

Study on Ru-B/MIL-53(AlxCr1) Catalysts for Partial Hydrogenation ofBenzene to Cyclohexene
Received date: 2016-02-01
Online published: 2016-05-13
Supported by
Project supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB224804), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21373055), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 08DZ2270500), Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, and the China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (S411063).
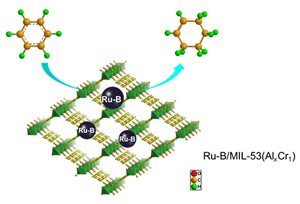
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted enormous research interests not only because of their merits such as high specific surface area, high porosity, and regular pore channels, but also due to their peculiarities of extremely abundant chemical and structural diversity and tunability. In this work, we synthesized MIL-53(Al) and MIL-53(Cr) containing one coordination metal and the novel MIL-53(AlxCr1)(x=1, 2, 3, and 4) MOFs containing two coordination metals as the supports for the Ru-B/MIL-53 catalysts, which were prepared by the facile impregnation-chemical reduction method. In the challenging partial hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexene, it is revealed that the Al/Cr ratio had pronounced influences on both the initial hydrogenation rate (r0) and the initial selectivity to cyclohexene (S0). In general, MIL-53 containing a higher fraction of Al affords a higher r0, while MIL-53 containing both Al and Cr is conducive to a higher S0 than either MIL-53(Al) or MIL-53(Cr) containing only one coordination metal. On the Ru-B/MIL-53(Al3Cr1) catalyst exhibiting the highest selectivity to cyclohexene, the r0 and S0 were 9.2 mmol/(min·g) and 71%, respectively. The best Ru-B/MIL-53(Al3Cr1) catalyst and the Ru-B/MIL-53(Cr) catalyst displaying the lowest selectivity to cyclohexene were comparatively characterized to have an insight into the difference in their catalytic performance. It is found that while both catalysts had similar Ru/B molar ratio, electronic property, and microstructure, the Ru-B/MIL-53(Al3Cr1) catalyst had higher active surface area (Sact), smaller and more highly dispersed Ru-B nanoparticles (NPs), and stronger metal-support interaction than the Ru-B/MIL-53(Cr) catalyst. The smaller Ru-B NPs could not only provide more active sites for the hydrogenation of benzene, but also be beneficial to the formation of cyclohexene. By further optimization of the reaction conditions, at 180 ℃, H2 pressure of 5.0 MPa, and using 100 mL of ethanolamine as the modifier, a cyclohexene yield of 29% was obtained over the Ru-B/MIL-53(Al3Cr1) catalyst.
Key words: dual metal-organic framework; ruthenium; benzene; cyclohexene; partial hydrogenation
Dou Rongfei , Tan Xiaohe , Fan Yiqiu , Pei Yan , Qiao Minghua , Fan Kangnian , Sun Bin , Zong Baoning . Study on Ru-B/MIL-53(AlxCr1) Catalysts for Partial Hydrogenation ofBenzene to Cyclohexene[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2016 , 74(6) : 503 -512 . DOI: 10.6023/A16020074
[1] Zhou, G. B.; Tan, X. H.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K. N.; Qiao, M. H.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. N. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2425.
[2] Odenbrand, C. U. I.; Andersson, S. L. T. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1982, 32, 365.
[3] Wang, J. Q.; Guo, P. J.; Qiao, M. H.; Yan, S. R.; Fan, K. N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62, 1765.(王建强, 郭平均, 乔明华, 闫世润, 范康年, 化学学报, 2004, 62, 1765.)
[4] Wang, W. T.; Liu, H. Z.; Ding, G. D.; Zhang, P.; Wu, T. B.; Jiang, T.; Han, B. X. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 1836.
[5] Wang, J. Q.; Wang, Y. Z.; Xie, S. H.; Qiao, M. H.; Li, H. X.; Fan, K. N. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 272, 29.
[6] Huang, G.; Chen, Y. Z.; Jiang, H. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 113.(黄刚, 陈玉贞, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 113.)
[7] Rosi, N. L.; Eckert, J.; Eddaoudi, M.; Vodak, D. T.; Kim, J.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Science 2003, 300, 1127.
[8] Sun, L.; Deng, W. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 579.(孙磊, 邓伟侨, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 579.)
[9] Li, J. R.; Kuppler, R. J.; Zhou, H. C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477.
[10] Lee, J.; Farha, O. K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K. A.; Nguyen, S. T.; Hupp, J. T. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450.
[11] Ren, H.; Zhu, G. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 587.(任浩, 朱广山, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 587.)
[12] Liu, Y.; Mo, K.; Cui, Y. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10286.
[13] Uemura, T.; Kitaura, R.; Ohta, Y.; Nagaoka, M.; Kitagawa, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4112.
[14] Zhao, H. H.; Song, H. L.; Chou, L. J. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2012, 15, 261.
[15] Wan, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiao, W. M.; Jian, L. J.; Zhang, N. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 171, 9.
[16] Guo, Z. Y.; Xiao, C. X.; Maligal-Ganesh, R. V.; Zhou, L.; Goh, T. W.; Li, X. L.; Tesfagaber, D.; Thiel, A.; Huang, W. Y. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1340.
[17] Luz, I.; Rösler, C.; Epp, K.; Xamena, F. L.; Fischer, R. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 23, 3904.
[18] Chen, D. C.; Huang, M.; He, S.; He, S. L.; Ding, L. P.; Wang, Q.; Yu, S. M.; Miao, S. D. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 109.
[19] Tan, X. H.; Zhou, G. B.; Dou, R. F.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K. N.; Qiao, M. H.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. N. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2014, 30, 932.(谭晓荷, 周功兵, 窦镕飞, 裴燕, 范康年, 乔明华, 孙斌, 宗保宁, 物理化学学报, 2014, 30, 932.)
[20] Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Thouvenot, C.; Noguès, M.; Marsolier, G.; Louër D.; Férey, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13519.
[21] Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Férey, G. Chem.-Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373.
[22] Zhao, Y. J.; Zhang, J. L.; Han, B. X.; Song, J. L.; Li, J. S.; Wang, Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 636.
[23] Liu, H. Z.; Liang, S. G.; Wang, W. T.; Jiang, T.; Han, B. X. J. Mol. Catal. A 2011, 341, 35.
[24] Millange, F.; Serre, C.; Férey, G. Chem. Commun. 2002, (8), 822.
[25] Sun, Z. G.; Li, G.; Liu, L. P.; Liu, H. O. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 200.
[26] Liu, J. L.; Zhu, L. J.; Pei, Y.; Zhuang, J. H.; Li, H.; Li, H. X.; Qiao, M. H.; Fan, K. N. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 353, 282.
[27] Larichev, Y. V.; Moroz, B. L.; Zaikovskii, V. I.; Yunusov, S. M.; Kalyuzhnaya, E. S.; Shur, V. B.; Bukhtiyarov, V. I. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 9427.
[28] Mazzieri, V.; Coloma-Pascual, F.; Arcoya, A.; L'Argentière, P.; F?goli, N. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 210, 222.
[29] Xie, S. H.; Qiao, M. H.; Li, H. X.; Wang, W. J.; Deng, J. F. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 176, 129.
[30] Pei, Y.; Zhou, G. B.; Luan, N.; Zong, B. N.; Qiao, M. H.; Tao, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8140.
[31] Pei, Y.; Guo, P. J.; Qiao, M. H.; Li, H. X.; Wei, S. Q.; He, H. Y.; Fan, K. N. J. Catal. 2007, 248, 303.
[32] Wang, X. G.; Yan, W. S.; Zhong, W. J.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wei, S. Q. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2001, 22, 349.(王晓光, 闫文胜, 钟文杰, 张新夷, 韦世强, 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22, 349.)
[33] Bu, J.; Wang, J. Q.; Qiao, M. H.; Yan, S. R.; Li, H. X.; Fan, K. N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2007, 65, 1338.(卜娟, 王建强, 乔明华, 闫世润, 李和兴, 范康年, 化学学报, 2007, 65, 1338.)
[34] Ronchin, L.; Toniolo, L. Catal. Today 1999, 48, 255.
[35] Schwab, F.; Lucas, M.; Claus, P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10453.
[36] Spod, H.; Lucas, M.; Claus, P. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1756.
[37] Sun, H. J.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, Y. X.; Jiang, H. B.; Qu, L. L.; Liu, S. C. Liu, Z. Y. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1482.
[38] Zhou, G. B.; Dou, R. F.; Bi, H. Z.; Xie, S. H.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K. N.; Qiao, M. H.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. N. J. Catal. 2015, 332, 119.
[38] Trung, T. K.; Trens, P.; Tanchoux, N.; Bourrelly, S.; Llewellyn, P. L.; Loera-Serna, S.; Serre, C.; Loiseau, T.; Fajula, F. O.; Férey, G. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16926.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |