

Polyaniline-graphene Hollow Spheres based on Graphene Stabilized Pickering Emulsions
Received date: 2016-11-25
Online published: 2017-03-07
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51573072) and the Six Talents Peak Project of Jiangsu Province (XNY-012).
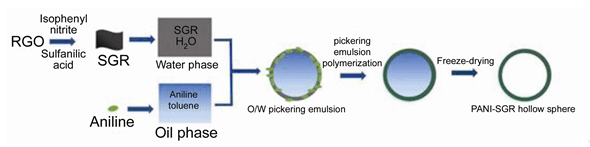
In recent years, hybrid nanomaterials of graphene and polyaniline have attracted extensive interest and have been considered as promising electrode materials for supercapacitor combining the advantages of both materials with synergistic effects. In contrast to the well-developed two-dimensional planar structure of graphene-PANI, the pursuit of hollow gra-phene-PANI hybrid structure is relatively less investigated. The hollow micro/nanostructured graphene-PANI materials with the nanoscale shell, inner cavity and pore structures, is highly expected to exhibit remarkable enhanced supercapacitor performance owing to the enhanced specific surface area and shortened diffusion length for both charge and mass transport. In this work, a novel kind of graphene-polyaniline hollow capsules (PANI-SGR HS) was prepared via Pickering emulsion polymerization using sulfonated graphene (SGR) as Pickering stabilizer. Amphiphilic sulfonated graphene is prepared by a covalent modification and used to stabilize oil phase containing aniline monomer. Aniline molecules were adsorbed to the oil-water interface owing to the electrostatic interaction between amino groups of aniline and sulfonic groups of SGR, which subsequently underwent interfacial polymerization at the oil/water interface upon the addition of initiator ammonium persulfate (APS). The effects of the sulfonation degree of graphene, the SGR concentration as well as the oil/water volume ratio on the stability and morphology of SGR stabilized emulsions were investigated in detail. The SGR with appropriate sulfonation degree can produce stable emulsions. The average diameter of the emulsion droplet decreased with the increasing concentration of SGR stabilizer. The emulsion stability can be improved with the increased water phase infraction. After polymerization of aniline and removal of the oil phase, three-dimensional hollow graphene-polyaniline sphere (PANI-SGR HS) was obtained. The morphology of PANI-SGR HS was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The special hollow sphere structure not only enlarged the liquid contact area but also improved charge carrier mobility. The hollow sphere modified electrode exhibited excellent performance with a specific capacitance of 480.59 F·g-1 at 1 A·g-1, which is much higher than 251 F·g-1 of the common two-dimensional stacked graphene-polyaniline film. This novel three-dimensional PANI-SGR HS material may have potential applications in energy storage.
Zheng Yuan , Luo Jing , Wei Wei , Liu Xiaoya . Polyaniline-graphene Hollow Spheres based on Graphene Stabilized Pickering Emulsions[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017 , 75(4) : 391 -397 . DOI: 10.6023/A16110624
[1] Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.; Potts, J.; Rouff, R. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906.
[2] He, Q.; Wu, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1764.
[3] Yang, L.; Tang, Y.; Yan, D.; Liu, T.; Liu, C.; Luo, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 8, 169.
[4] Tong, Z.; Fang, S.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 185. (童震坤, 方姗, 郑浩, 张校刚, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 185.)
[5] Gao, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7215.
[6] Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Lei, S.; Song, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4491.
[7] Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, X. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4818.
[8] Domingues, S. H.; Salvatierra, R. V.; Oliveira, M. M.; Zarbin, A. J. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2592.
[9] Sun, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lai, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, X. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2015, 36, 581. (孙军, 朱正意, 赖健平, 罗静, 刘晓亚, 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36, 581.)
[10] Fan, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 107.
[11] Du, P.; Liu, H. C.; Yi, C.; Wang, K.; Gong, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23932.
[12] Yang, F.; Xu, M.; Bao, S. J.; Wei, H.; Chai, H. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 381.
[13] Fan, W.; Zhang, C.; Tjiu, W. W.; Pramoda, K. P.; He, C.; Liu, T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3382.
[14] Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Fan, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 839.
[15] Fan, W., Xia, Y. Y.; Tjiu, W. W.; Pallathadka, P. K.; He, C.; Liu, T. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 973.
[16] Luo, J.; Ma, Q.; Gu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 173, 184.
[17] Trung, N. B.; Van Tam, T.; Kim, H. R.; Hur, S. H.; Kim, E. J.; Choi, W. M. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 89.
[18] Binks, B. P. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 21.
[19] Wei, W.; Wang, T.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X. Colloids Surf., A 2015, 487, 58.
[20] McCoy, T. M.; Pottage, M. J.; Tabor, R. F. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4529.
[21] Hu, Z.; Marway, H. S.; Kasem, H.; Pelton, R.; Cranston, E. D. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 185.
[22] Kim, S. D.; Zhang, W. L.; Choi, H. J. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7541.
[23] Yin, G.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, Q.; Zhang, H. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 192.
[24] Fei, X.; Xia, L.; Chen, M.; Wei, W.; Luo, J.; Liu, X. Materials 2016, 9, 731.
[25] Wan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hughes, T. C.; Qian, B.; Peng, S.; Hao, X.; Qiu, J. Carbon 2015, 85, 16.
[26] Chen, X.; Eggers, P. K.; Slattery, A. D.; Ogden, S. G.; Raston, C. L. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 174.
[27] Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5304.
[28] Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 96, 103.
[29] Yang, J.; Shi, T.; Jin, W.; Zou, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2008, 66, 552. (杨家义, 史铁钧, 金维亚, 邹燕, 化学学报, 2008, 66, 552.)
[30] Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yi, C.; Wei, W.; Liu, X. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 7577.
[31] Binks, B. P.; Lumsdon, S. O. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8622.
[32] Zheng, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7974.
[33] Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6847.
[34] Aveyard, R.; Binks, B. P.; Clint, J. H. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 503.
[35] Yi, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. Langmuir 2016, 32, 982.
[36] Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, X. J. Polym. Sci., Part A:Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4888.
[37] Fan, W.; Zhang, C.; Tjiu, W. W.; Pramoda, K. P.; He, C.; Liu, T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3382.
[38] Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Lu, Y. Polymer 2014, 55, 4459.
[39] Zang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Zhen, Z.; He, Y.; Zhu, H. Na-noscale 2015, 7, 7318.
[40] Mu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, A. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 1.
[41] Co?kun, E.; Zaragoza-Contreras, E. A.; Salavagione, H. J. Carbon 2012, 50, 2235.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |