

Facile Electrochemical Synthesis of CeO2@Ag@CdSe Nanotube Arrays with Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance
Received date: 2016-05-24
Online published: 2016-10-20
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51272094, 51302111) and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20123227110018).
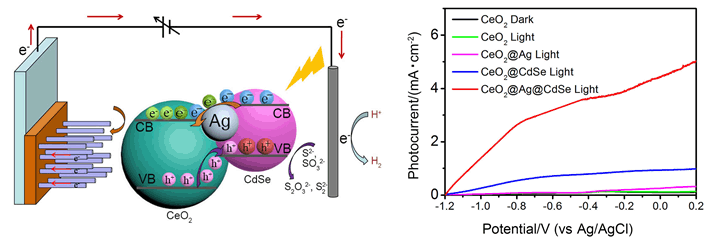
In this work, for the first time, three-component CeO2@Ag@CdSe heterostructured nanotube arrays with remarkable photoelectrochemical (PEC) properties have been synthesized on the FTO conductive glass substrate by an electrodeposition method. One-dimensional vertically ordered CeO2 nanotube arrays were prepared on the FTO substrate by electrodeposition method with Ce(NO3)2·6H2O and C2H6SO as the raw materials. Ag nanoparticles were deposited on the surface of CeO2 nanotube arrays through a successive electrodeposition in a solution of AgNO3, and a composite system of CeO2@Ag was obtained. Then a thin CdSe layer was deposited and covered on the CeO2@Ag system to form three-component CeO2@Ag@CdSe heterostructured nanotube arrays. The as-synthesized products were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. The PEC properties of the obtained products were recorded with electrochemical workstation, and the results showed that the CdSe layer could greatly enhance light harvesting and significantly improve charge separation. Moreover, the modification with Ag nanoparticles can significantly strengthen the light-harvesting ability through the localized surface plasma resonance effect and provide an interior direct pathway to facilitate the separation and transport of photogenerated carriers. It has been demonstrated that the enhanced PEC properties of CeO2@Ag@CdSe heterostructures are direct consequence of the synergetic effects of enhanced visible light absorption and the effective separation and transportation of photogenerated carriers at interface of type-II heterostructure via the Ag nanoparticles. Therefore, the CeO2@Ag@CdSe heterostructured nanotubes generate a remarkable photocurrent density of 3.92 mA·cm-2 at a potential of -0.2 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), which is 4.9 and 17.9 times higher than that of two-component CeO2@CdSe (0.802 mA·cm-2) and CeO2@Ag (0.218 mA·cm-2) systems, respectively. It also gives an incident photon to current conversion efficiency (IPCE) as high as 72% at around 360 nm. Moreover, the photoelectrode shows high photostability during the test period over 16 min.
Zhao Mi , Li Haohua , Shen Xiaoping . Facile Electrochemical Synthesis of CeO2@Ag@CdSe Nanotube Arrays with Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2016 , 74(10) : 825 -832 . DOI: 10.6023/A16050256
[1] Chen, H. M.; Chen, C. K.; Liu, R. S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wil-kinson, D. P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41(17), 5654.
[2] Wang, G.; Lu, X.; Zhai, T.; Ling, Y.; Wang, H.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y. Nanoscale 2012, 4(10), 3123.
[3] Prieto-Centurion, D.; Eaton, T. R.; Roberts, C. A.; Fanson, P. T.; Notestein, J. M. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 168, 68.
[4] Zhu, H.; Song, N.; Lian, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132(42), 15038.
[5] Song, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 133(in Chinese). (宋芳源, 丁勇, 赵崇超, 化学学报, 2014, 72(2), 133.)
[6] Wan, G.; Fu, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 557(in Chinese). (万刚, 付宇昂, 郭佳宁, 向中华, 化学学报, 2015, 73(6), 557.)
[7] Li, Y.; Qi, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73(9), 869(in Chinese). (李扬, 齐利民, 化学学报, 2015, 73(9), 869.)
[8] Khan, M. M.; Ansari, S. A.; Ansari, M. O.; Min, B. K.; Lee, J.; Cho, M. H. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118(18), 9477.
[9] Lu, X.; Zhai, T.; Cui, H.; Shi, J.; Xie, S.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C.; Tong, Y. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21(15), 5569.
[10] Li, W.; Xie, S.; Li, M.; Ouyang, X.; Cui, G.; Lu, X.; Tong, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1(13), 4190.
[11] Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Li, G. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22(21), 10480.
[12] Khan, M. M.; Ansari, S. A.; Lee, J. H.; Ansari, M. O.; Lee, J.; Cho, M. H. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 255.
[13] Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y. J. Nanoscale 2012, 4(7), 2227.
[14] Li, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Leng, Y.; Hou, M.; Xiao, X.; Bao, J.; You, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hope, G. A. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 915.
[15] Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2015, 261, 356.
[16] Srivastava, M.; Das, A. K.; Khanra, P.; Uddin, M. E.; Kim, N. H.; Lee, J. H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1(34), 9792.
[17] Al-Kuhaili, M. F.; Durrani, S. M. A.; Bakhtiari, I. A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255(5), 3033.
[18] Li, W.; Xie, S.; Li, M.; Ouyang, X.; Cui, G.; Lu, X.; Tong, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1(13), 4190.
[19] Khan, M. M.; Ansari, S. A.; Lee, J.; Ansari, M. O.; Lee, J.; Cho, M. H. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 255.
[20] Kuang, P.; Su, Y.; Xiao, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16387.
[21] Li, S. J.; Ping, Y.; Yan, J. M.;Wang, H. L.; Wu, M.; Jiang, Q. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3(28), 14535.
[22] Saravanan, R.; Karthikeyan, N.; Gupta, V. K.; Thirumal, E.; Thangadurai, P.; Narayanan, V.; Stephen, A. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33(4), 2235.
[23] Weber, W. H.; Hass, K. C.; McBride, J. R. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 178.
[24] Lu, X.; Huang, X.; Xie, S.; Zheng, D.; Liu, Z.; Liang, C.; Tong, Y. Langmuir 2010, 26(10), 7569.
[25] Hou, Y.; Zuo, F.; Dagg, A.; Feng, P. Nano Lett. 2012, 12(12), 6464.
[26] Chandrasekharan, N.; Kamat, P. V. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104(46), 10851.
[27] Miao, J.; Yang, H. B.; Khoo, S. Y.; Liu, B. Nanoscale 2013, 5(22), 11118.
[28] Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Dai, H.; Sun, X. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 466.
[29] Pu, Y. C.; Ling, Y.; Chang, K. D.; Liu, C. M.; Zhang, J. Z.; Hsu, Y. J.; Li, Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118(27), 15086.
[30] Ling, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. ChemSusChem 2014, 7(3), 848.
[31] Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X. A.; Huang, W. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3(2), 535.
[32] Lu, X. H.; Xie, S. L.; Zhai, T.; Zhao, Y. F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y. L.; Tong, Y. X. RSC Adv. 2011, 1(7), 1207.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |