCB24024) and Nanchang Science & Technology Program of Jiangxi Province in 2012 (No. 2012-sys-003).
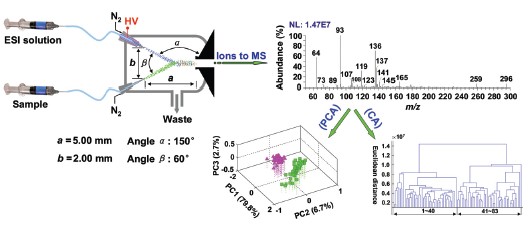
A novel analytical platform based on a home-made extractive electrospray ionization (EESI) source coupled with LTQ-XL mass spectrometer has been developed for fast and accurate identification of eight different kinds of adulterated Chinese liquors such as Maotai. Alcohol concentration in each liquor sample was measured by an alcohol meter and was adjusted to the same value by adding water and industrial alcohol. Measurements were done in positive ion detection mode under optimized experimental conditions. The ESI voltage was set to +4 kV, the pressure of the sheath gas (N2) was 1.2 MPa, the temperature of the heated capillary was set to 150 ℃, and the primary ions were created by electrospraying methanol/water/acetic acid mixture (4:4:2, V:V:V) at 5 μL·min-1. Normalized mass spectra of authentic and counterfeit liquors were differentiated by principal component analysis (PCA). Reproducibility of the method was characterized by cluster analysis (CA). Several constituents of liquor vapor were identified by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). To perform MS/MS experiments, ions of interest were isolated with a mass-to-charge window width of 1.4 u. and then subjected to collision-induced dissociation (CID) with 16%~24% collision energy for 30 ms. The analysis time for a single sample was less than 1 min. The accuracy of identification predicted by PCA was 96.5%. The feasibility of this method was verified by testing several unknown samples. In addition to EESI-LTQ-MS, volatile compounds in Maotai vapor were also studied by single photon ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SPI-TOF-MS), and molecular fingerprints obtained by these two methods were compared. These two detection means showed their respectively outstanding advantages and synergy for the analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The introduced method provides an important tool for the quality control of alcoholic beverages with high speed and simplicity of analysis on the market.
Ouyang Yongzhong , Li Cao , Zhou Yafei , Zhou Zhen . Rapid Analysis of Adulterated Chinese Liquor by Extractive Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013 , 71(12) : 1625 -1632 . DOI: 10.6023/A13070738
[1] Domínguez, M. J. N.; Durán, D.; Chamorro, M. P. V.; Arroyo, R. M. J. Int. Sci. Vigne. Vin. 2010, 44, 179.
[2] Shen, F.; Yang, D.; Ying, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, T. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2012, 5, 786.
[3] Contreras, U.; Barbosa-García, O.; Pichardo-Molina, J.; Ramos-Ortíz, G.; Maldonado, J.; Meneses-Nava, M.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; López-de-Alba, P. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2356.
[4] Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Toepfer, R.; Choi, Y. H.; Verpoorte, R. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 255.
[5] Guadalupe, Z.; Martínez-Pinilla, O.; Garrido, á.; Carrillo, J. D.; Ayestarán, B. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 367.
[6] Toci, A. T.; Crupi, P.; Gambacorta, G.; Dipalmo, T.; Antonacci, D.; Coletta, A. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1104.
[7] Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; García-Campaña, A. M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2987.
[8] Cynkar, W.; Dambergs, R.; Smith, P.; Cozzolino, D. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 660, 227.
[9] Chen, H. W.; Touboul, D.; Jecklin, M. C.; Zheng, J.; Luo, M. B.; Zenobi, R. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 13, 273.
[10] Chen, H. W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, X. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 38, 1069. (陈焕文, 胡斌, 张燮, 分析化学, 2010, 38, 1069.)
[11] Li, X.; Hu, B.; Ding, J. H.; Chen, H. W. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1010.
[12] Jia, B.; Zhang, X. L.; Ding, J. H.; Yang, S. P.; Chen, H. W. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57(20), 1918. (贾滨, 张兴磊, 丁健桦, 杨水平, 陈焕文, 科学通报, 2012, 57(20), 1918.)
[13] Xu, N.; Zhu, Z. Q.; Yang, S. P.; Wang, J.; Gu, H. W.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, H. W. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41(4), 523. (许柠, 朱志强, 杨水平, 王姜, 顾海巍, 周振, 陈焕文, 分析化学, 2013, 41(4), 523.)
[14] Gu, H. W.; Yang, S. P.; Li, J. Q.; Hu, B.; Chen, H. W.; Zhang, L. L.; Fei, Q. Analyst 2010, 135, 779.
[15] Yang, P. R. Liquor-making Science & Technology 2003, (4), 106. (杨佩荣, 酿酒科技, 2003, (4), 106.)
[16] Zhu, S. K.; Lu, X.; Ji, K. L.; Guo, K. L.; Li, Y. L.; Wu, C. Y.; Xu, G. W. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 340.
[17] Hu, B.; Chen, H. W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. P.; Feng, S. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67(12), 1331. (胡斌, 陈焕文, 张燮, 杨水平, 冯守华, 化学学报, 2009, 67(12), 1331.)
[18] Yang, D. W.; Fan, X. L.; Kind, T.; Fiehn, O.; Guo, R. B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 663. (杨大伟, 范晓蕾, Kind Tobias, Fiehn Oliver, 郭荣波, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 663.)
[19] Zhu, L.; Hu, Z.; Gamez, G.; Law, W. S.; Chen, H. W.; Yang, S. P.; Chingin, K.; Balabin, R. M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T. T.; Zenobi, R. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 405.
[20] Zhang, X. L.; Jia, B.; Huang, K. K.; Hu, B.; Chen, R.; Chen, H. W. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8060.
[21] Jia, B.; Ouyang, Y. Z.; Sodhi, R. N.; Hu, B.; Zhang, T. T.; Li, J. Q.; Chen, H. W. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 313.
[22] Zhu, Z. Q.; Yan, J. P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Z.; Chen, H. W. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41(6), 905. (朱志强, 闫建平, 汪雨, 陈瞬宗, 陈焕文, 分析化学, 2013, 41(6), 905.)
[23] Luo, L. P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. J.; Dai, X. M.; Fang, X. W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. L.; Chen, H. W. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41(7), 1050. (罗丽萍, 王姜, 章文军, 戴喜末, 方小伟, 张茜, 刘亚丽, 陈焕文, 分析化学, 2013, 41(7), 1050.)
[24] Chen, H. W.; Liang, H. Z.; Ding, J. H.; Lai, J. H.; Huan, Y. F.; Qiao, X. L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10093.
[25] Hua, L.; Wu, Q. H.; Hou, K. Y.; Cui, H. P.; Chen, P.; Wang, W. G.; Li, J. H.; Li, H. Y. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5309.
[26] Geissler, R.; Saraji-Bozorgzad, M. R.; Gröger, T.; Fendt, A.; Streibel, T.; Sklorz, M.; Krooss, B. M.; Fuhrer, K.; Gonin, M.; Kaisersberger, E. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6038.
[27] Li, C.; Zhou, Y. F.; Tan, G. B.; Liu, Y. L.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, H. W.; Ouyang, Y. Z. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41(9), 1359. (李操, 周亚飞, 谭国斌, 刘亚丽, 高伟, 周振, 陈焕文, 欧阳永中, 分析化学, 2013, 41(9), 1359.)
[28] Li, M.; Hu, B.; Li, J. Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X. L.; Chen, H. W. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7724.
[29] Chen, H. W.; Wortmann, A.; Zhang, W. H.; Zenobi, R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 580.
[30] Gu, H. W.; Hu, B.; Li, J. Q.; Yang, S. P.; Han, J.; Chen, H. W. Analyst 2010, 135, 1259.
[31] Chen, H. W.; Yang, S. P.; Li, M.; Hu, B.; Li, J. Q.; Wang, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3053.
[32] Chen, H. W.; Venter, A.; Cooks, R. G. Chem. Commun. 2006, 42, 2042.
[33] Chen, H. W.; Zenobi, R. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1467.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |