

Glucose Responsive Bio-based Polyelectrolyte Capsules by Layer-by-Layer Assembly: Synthesis and Properties
Received date: 2015-06-11
Online published: 2015-07-23
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51173072) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51408B).
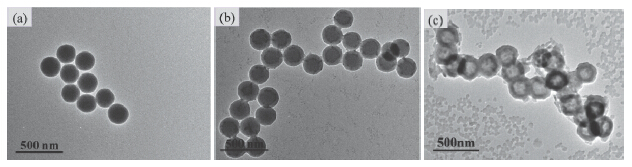
Phenylboronic acid and derivatives that conjugate with diol units to form a reversible ester bond could be used for preparation glucose responsive materials. Glucose responsive materials, such as films, hydrogels, and nanoparticles based on phenylboronic acid have been reported to have well glucose-regulated release insulin. However, in these examples, employed polymers were not full degradability or low biocompatibility. Therefore, this study aims to prepare the bio-based capsules with multi-layers structure to response glucose through the layer-by-layer self-assembly of two natural polymers. Poly(γ-glutamic acid-g-3-aminophenylboronic acid) (γ-PGA-g-APBA) and galactosed chitosan oligosaccharide (GC) were synthesized by grafting 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) and lactobionic acid (LA) to poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) and chitosan oligosaccharide (CS), respectively, in the presence of N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethylcarbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) as catalysts. Chemical structures of γ-PGA-g-APBA and GC were determined by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra. Then, polyelectrolyte microspheres (γ-PGA-g-APBA/GC)5@SiO2 were prepared with particle sizes of 240±10 nm, using functionalized silica microspheres as templates by layer-by-layer processes of γ-PGA-g-APBA and GC. Capsules ((γ-PGA-g-APBA/GC)5) with multi-layer structures were obtained by removing SiO2 templates in NH4F/HF (8 mol/L)/(2 mol/L) buffer solution. Sizes and morphologies of polyelectrolyte capsules were characterized by zeta potential, scanning electron micrographs (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The results showed that ((γ-PGA-g-APBA/GC)5) capsules presented unique hollow structures and had a good stability when capsules were incubated at different temperatures, salt concentrations and pH values. Moreover, ((γ-PGA-g-APBA/GC)5) capsules showed a good glucose-responsive property. The capsules were swollen and intact at low glucose concentration, while were destroyed at high glucose concentration. These ((γ-PGA-g-APBA/GC)5) capsules with good stability and glucose-response are expected to be used to the fields of the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes.
Ran Maoshuang , Shi Dongjian , Dong Hanxing , Chen Mingqing , Zhao Zengliang . Glucose Responsive Bio-based Polyelectrolyte Capsules by Layer-by-Layer Assembly: Synthesis and Properties[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2015 , 73(10) : 1047 -1054 . DOI: 10.6023/A15060405
[1] Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Liang, R. P.; Qiu, J. D. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 430.
[2] Niu, Z. Z.; Yu, L. L.; Yang, R.; Qu, L. B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 1457. (牛真真, 于岚岚, 杨冉, 屈凌波, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 1457.)
[3] Kim, H.; Kang, Y. J.; Jeong, E. S.; Kang, S.; Kim, K. T. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1194.
[4] Xia, Q. F.; Luo, D.; Li, Z. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 2079. (夏前芳, 罗丹, 李在均, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 2079.)
[5] Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, G. S.; Jiang, M. Small 2015, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201403838.
[6] Zhang, Y. Q.; Yu, J. C.; Shen, Q. D.; Gu, Z. Prog. Chem. 2015, 27, 11. (张宇琪, 俞计成, 沈群东, 顾臻, 化学进展, 2015, 27, 11.)
[7] Samoszuk, M.; EhrLich, D.; Ramzi, E. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 266, 1643.
[8] Ralph, B.; Colton, E.; Roger, M.; Ashok, G. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 275.
[9] Liang, Y.; Zhou, Q. M.; Zeng, Y. L.; Xu, M. C.; Xie, Q. J. Acta Polymerica Sinica 2007, (11), 1017. (梁源, 周庆美, 曾佑林, 徐满才, 谢青季, 高分子学报, 2007, (11), 1017.)
[10] Peng, J. H.; Wang, Y. H.; Wang, J. L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. H. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 414.
[11] Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Ma, R. J.; Shi, L. Q. Acta Polymerica Sinica 2014, (9), 1161. (刘赣, 杨浩, 马如江, 史林启, 高分子学报, 2014, (9), 1161.)
[12] Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Yin, J.; Liu, S. Y. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2282.
[13] Matsumoto, A.; Yoshida, R.; Kataoka, K. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1038.
[14] Wu, Z. M.; Zhang, X. G.; Guo, H. L.; Li, C. X.; Yu, D. M. J. Mater Chem. 2012, 22, 22788.
[15] Zhao, L.; Ding, J. X.; Xiao, C. S.; He, P.; Tang, Z. H.; Pang, X.; Zhuang, X. L.; Chen, X. S. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12319.
[16] Ma, R. J.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Sun, X. C.; Liu, X. J.; An, Y. L.; Shi, L. Q. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3409.
[17] Pan, G. Q.; Guo, B. B.; Ma, Y.; Cui, W. G.; He, F.; Li B.; Yang, H. L.; Shea, K. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6203.
[18] Taek, W. C.; Yang, J.; Toshihiro, A.; Kwang, Y. C.; Jae, W. N.; Su, K.; Chong, S. C. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2827.
[19] Yu, S. F.; Gu, X.; Wu, G. L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. L.; Gao, H.; Ma, J. B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 177. (于树芳, 顾鑫, 伍国琳, 王铮, 王亦农, 高辉, 马建标, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 177.)
[20] Raquel, F.; Connie, O.; Susana, C. M. F.; Arantxa, E.; Agnieszka, T. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1399.
[21] Wang, D.; Liu, S. Y. Scientia Sinica Chimica 2011, 41, 351. (王頔, 刘世勇, 中国科学, 2011, 41, 351.)
[22] Chaturbedy, P.; Jagadeesan, D.; Eswaramoorthy, M. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5921.
[23] Jiang, H. L.; Kim, Y. K.; Rohidas, A.; Nah, J. W.; Cho, M. H.; Choi, Y. J.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C. S. J. Controlled Release 2007, 117, 273.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |