

Sensitive Detection of Aeromonas Hydrophila by Time-Resolved Fluorimmunoassay
Received date: 2016-11-21
Online published: 2017-02-23
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31272685).
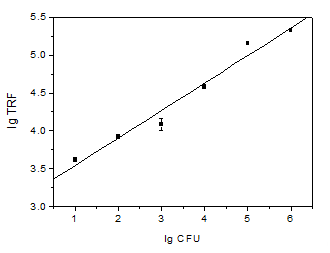
The aim of this study is to establish a biotin-avidin system and time-resolved fluorimmunoassay (BAS-TRFIA) for quantitative analysis of Aeromonas Hydrophila. First, A. Hydrophila strain B18 isolated from diseased Anguilla rostrata, was used for rabbit anti-serum preparation by injecting the formalin-inactivated bacteria. The rabbit immunoglobulin (IgG) was purified by SPA affinity column. Then, a 96-well microtiter plate precoated with the rabbit IgG was incubated with the strain B18, and biotinylated IgG was pipette to the wells to form a typical double-antibody-sandwich immune complex. Finally, Eu3+-labeled streptavidin was added the wells to produce affinity reaction. Time-resolved fluorescence (TRF) of Eu3+ was measured in enhancement solution to reflect the quantity of the strain B18. This assay showed a good relationship between TRF and the concentration of the strain B18. The limit of detection (LOD) was 1.0×102 cfu/mL, and the LOD of BAS-TRFIA was improved 400-fold compared to the already reported ELISA. The established sandwich BAS-TRFIA showed a good sixth order polynomial fitting from 1.0×10 to 1.0×106 cfu/mL for the strain B18 with the correlation coefficient 0.9716. The strain B18 was positive in BAS-TRFIA, while 19 other contrast strains of Aeromonas eucrenophila, Aeromonas jandaei, Aeromonas enteropelogenes, Escherichia coli, Aeromonas bestiarum and Aeromonas media etc. were negative in the assay, indicating that the antibody had high specificity. The intra-assay and inter-assay standard deviation were less than 5.00% and 9.00%, respectively. The TRF didn't change obviously after the related reagents were placed at 37℃ for 6 days. The method was used to detect the tissues including liver, kidney, intestine, gill and muscle from A. rostrata infected artificial with the strain B18. The result showed 98.33% of 60 samples were positive. BAS-TRFIA for A. hydrophila strain B18 was sensitive, specific and simple. The results indicate that the established BAS-TRFIA has potential application for screening A. hydrophila in aquaculture.
Lin Peng , Lu Jie , Guo Songlin , Feng Jianjun , Wang Yilei , Chen Jinmin . Sensitive Detection of Aeromonas Hydrophila by Time-Resolved Fluorimmunoassay[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017 , 75(4) : 398 -402 . DOI: 10.6023/A16110619
[1] Meng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Ye, C. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61(2), 171.
[2] Chalifoux, L. V.; Hajema, E. M.; Leeparritz, D. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1993, 43(4), 355.
[3] Fu, X. Z.; Lin, Q.; Liu, L. H.; Liang, H. R.; Huang, Z. B.; Li, N. Q. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2016, 56, 286.
[4] Griffin, M. J.; Goodwin, A. E.; Merry, G. E.; Liles, M. R.; Wil-liams, M. A.; Ware, C.; Waldbieser, G. C. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2013, 25(4), 473.
[5] Guo, S.-L.; Guan, R.-Z. Journal of Huazhong Agriculture University 2009, 28(4), 463(in Chinese). (郭松林, 关瑞章, 华中农业大学学报, 2009, 28(4), 463.)
[6] Chauret, C.; Volk, C.; Creason, R.; Jarosh, J.; Robinson, J.; Warnes, C. Can. J. Microbiol. 2001, 47(8), 782.
[7] Hussain, I. A.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Shakila, R. J.; Raj, K. T.; Jeevithan, E. J. Food Sci. Tech. Mys. 2014, 51(2), 401.
[8] Chen, C.-F. J. Huazhong Agriculture University 1998, 17(3), 264(in Chinese). (陈昌福, 华中农业大学学报, 1998, 17(3), 264.)
[9] Hu, D.-Y.; Qian, D.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Pan, Q.-Q.; Chen, C.-F. Journal of Huazhong Agriculture University 2008, 27(1), 80(in Chinese). (胡大雁, 钱冬, 刘问, 张友平, 潘清清, 陈昌福, 华中农业大学学报, 2008, 27(1), 80.)
[10] Jiang, H. F.; Wang, G. L.; Zhang, W. Z.; Liu, X. Y.; Ye, Z. Q.; Jin, D. Y.; Yuan, J. L.; Liu, Z. G. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20(1), 321.
[11] Kupstat, A.; Kumke, M. U.; Hildebrandt, N. Analyst 2011, 136(5), 1029.
[12] Lu, J.; Guo, S.-L.; Feng, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhu, H.-Q.; Lin, P. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40(11), 1709(in Chinese). (卢洁, 郭松林, 冯建军, 王艺磊, 朱洪泉, 林鹏, 分析化学, 2012, 40(11), 1709.)
[13] Huang, Y. H.; Xu, Y.; He, Q. H.; Chu, J. S.; Du, B. B.; Liu, J. Food Agr. Immunol. 2014, 25(2), 186.
[14] Tang, J.; Huang, Y. P.; Liu, H. Q.; Zhang, C. C.; Tang, D. P. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 508.
[15] Zhu, L.-P.; Chen, X.-Q. Experimental Methods Used in Immunology, People's Military Medical Press, Beijing, 2000, pp. 18~22(in Chinese). (朱立平, 陈学清, 免疫学常用实验方法, 人民军医出版社, 北京, 2000, pp. 18~22.)
[16] Zheng, W.-F. Medical Immunology, People's Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 1989, p. 38(in Chinese). (郑武飞, 医学免疫学, 人民卫生出版社, 北京, 1989, p. 38.)
[17] Shen, J.; Lin, D.-Q.; Xu, J. Chinese Bulletin of Life Science 2004, 16(1), 55(in Chinese). (沈健, 林德球, 徐杰, 生命科学, 2004, 16(1), 55.)
[18] Li, W.-H.; He, X.-W.; Qi, W.; Chen, F.-Y. Modern Food Science & Technology 2011, 27(12), 1480(in Chinese). (李伟汉, 何小维, 齐维, 陈富裕, 现代食品科技, 2011, 27(12), 1480.)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |