

Construction of AgrC Proteoliposomes by Detergent-Mediated Method
Received date: 2013-11-03
Online published: 2013-12-23
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21272031, 21172028).
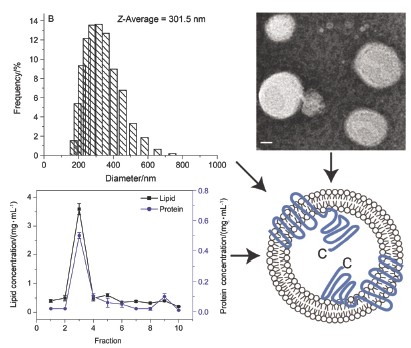
To respond appropriately to different environmental changes, bacteria have evolved two-component signal transduction systems (TCSTs), which are absent in mammals (including human beings). A typical TCST consisted of a sensor kinase (histidine kinase, HK) and a response regulator (RR). HK is capable of autophosphorylation in response to an environmental signal, while RR interacts with the phosphorylated HK. Membrane protein AgrC is a sensor kinase of a TCST from Staphylococcus aureus. Illumination of signal transduction mechanism is of great significance to solve the problem of bacterial resistance. At present, the main bottleneck of membrane protein is the difficulties in obtaining large quantities of sufficiently pure and functional protein. The target protein was overexpressed in Escherichia coli, solubilized from cell membranes and purified in detergent micelles. This series of steps tend to lead to destabilizations of membrane protein and loss of function. In this study, AgrC was incorporated into liposomes by a detergent-mediated method. For standard incorporation, protein solution was added to detergent-lipid suspension containing lipid at 2.5 mmol/L at a lipid-to-protein ratio of 300 (mol/mol). For slow detergent removal, successive additions of small amounts of beads at Bio-bead-to-detergent ratios of 2 (w/w) will allow the removal of the detergent, resulting in formation of proteoliposome. The structure, morphology and average diameter of liposomes and proteoliposomes were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS), respectively. Sucrose density gradient centrifugation was employed to separate proteoliposomes. The result showed efficiency of protein incorporation and liposomes recovery reached 80% and 90%, respectively. Thiol reagent labeling test showed the cytoplasmic domain of AgrC was almost exclusively oriented towards the inside of the liposome vesicles. In vitro phosphorylation experiments showed that kinase activity of AgrC in proteoliposomes was significantly higher than in detergent micelles. Proteoliposomes could be stored for two weeks with little loss of function. Preparation of proteoliposome not only solves the instability problem of membrane proteins, but also provides a new approach of the study of membrane protein structure, function and signal transduction mechanism in vitro.
Key words: Staphylococcus aureus; AgrC; detergent; proteoliposome; membrane protein
Wang Lina , Quan Chunshan , Xu Yongbin , Li Xihui , Qu Xiaojing , Fan Shengdi . Construction of AgrC Proteoliposomes by Detergent-Mediated Method[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014 , 72(2) : 233 -240 . DOI: 10.6023/A13111123
[1] Lowy, F. D. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520.
[2] Emori, T. G.; Gaynes, R. P. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 428.
[3] Klevens, R. M.; Morrison, M. A.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.; Harrison, L. H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; Townes, J. M.; Craig, A. S.; Zell, E. R.; Fosheim, G. E.; McDougal, L. K.; Carey, R. B.; Fridkin, S. K. JAMA. 2007, 298, 1763.
[4] De Lencastre, H.; Oliveira, D.; Tomasz, A. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 428.
[5] Novick, R. P. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1429.
[6] Stauff, D. L.; Skaar, E. P. Contrib. Microbiol. 2009, 16, 120.
[7] Cheung, A. L.; Nishina, K. A.; Trotonda, M. P.; Tamber, S. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2008, 40, 355.
[8] Novick, R. P.; Ross, H. F.; Projan, S. J.; Kornblum, J.; Kreiswirth, B.; Moghazeh, S. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3967.
[9] Thoendel, M.; Kavanaugh, J. S.; Flack, C. E.; Horswill, A. R. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 117.
[10] Geisinger, E.; George, E. A.; Muir, T. W.; Novick, R. P. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8930.
[11] Geisinger, E.; Muir, T. W.; Novick, R. P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 1216.
[12] Grebe, T. W.; Stock, J. B. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1999, 41, 139.
[13] George Cisar, E. A.; Geisinger, E.; Muir, T. W.; Novick, R. P. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 74, 44.
[14] Taubes, G. Science. 2008, 321, 356.
[15] Chambers, H. F.; Deleo F. R. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 629.
[16] Gordon, C. P.; Williams, P.; Chan, W. C. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1389.
[17] Gotoh, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okamoto, S.; Doi, A.; Utsumi, R. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 232.
[18] Sanowar, S.; LeMoual, H. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 769.
[19] Martin, M.; Albanesi, D.; Alzari, P. M.; de Mendoza, D. Protein Expr. Purif. 2009, 66, 39.
[20] Janausch, I. G.; Garcia-Moreno, I.; Unden, G. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39809.
[21] Liu, C. G.; Quan, C. S.; Wang, J. F.; Yu, G. M.; Fan, S. D. China Biotechnology 2012, 32, 1. (刘春光, 权春善, 王剑锋, 于桂梅, 范圣第, 中国生物工程杂志, 2012, 32, 1.)
[22] Wang, L. N.; Quan, C. S.; Liu, B. Q.; Wang, J. F.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, P. C.; Fan, S. D. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e80400. doi: 10. 1371/journal. pone. 0080400.
[23] Lina, G.; Jarraud, S.; Ji, G.; Greenland, T.; Pedraza, A.; Etienne, J.; Novick, R. P.; Vandenesch, F. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 655.
[24] Hofmann, K.; Stoffel, W. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1993, 347, 166.
[25] Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E. L. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567.
[26] Li, W.; Wang, J. H.; Quan, C. S.; Zheng, W.; Fan, S. D. Acta Biophysica Sinica 2009, 25, 219. (李巍, 王军华, 权春善, 郑维, 范圣第, 生物物理学报, 2009, 25, 219.)
[27] Claros, M. G.; von Heijne, G. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1994, 10, 685.
[28] Bernsel, A.; Viklund, H.; Hennerdal, A.; Elofsson, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W465.
[29] Hirokawa, T.; Boon-Chieng, S.; Mitaku, S. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 378.
[30] Jones, D. T.; Taylor, W. R.; Thornton, J. M. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 3038.
[31] McGuffin, L. J.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D. T. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 404.
[32] Wang, L. N.; Quan, C. S.; Xiong, W.; Qu, X. J.; Fan, S. D. BBA-Biomembranes 2013, (Available online 17 December 2013. DOI information: 10. 1016/j. bbamem. 2013. 12. 006).
[33] Van Den Ent, F.; Löwe, J. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2006, 67, 67.
[34] Wang, L. N.; Quan, C. S.; Liu, B. Q.; Xu, Y. B.; Zhao, P. C.; Xiong, W.; Fan, S. D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18470.
[35] Rigaud, J. L.; Lévy, D. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 372, 65.
[36] Bartlett, G. R. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 466.
[37] Quan, C. S.; Ma, J. L.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Fan, S. D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 1167. (权春善, 马金龙, 王雪, 李巍, 范圣第, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 1167.)
[38] Sanowar, S.; LeMoual, H. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 769.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |