

Investigation of Base Pairs Containing 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine by Quantum Chemistry
Received date: 2014-04-01
Online published: 2014-05-29
Supported by
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 21133005).
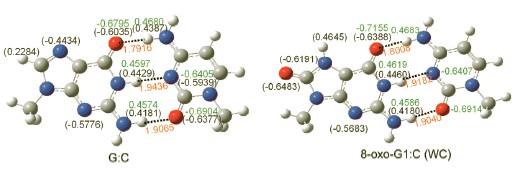
The integrity of the genetic information is constantly threatened by oxidized agents. 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxo-G) is the most common form of oxidative DNA damage. The accumulation of oxidized bases has associated with numerous diseases and cancers. The properties of oxidized base pairs containing 8-oxo-G were investigated by quantum mechanics methods. In this paper all model molecular structures were optimized by B3LYP/6-31+G* method, the frequency calculations are carried out to confirm that all the structures obtained are geometrically stable. The energies were determined at the MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ level with basis set superposition error corrections and the molecular orbital diagrams were obtained at HF/STO-3G level. The calculation results show that when guanine (G) is oxidized to 8-oxo-G, the charge distribution, site number and location of H-bond donor and accepter have been changed. Oxidation on C8 of G has the most influence on the partial charge of N7 and O6, which enhances their ability as H-bond donor. Then, G is misread as other bases to form varied H-bonding compounds with canonical bases. 8-oxo-G has three sites to pair with other bases. Compared with canonical bases, the partial charge of proton acceptors in H-bond complexes increased by 0.05e averagely, which is 8% of the original charge; the partial charges for proton donors have a decrease of 0.02e, which is 4% of the original charge. The calculation results of binding energy and second-order stabilization energy show that the hydrogen-bonded complexes formed at site 1 are more stable. The sites 2 and 3 have similar properties. Only 8-oxo-G1:C (WC) has three hydrogen bonds and its binding energy is the closest to that of G:C in all the oxidized base pairs. The binding energies of base pairs have been weakened by solution, where the complexes pairs with C have been significantly reduced. And the order of the binding energy has been changed. From the HOMO and LUMO, we can come out that the HOMOs of all the oxidized base pairs are on 8-oxo-G, which is the same as G:C, and LUMOs have no good rules. In the GC→TA transition induced by 8-oxo-G, the nucleophilic reaction site will transfer from the strand containing G to the other strand containing A(C). This will affect the recognition by the enzyme, and lead to genetic mutations.
Key words: ab initio; oxidized base pairs; hydrogen bond; charge population; energy
Zhang Qianhui , Wang Yang , Liu Cui , Yang Zhongzhi . Investigation of Base Pairs Containing 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine by Quantum Chemistry[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014 , 72(8) : 956 -962 . DOI: 10.6023/A14040238
[1] Watson, J. D.; Crick, F. H. C. Nature 1953, 171, 737.
[2] Greenberg, M. M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 588.
[3] Lord, C. J.; Ashworth, A. Nature 2012, 481, 287.
[4] Crenshaw, C. M.; Wade, J. E. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8463.
[5] Naôme, A.; Schyman, P.; Laaksonen, A.; Vercauteren, D. P. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 4789. [6] Hamm, M. L.; Crowley, K. A.; Ghio, M.; Lindell, M. A. M.; McFadden, E. J.; Silberg, J. S. L.; Weaver, A. M. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2577.
[7] Volle, C. B.; Jarem, D. A.; Delaney, S. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 52.
[8] Mazurek, A.; Berardini, M.; Fishel, R. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8260.
[9] Shukla, L. I.; Adhikary, A.; Pazdro, R.; Becker, D.; Sevilla, M. D. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 6565.
[10] Hu, X. B.; Li, H.; Ding, J. Y.; Han, S. J. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6361.
[11] Shibutani, S.; Takeshita, M.; Grollman, A. P. Nature 1991, 349, 431.
[12] Hsu, G. W.; Ober, M.; Carell, T.; Beese, L. S. Nature 2004, 431, 217.
[13] David, S. S. O.; Shea, V. L.; Kundu, S. Nature 2007, 447, 941.
[14] Thiviyanathan, V.; Somasunderam, A.; Volk, D. E.; Hazra, T. K.; Mitra, S.; Gorenstein, D. G. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 752.
[15] Dey, M.; Moritz, F.; Grotemeyer, J.; Schlag, E. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 9211.
[16] Manas, E. S.; Getahun, Z.; Wright, W. W.; DeGrado, W. F.; Vanderkooi, J. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9883.
[17] Shukla, A.; Barbiellini, B.; Buslaps, T.; Suortti, P. Phys. Chem. (Munich) 2001, 215, 1315.
[18] Hobza, P.; Sandorfy, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 1302.
[19] Fan, W. J.; Zhang, R. Q.; Liu, S. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 967.
[20] Kino, K.; Sugiyama, H. Chemistry & Biology 2001, 8, 369.
[21] He, Q.; Zhou, L. X. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2005, 21, 846. (和芹, 周立新, 物理化学学报, 2005, 21, 846.)
[22] Qiu, Z. M.; Wang, H. J.; Xia, Y. M. Struct. Chem. 2010, 21, 931.
[23] Lin, X. F.; Sun, C. K.; Yao, L. F.; Chen, Y. S.; Yang, S. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 1553. (林雪飞, 孙成科, 姚立峰, 陈益山, 杨思娅, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 1553.)
[24] Suzuki, M.; Kino, K.; Morikawa, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Komori, R.; Miyazawa, H. Molecules 2012, 17, 6705.
[25] Liu, S.; Li, S. S.; Liu, D. J.; Wang, C. S. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2013, 29, 2551. (刘帅, 李书实, 刘冬佳, 王长生, 物理化学学报, 2013, 29, 2551.)
[26] Zheng, Y.; Cai, W. F.; Li, L. C. J. At. Mol. Phys. 2013, 30, 66. (郑妍, 蔡皖飞, 李来才, 原子与分子物理学报, 2013, 30, 66.)
[27] Huo, H. J.; Zhao, D. X.; Yang, Z. Z. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2011, 32, 2877. (霍红洁, 赵东霞, 杨忠志, 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32, 2877.)
[28] Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. X.; Gong, L. D.; Yang, Z. Z. J. Mol. Graphics Modell. 2014, 47, 62.
[29] Villani, G. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 1256.
[30] Chen, X. L.; Kelso, C.; Hornak, V.; Santos, C. D. L.; Grollman, A. P.; Simmerling, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13906.
[31] Mark, D. E.; Miral, D.; Marcus, S. C. Mutat. Res. 2004, 567, 1.
[32] Hu, X. B.; Li, H. R.; Ding, J. Y.; Han, S. J. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6361.
[33] Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgomery, J. A.; Jr.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Cross, J. B.; Balkken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R. E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Voth, G. A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A. D.; Farkas, Φ; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J.; Fox, D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision A.02, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2009. NBO, Version 3.1, Glendening, E. D.; Reed, A. E.; Carpenter, J. E.; Weinhold, F.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |