

Synthetic of pH-Sensitive PEG-b-PHEMA(His) Polymers andthe Study of Micelle
Received date: 2015-01-22
Online published: 2015-03-10
Supported by
Project supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20904014).
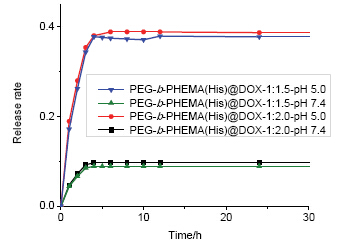
One-pot reaction strategy has been widely used in the synthesis of different polymer architectures which accelerates synthetic procedure and reduces the number of reactions as well as purification steps, therefore leading to more environmentfriendly products. Imidazole group of histidine (His) can exhibit proton sponge effect at different pH values. We design a polymer micelles with histidine to achieve the pH response capability. Synthesis of (PEG-b-poly-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) PEG-b-PHEMA block copolymer combined click chemistry and atom transfer radical polymerization by one-pot syntheses strategy, then through esterification reaction graft histidine on the polymer side chain to get (polyethylene glycol- b-poly-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-g-histidine) PEG-b-PHEMA(His). The reactions are controllable, and the structure of obtained copolymer is well characterized. PEG-b-PHEMA, PEG-b-PHEMA(His)'s structures were characterized by 1H NMR and GPC tests. The resulting data shown by GPC to give the exact molecular weight and narrow distribution. Mn=8.2×103~13.0×103 g/mol, PDI=1.27~1.51. After the preparation of pH-sensitive drug copolymer micelles in borate buffer solution, the dynamic light scattering (DLS) test was done to test the particle size of the micelles. Then we used fluorescence spectroscopy to test its critical micelle concentration. The micelle diameter increases and the critical micelle concentration gradually reduces as the histidine graft ratio increase. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) tests showed that the polymer micelle is spherical and narrow particle size distribution and the conclusion is consistent with the DLS test. Also, the acid-base titration and medicine released experiments curves proved that the product micelles have the ability of pH-sensitive response. The embedding of anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) was achieved by phase transfer method to get PEG-b-PHEMA(His)@DOX. The drug release rate was measured by counting the optical density (OD) value. The result shows that the release rate of DOX increased from 10% to 40%, thus demonstrating that the PEG-b-PHEMA(His) DOX system has a pH-sensitive response capability. Such micelles can be used as drug carriers for biomedical applications.
Key words: one-pot reaction; histidine; pH-sensitive micelle
Hu Qi , Li Yuxiang , Wang Jingyuan , Li Yapeng . Synthetic of pH-Sensitive PEG-b-PHEMA(His) Polymers andthe Study of Micelle[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2015 , 73(5) : 416 -422 . DOI: 10.6023/A15010060
[1] Fu, C. K.; Yang, B.; Zhu, C. Y.; Wang, S. Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Tao, L. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 5720.
[2] Yuan, C.; Lu, H. C.; Li, Q. Z.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Q. L.; Huang, J.; Wei, L. H.; Ma, Z. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2398.
[3] Li, B. Z.; Li, Y. H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 2148. (李炳臻, 李义和, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 2148.)
[4] Wang, J. S.; Matyjaszewski, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5614.
[5] Zhang, P. Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, L. C.; Guo, Y. G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 1663. (张普玉, 刘洋, 彭李超, 郭有钢, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 1663.)
[6] Gao, H. F.; Matyjaszewski, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6633.
[7] Abdellatif, M. M.; Nomura, K. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 423.
[8] Jung, S. H.; Song, H. Y.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, H. M.; Lee, H. I. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1628.
[9] Frankel, M.; Berger, A. Nature 1949, 163, 213.
[10] Nakato, T.; Yoshitake, M.; Matsubara, K.; Tomida, M.; Kakuchi, T. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2107.
[11] Gyenes, T.; Torma, V.; Gyarmati, B.; Zrinyi, M. Acta Biomaterialia 2008, 4, 733.
[12] Liao, M. X.; Li, Y.; Han, W. W. Amino Acids Biotic Resources 2010, 32, 34. (廖明霞, 李晔, 韩伟伟, 氨基酸和生物资源, 2010, 32, 34.)
[13] Lee, Y. J.; Kang, H. C.; Hu, J.; Nichols, J. W.; Jeon, Y. S.; Bae, Y. H. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2945.
[14] Liu, B.; Zhang, J. C.; Chen, H. B.; Song, X. J. Chin. J. Labor. Diagnosis 2006, 10(9), 975. (刘斌, 张基昌, 陈宏勃, 宋显晶, 中国实验诊断学, 2006, 10(9), 975.)
[15] Sukhoverkov, K. V.; Kudryashova, E. V. Biochemistry-Moscow 2015, 80, 113.
[16] Midoux, P.; Pichon, C.; Yaouanc, J. J.; Jaffres, P. A. British J. Pharmocol. 2009, 157, 166.
[17] Lee, E. S.; Shin, H. J.; Na, K; Bae, Y. H. J. Controlled Release 2003, 90, 363.
[18] Johnson, R. P.; Jeong, Y. I.; Choi, E.; Chung, C. W.; Kang, D. H.; Oh, S. O.; Suh, H.; Kim, I. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1058.
[19] Mespouille, L.; Vachaudez, M.; Suriano, F.; Gerbaux, P.; Coulembier, O.; Degee, P.; Flammang, R.; Dubois, P. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2151.
[20] Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. P.; Li, X. D.; Shen, Z. Q. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2045.
[21] Shen, Y.; Tang, H.; Ding, S. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1053.
[22] Kalyanasundaram, K.; Thomas, J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 2039.
[23] Martic, P. A.; Nair, M. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 163, 517.
[24] Zhang, C.; Ping, Q. N.; Zhang, H. J. Colloids Surfaces B-Biointerfaces 2004, 39, 69.
[25] Li, Y.-X. M. S. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, 2013. (李玉祥, 硕士论文, 吉林大学, 长春, 2013.)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |