

Novel Cu Based Oxides with Tunnel Structure as Cathode for Sodium-ion Batteries
Received date: 2016-08-21
Revised date: 2016-11-10
Online published: 2016-11-24
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51222210 and 11234013), and One Hundred Talent Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
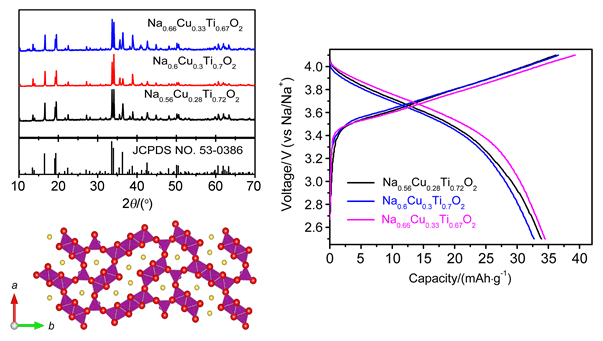
Lithium-ion batteries have dominated the electronic and portable device market, since its commercialization in 1990s. However, the cost gets boosted because of the shortage and uneven distribution of lithium. Due to the advantage of cost compared with lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion batteries are considered as the potential candidates for large scale energy storage systems. Cu based tunnel type materials were first synthesized through simple solid state reaction, with Na2CO3, CuO, Fe2O3, MnO2 and TiO2 as starting materials. These raw materials were weighed and grounded in an agate mortar, followed by heat treatment at 950℃ for 24 h in air. The obtained samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrochemical performance test. The XRD results demonstrate the tunnel structure was formed with space group pbam (the same with Na0.44MnO2) for each compound. SEM observation manifests that the distribution of particle size is from several hundred of nanometers to several micrometers. The specifically designed compound with Mn substitution (Na0.66Cu0.17Mn0.33Ti0.50O2) can deliver 90 mAh/g cycled between 1.5~4.1 V. Good cycling stability was verified for this compound, of which 90% of its capacity maintained after 50 cycles at 0.1C rate. Moreover, the rate capability is also good and 74% of its capacity remained when cycled at 1C rate. Charge transfer mechanism was studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and the electroactivity of Cu3+/Cu2+ in this tunnel structure was proved. In addition, we also performed in-situ XRD in order to examine the structure change during sodium extraction and intercalation. Only solid solution reaction took place during the test with shift of peaks or change of the peaks' intensity, however without the appearance of new peaks or disappearance of existed peaks. Here we report, for the first time, the electroactivity of Cu3+/Cu2+ in tunnel type structure. Our results provide new insights in designing tunnel type compound as cathode material for sodium-ion batteries.
Liu Lilu , Qi Xingguo , Hu Yongsheng , Chen Liquan , Huang Xuejie . Novel Cu Based Oxides with Tunnel Structure as Cathode for Sodium-ion Batteries[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017 , 75(2) : 218 -224 . DOI: 10.6023/A16080424
[1] Lyu, Z. Y.; Feng, R.; Zhao, J.; Fan, H.; Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L. J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1013. (吕之阳, 冯瑞, 赵进, 范豪, 徐丹, 吴强, 杨立军, 陈强, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1013.)
[2] Hua, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhong, B.; Fang, B.; Guo, X.; Liao, S.; Wang, H. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 261.
[3] Ou, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, D. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1293.
[4] Armand, M.; Tarascon, J. M. Nature 2008, 451, 652.
[5] Wang, Y. S.; Rong, X. H.; Xu, S. Y.; Hu, Y. S.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Q. Energy Storage Science and Technology 2016, 5, 268. (王跃生, 容晓晖, 徐淑银, 胡勇胜, 李泓, 陈立泉, 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5, 268.)
[6] Pan, H. L.; Hu, Y. S.; Chen, L. Q. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2338.
[7] Li, H.; Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Bai, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 21. (李慧, 吴川, 吴锋, 白莹, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 21.)
[8] Xiang, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5343.
[9] Wu, D.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Twu, N.; Liu, L.; Ceder, G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 8, 195.
[10] Hamani, D.; Ati, M.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Rozier, P. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 938.
[11] Kubota, K.; Ikeuchi, I.; Nakayama, T.; Takei, C.; Yabuuchi, N.; Shiiba, H.; Nakayama, M.; Komaba, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119,166.
[12] Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Cui, S.; Shi, Q.; Mi, L.; Chen, W. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 3136.
[13] Lee, E.; Brown, D. E.; Alp, E. E.; Ren, Y.; Lu, J.; Woo, J.-J.; Johnson, C. S. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6755.
[14] Reddy, B. V. R.; Ravikumar, R.; Nithya, C.; Gopukumar, S. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18059.
[15] Han, M.; Gonzalo, E.; Casas-Cabanas, M.; Rojo, T. J. Power Sources 2014, 258, 266.
[16] Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, A.; Shen, C.; Liu, Q.; Enaya, H. A.; Zhou, C. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 27.
[17] Zhu, Y.-E.; Qi, X. G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Z. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11103.
[18] Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mu, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L.; Huang, X. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 538.
[19] Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Yu, Z.; Qi, X.; Sun, K.; Hu, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, L. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 258.
[20] Delmas, C.; Fouassier, C.; Hagenmuller, P. Physica B & C 1980, 99, 81.
[21] Doeff, M. M.; Richardson, T. J.; Hollingsworth, J.; Yuan, C. W.; Gonzales, M. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 294.
[22] Doeff, M. M.; Peng, M. Y.; Ma, Y.; De Jonghe, L. C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, L145.
[23] Parant, J.-P.; Olazcuag, R.; Devalett, M.; Fouassie, C.; Hagenmuller, P. J. Solid State Chem. 1971, 3, 1.
[24] Whitacre, J. F.; Tevar, A.; Sharma, S. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 463.
[25] Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lee, B.; Qiao, R.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Yu, X.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y. S.; Yang, W.; Kang, K.; Li, H.; Yang, X. Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, X. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6401.
[26] Wang, Y.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y. S.; Li, H.; Yang, X. Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, X. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501005.
[27] Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ben, L.; Lyu, Y.; Song, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Mu, L.; Yang, H.-T.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Cheng, Z.-H.; Chen, L. Huang, X. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501156.
[28] Wang, J.; Qiu, B.; He, X.; Risthaus, T.; Liu, H.; Stan, M. C.; Schulze, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Winter, M.; Li, J. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4374.
[29] Zhan, P.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Jiao, K.; Jiao, S. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A1028.
[30] Jiang, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8480.
[31] Chu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, X. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2011, 67, i10.
[32] Kim, H.; Kim, D. J.; Seo, D.-H.; Yeom, M. S.; Kang, K.; Kim, D. K. Jung, Y. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1205.
[33] Xu, S. Y.; Wu, X. Y.; Li, Y. M.; Hu, Y. S.; Chen, L. Q. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 118202.
[34] Mu, L.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Huang, X. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6928.
[35] Mu, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 038202.
[36] Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Mu, L.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500031.
[37] Li, Y.; Hu, Y.-S.; Qi, X.; Rong, X.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 191.
[38] Sharma, N.; Gonzalo, E.; Pramudita, J. C.; Han, M. H.; Brand, H.; Hart, J. N.; Peng, W. K.; Guo, Z. P.; Rojo, T. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 25, 4994.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |