

One-pot Enantioselective Multi-component Cascade Reactions for Synthesis of Chiral Functionalized Hydro-epoxyisochromenes: A Rapid Access toMolecular Complexity
Received date: 2015-09-25
Online published: 2015-11-19
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21125209 and 21332003), Ministry of science and Technology of the Peoples's Republic of China (No. 2011CB808600), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 12JC1403800).
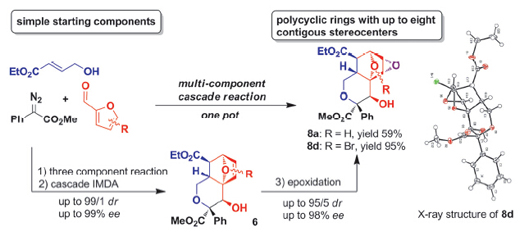
An Rh2(OAc)4/Zr-3-I-binol co-catalyzed enantioselective three-component cascade reaction of diazo compounds, ethyl 4-hydroxybutenoate and furfurals has been designed to build complex fused O-heterocycles in a one pot fashion. The reaction was conducted in CH2Cl2 or CHCl3 at ambient temperature with 3 Å molecular sieves as an additive. The multi- component process was completed within 3 h to give multi-component products and the following Diels-Alder (DA) cyclization product was observed in the next several hours. It was found that the DA process was slow but could be completed after 7~12 d by standing the crude reaction mixture after evaporating solvent. Following a one-pot epoxidation of the product further increases the molecular complexity to give fused epoxidation products bearing multiple chiral carbon centers. Especially to be noted, all of the products are very easy to be purified by simple recrystallization in mixture solvent of ethyl acetate (EA)/petroleum ether (PE, 60~90 ℃) and do not need any column chromatography method. Using the developed method, hydroepoxyisochromene derivatives with up to eight contiguous chiral carbon centers have been readily prepared from simple starting materials with high diastereoselectivity (up to 99/1 dr) and enantioselectivity (up to 99% ee). The absolute stereochemistry of product was determined by the single crystal X-ray analysis as a chair conformation with absolute configurations. The possible mechanisms were theoretically investigated by DFT calculation and proposed as an oxonium ylide-trapping three-component reaction subsequently followed with a spontaneous intramolecular Diels-Alder process and an epoxidation at the end. The developed three-component cascade reaction provides a rapid access to the construction of chiral fused polycyclic O-heterocycles with molecular complexity.
Tang Min , Wu Yong , Liu Yuan , Cai Maoqiang , Xia Fei , Liu Shunying , Hu Wenhao . One-pot Enantioselective Multi-component Cascade Reactions for Synthesis of Chiral Functionalized Hydro-epoxyisochromenes: A Rapid Access toMolecular Complexity[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2016 , 74(1) : 54 -60 . DOI: 10.6023/A15090627
[1] (a) Schreiber, S. L. Science 2000, 287, 1964;
(b) Lee, D.; Sello, J. K.; Schreiber, S. L. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 709;
(c) Ruijter, E.; Scheffelaar, R.; Orru, R. V. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6234
[2] (a) Xu, Z.; Moliner, F. D.; Cappelli, A. P.; Hulme, C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8037;
(b) Khoury, K.; Sinha, M. K.; Nagashima, T.; Herdtweck, E.; Dömling, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10280;
(c) Huigens III, R. W.; Morrison, K. C.; Hicklin, R. W.; Flood Jr, T. A.; Richter, M. F.; Hergenrother, P. J. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 195.
[3] (a) Imashiro, R.; Uehara, H.; Barbas, C. F. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5250;
(b) Urushima, T.; Sakamoto, D.; Ishikawa, H.; Hayashi, Y. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4588;
(c) Reyes, E.; Jiang, H.; Milelli, A.; Elsner, P.; Hazell, R. G.; Jorgensen, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9202;
(d) Hayashi, Y.; Okano, T.; Aratake, S.; Hazelard, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4922;
(e) Carlone, A.; Cabrera, S.; Marigo, M.; Jorgensen, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1101;
(f) Enders, D.; Huttl, M. R. M.; Grondal, C.; Raabe, G. Nature 2006, 441, 861;
(g) Marigo, M.; Bertelsen, S.; Landa, A.; Jorgensen, K. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5475;
(h) Guo, S.; Xie, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2728;
(i) Lipshutz, B. H.; Amorelli, B.; Unger, J. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14378;
(j) Arai, T.; Yokoyama, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4989.
[4] (a) Enders, D.; Huttl, M. R. M.; Runsink, J.; Raabe, C.; Wendt, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 467.
(b) Shi, D.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xia, C.; Huang, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1248.
(c) Spangler, J. E.; Lian, Y.; Raikar, S. N.; Davies, H. M. L. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4794.
[5] (a) Yamada, T.; Doi, M.; Shigeta, H.; Muroga, Y.; Hosoe, S.; Numata, A.; Tanaka, R. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4192;
(b) Brossi, A.; Venugopalan, B.; Gerpe, L. D.; Yeh, H. J. C.; Flippen-Anderson, J. L.; Buchs, P.; Luo, X. D.; Milhous, W.; Peters, W. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 645;
(c) Ding, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Wild, C.; Chu, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5048.
[6] (a) Ruberto, G.; Renda, A.; Tringali, C.; Napoli, E. M.; Simmonds, M. S. J. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6766;
(b) Ding, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Wild, C.; Chu, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5048.
[7] (a) Norris, D. J.; Gavai, A. V.; Balog, J. A.; Austin, J. F.; Shan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Nation, A. J.; Han, W. C. WO2009003077 (A1) [Chem. Abstr. 2009, 150, 98294];
(b) Santhosh, K. C.; Gopalsamy, A.; Balasubramanian, K. K. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 3461.
[8] (a) Shan, W.; Balog, J. A.; Gavai, A. V.; Zhao, Y. WO2009059077 (A1) [Chem. Abstr. 2009, 150, 494854];
(b) Das, J.; Vu, T.; Harris, D. N.; Ogletree, M. L. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 930.
[9] (a) Grondal, C.; Jeanty, M.; Enders, D. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 167;
(b) Enders, D.; Grondal, C.; Huttl, M. R. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1570;
(c) Nicolaou, K. C.; Edmonds, D. J.; Bulger, P. G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7134;
(d) Tietze, L. F. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 115;
(e) Qiu, L.; Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Qiu, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, W. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2196.
[10] Tang, M.; Xing, D.; Huang, H.; Hu, W. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10612.
[11] (a) Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Guo, X.; Guan, X.; Yang, L.; Hu, W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6647;
(b) Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Mi, A. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 83;
(c) Guo, X.; Hu, W. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2427.
[12] (a) Corey, E. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1650;
(b) Nicolaou, K. C.; Snyder, S. A.; Montagnon, T.; Vassilikogiannakis, G. E. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1668;
(c) Brieger, G.; Bennett, J. N. Chem. Rev. 1980, 80, 63.
[13] (a) Bedeschi, P.; Casolari, S.; Costa, A. L.; Tagliavini, E.; Ronchi, A. U. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7897;
(b) Casolari, S.; Cozzi, P. G.; Orioli, P. A.; Tagliavini, E.; Ronchi, A. U. Chem. Commun. 1997, 2123;
(c) Kurosu, M.; Lorca, M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1765;
(d) Hanawa, H.; Kii, S.; Asao, N.; Maruoka, K. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 5543.
[14] For the ZrMs-catalyzed reactions, as indicated by Kobayashi and his co-workers, water played a crucial role in generating active catalytic species: (a) Kobayashi, S.; Ishitani, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Ueno, M.; Shimizu, H. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 861;
(b) Yamashita, Y.; Ishitani, H.; Shimizu, H.; Kobayashi, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3292;
(c) Kobayashi, S.; Ueno, M.; Saito, S.; Mizuki, Y.; Ishitani, H.; Yamashita, Y. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 5476.
[15] (a) Hoffmann, R.; Woodward, R. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 4388;
(b) Garcia, J. I.; Mayoral, J. A.; Salvatella, L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 658;
(c) Wannere, C. S.; Paul, A.; Herges, R.; Houk, K. N.; Schaefer III, H. F.; Schleyer, P. V. R. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 344.
[16] Adam, W.; Pastor, A.; Peters, K.; Peters, E. M. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1019.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |