

Highly Sensitive Protein Biosensor based on a Conjugated Polymer Brush
Received date: 2016-04-25
Online published: 2016-08-10
Supported by
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Nos. 2012CB933301, 2012CB723402), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21005040, 51173080), the Ministry of Education of China (No. IRT1148), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20141424), Program of Scientific Innovation Research of College Graduate in Jiangsu Province (CXLX12_0792) and Research Program of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (NY215171).
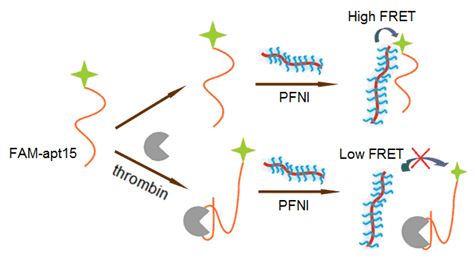
Simple and sensitive detection of proteins is crucial in biological analysis and medical diagnosis. Conjugated polymers (CPs) with π-conjugated backbones were recognized as having excellent light-harvesting capability and high fluorescent quantum yield. They have been widely used as an energy donor to amplify fluorescence signal via high efficient Föster resonance energy transfer (FRET). In particular, conjugated polymer brush with high charge density provides more possibilities due to stronger electrostatic interactions with negatively charged biomolecules. Here, we developed a highly sensitive protein biosensor for thrombin detection based on a conjugated polymer brush (PFNI) and a fluorescein-labeled aptamer (FAM-apt15). PFNI is a water-soluble cationic polyfluorene derivate with extremely high charge density (78 positive charges per repeat unit). PFNI can attract negatively charged aptamer through strong electrostatic interactions. In this case, the energy donor (PFNI) and acceptor (FAM) are in a close proximity, which results in an efficient FRET process and a high FRET signal. However, when the FAM-apt15 combines with the target protein, a rigid and big-sized G-quadruplex/thrombin complex formed. Due to the steric hindrance from the densely brush of PFNI, the distance between the two fluorophores increased significantly, leading to an inefficient FRET process and a low FRET signal. The strategy exhibits excellent specificity and the limit of detection (LOD) for thrombin in buffer was estimated to be 0.05 nmol/L. It also works well in diluted serum and a LOD of 0.2 nmol/L can be obtained. Compared to the biosensors based on traditional linear conjugated polymers, the sensitivity was improved by one order of magnitude. In addition, our strategy also shows the merits of simple, label-free, and low-cost because labeled DNA is much more expensive than unlabeled one. Based on the specific binding of aptamer and protein, this novel method can be extended to a highly sensitive detection of more proteins.
Key words: conjugated polymer; aptamer; Föster resonance energy transfer; thrombin; biosensor
Liu Xingfen , Wang Yateng , Huang Yanqin , Feng Xiaomiao , Fan Quli , Huang Wei . Highly Sensitive Protein Biosensor based on a Conjugated Polymer Brush[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2016 , 74(8) : 664 -668 . DOI: 10.6023/A16040205
[1] Cera, E. D.; Dang, Q. D.; Ayala, Y. M. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 701.
[2] Maragoudakis, M. E.; Tsopanoglou, N. E.; Andriopoulou, P. Biochem. Soc. T. 2002, 30, 173.
[3] Liu, C. W.; Huang, C. C.; Chang, H. T. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2383.
[4] Song, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 51.
[5] Pavlov, V.; Xiao, Y.; Shlyahovsky, B.; Willner, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11768.
[6] Liang, H. R.; Hu, G. Q.; Xue, X. H.; Li, L.; Zheng, X. X.; Gao, Y. W.; Yang, S. T.; Xia, X. Z. Virus Res. 2014, 184, 7.
[7] Kim, Y. S.; Song, M. Y.; Jurng, J.; Kim, B. C. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 436, 22.
[8] Cao, H. Y.; Yuan, A. H.; Shi, X. S.; Chen, W.; Miao, Y. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2054.
[9] Song, Q. W.; Peng, M. S.; Wang, L.; He, D. C.; Ouyang, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 237.
[10] Neves Miguel, A. D.; Blaszykowski, C.; Thompson, M. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3098.
[11] Jiang, L. Y.; Xiao, X. N.; Zhou, P. L.; Zhang, P.; Yan, Y. X.; Jiang, S. X.; Chen, Q. H. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 44, 310. (姜利英, 肖小楠, 周鹏磊, 张培, 闫艳霞, 姜素霞, 陈青华, 分析化学, 2016, 44, 310.)
[12] Ge, J.; Liu, Z. F.; Zhao, X. S. Chinese J. Chem. 2012, 30, 2023.
[13] Zhang, S. B.; Zheng, L. Y.; Hu, X.; Shen, G. Y.; Liu, X. W.; Shen, G. L.; Yu, R. Q. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 1688. (张松柏, 郑丽英, 胡霞, 沈广宇, 刘学文, 沈国励, 俞汝勤, 分析化学, 2015, 43, 1688.)
[14] Wu, C.; Yang, S. Y.; Wu, Z. Y.; Shen, G. L.; Yu, R. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 367. (吴超, 杨胜园, 吴朝阳, 沈国励, 俞汝勤, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 367.)
[15] He, F.; Tang, Y. L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. L.; Zhu, D. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12343.
[16] Chen, Z. B.; Tan, L. L.; Hu, L. Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Wang, S. X.; Lv, F. Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 102.
[17] Liu, X. F.; Shi, L.; Hua, X. X.; Fan, Q. L.; Chao, J.; Su, S.; Huang, Y. Q.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 16458.
[18] Kong, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 193.
[19] Chen, Z. B.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, C. M.; Yin, L.; Ma, H.; Ye, N. S.; Qiang, H.; Lin, Y. Q. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 46
[20] Baek, S. H.; Wark, A. W.; Lee, H. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9824.
[21] Jiang, C. N.; Liang, A. H.; Jiang, Z. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 713. (蒋彩娜, 梁爱惠, 蒋治良, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 713.)
[22] Le Floch, F.; Ho, H. A.; Leclerc, M. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4727.
[23] Zhao, J.; Hu, S. S.; Zhong, W. D.; Wu, J. G.; Shen, Z. M.; Chen, Z.; Li. G. X. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 7070.
[24] Liu, L. Z.; Liu, Z. H.; He, Z. K.; Cai, R. X. Prog. Chem. 2006, 18, 337.
[25] Huang, F.; Wu, H. B.; Cao, Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2500.
[26] Wang, M.; Li, C. H.; Lv, A. F.; Wang, Z. H.; Bo, Z. S. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 3017.
[27] Thomas, S. W.; Joly, G. D.; Swagger, T. M. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1339.
[28] Rochat, S.; Swagger, T. M. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 4488.
[29] Zhu, C. L.; Liu, L. B.; Yang, Q.; Lv, F. T.; Wang, S. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4687.
[30] Wang, M. F.; Zou, S.; Guerin, G. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6993
[31] Pu, K. Y.; Li, K.; Liu, B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2770.
[32] Zhang, Z. Y.; Lu, X. M.; Fan, Q. L.; Hu, W. B.; Huang, W. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 2369.
[33] Liu, X. F.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, Y. Q.; Su, S.; Fan, C. H.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. Analyst 2015, 140, 1842.
[34] Hu, W. B.; Lu, X. M.; Jiang, R. C.; Fan, Q. L.; Zhao, H.; Deng, W. X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L.; Huang, W. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9012.
[35] Jiang, R. C.; Lu, X. M.; Yang, M. H.; Deng, W. X.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3643.
[36] Zhang, Z. Y. Ph.D. Dissertation, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 2014. (张志勇, 博士论文, 南京邮电大学, 南京, 2014.)
[37] Zhang, L. B.; Zhu, J. B.; Li, T.; Wang, E. K. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8871.
[38] Golub, E.; Freeman, R.; Willner, I. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12126.
[39] Lin, Z. H.; Pan, D.; Hu, T. Y.; Liu, Z. P.; Su, X. G. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1933.
[40] Yang, X. H.; Wang, S. F.; Wang, K. M.; Luo, X. M.; Tan, W. H.; Cui, L. Chem. J. Chinese Univ. 2009, 30, 899. (羊小海, 王胜锋, 王柯敏, 罗晓明, 谭蔚泓, 崔亮, 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30, 899.)
[41] Wang, Y. Y.; Liu, B. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12787.
[42] Liu, X. F.; Shi, L.; Hua, X. X.; Huang, Y. Q.; Su, S.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, L. H.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 3406.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |