

Enrichment of Silver from Water Using Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI)
Received date: 2017-07-28
Online published: 2017-09-18
Supported by
Project supported by the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX201700172) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51578398).
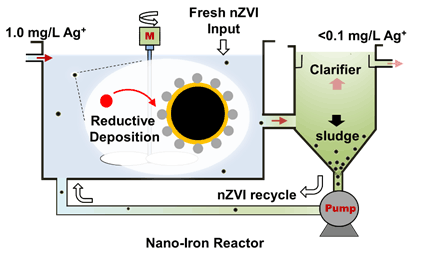
Increasing evidence suggests that nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) is an effective nanomaterial for the enrichment and separation of heavy metals from water, especially for recovering precious metals such as gold and silver from trace level sources. In this work, a nano-iron reactor, consisting of reaction zone, separation zone and reuse facilities, is applied to recovery of silver from aqueous solution using nZVI. We demonstrate that nZVI could sequester Ag+ (ca. 1 mg/L) and be transformed into high-grade (32.0 mg/g) silver solids ("ore") as nZVI is recycled in this "reaction-separation-reuse" system. Besides, increasing hydraulic retention time (HRT), from 10 min to 60 min, could enhance the enrichment efficiency and finally improve silver content in solid phase. We further demonstrate that there is a positive correlation between solution oxidation-reduction potential in reaction zone and Ag+ concentration in effluent, and this relationship can be used to regulate the reaction kinetics and separation efficiency. Data from oxidation-reduction potential regulating experiment are presented and a mathematic formula is provided, proving this system is reliable and controllable. Solid phase characterizations with X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirm that Ag+ is reduced to metallic silver (Ag0). Images acquired via high-resolution transmission electron microscopy reveal that Ag0 (<10 nm) is deposited on the surface of nZVI (Ag-nZVI). Pure silver nanoparticles (AgNPs, 9~32 nm) could be acquired by simply processing Ag-nZVI with sulfuric acid and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. Batch experiments confirm that nZVI is far more efficient and less pH-dependent, comparing to other materials (e.g., mZVI, α-Fe2O3, nTiO2). 99% Ag+ (1000 mg/L) could be sequestrated in less than 15 s with 1 g/L nZVI. And the separation coefficient of nZVI for Ag+ reaches 3.2×104, which is several orders of magnitude higher than that of conventional adsorbents and reductants (102~741). This study demonstrates that nZVI is a powerful candidate to recover Ag from water (e.g., industrial wastewater, groundwater) with trace level silver and produce valuable AgNPs.
Gu Tianhang , Shi Junming , Hua Yilong , Liu Jing , Wang Wei , Zhang Wei-xian . Enrichment of Silver from Water Using Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI)[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017 , 75(10) : 991 -997 . DOI: 10.6023/A17070345
[1] Yu, S. L.; Yin, Y. G.; Liu, J. F. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Imp. 2013, 15, 78.
[2] Syed, S. Waste. Manage. 2016, 50, 234.
[3] World Silver Survey, 2017, GFMS Limited/The Silver Institute. http://www.silverinstitute.org
[4] Benn, M. T.; Westerhoff, P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4133.
[5] Zhou, X. X.; Liu, J. F.; Yuan, C. G.; Chen, Y. S. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 2285.
[6] Eckelman, M. J.; Graedel, T. E. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6283.
[7] Li, R.; Lu, Y. Y.; Lei, K. X.; Li, F. J.; Cheng, F. Y.; Chen, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 199(in Chinese). (李冉, 卢艳莹, 雷凯翔, 李福军, 程方益, 陈军, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 199.)
[8] Wang, C.; Deng, N.; Wang, L. L.; Xu, D. J.; Yao, X. Q. Chinese J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1034(in Chinese). (王超, 邓楠, 王玲玲, 许定健, 姚小泉, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1034.)
[9] Vance, M. E.; Kuiken, T.; Vejerano, E. P.; McGinnis, S. P.; Hochella, M. F.; Rejeski, D.; Hull, M. S. Beilstein. J. Nanotech. 2015, 6, 1769.
[10] Song, X. H.; Gunawan, P.; Jiang, R. R.; Leong, S. S. J.; Wang, K.; Xu, R. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 162.
[11] Zhou, Y. M.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, R. A.; Cao, X. D. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 801.
[12] Celik. Z.; Gulfen. M.; Aydin, A. O. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 556.
[13] Wang, H. Y.; Gao, H.; Sun, J. S.; Li, J.; Su, Y. X.; Ji, Y. L.; Gong, C. M. Desalination 2011, 270, 258.
[14] Huo, H. Y.; Su, H. J.; Tan, T. W. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 139.
[15] Huang, X. Y.; Wang, W.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 529(in Chinese). (黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 529.)
[16] Mu, Y.; Jia, F. L.; Ai, Z. H.; Zhang, L. Z. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2017, 4, 27.
[17] Fu, F. L.; Dionysiou, D. D.; Liu, H. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194.
[18] Zhang, Y. L.; Yan, J.; Dai, C. M.; Li, Y. T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. F. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 1110.
[19] Teng, W.; Fan, J. W.; Wang, W.; Bai, N.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. H.; Kong, B.; Yang, J. P.; Zhao, D. Y.; Zhang, W. X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4478.
[20] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788.
[21] Sheng, G. D.; Yang, P. J.; Tang, Y. N.; Hu, Q. Y.; Li, H.; Ren, X. M.; Hu, B. W.; Wang, X. K.; Huang, Y. Y. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 193, 189.
[22] Xia, X. F.; Hua, Y. L.; Huang, X. Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 594(in Chinese). (夏雪芬, 滑熠龙, 黄潇月, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 594.)
[23] Sheng, G. D.; Alsaedi, A.; Shammakh, W.; Monaquel, S.; Sheng, J.; Wang, X. K.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. Y. Appl. Carbon. 2016, 99, 123.
[24] Li, S. L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Y.; Zhang, W. X. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 115.
[25] Wang, W.; Hua, Y. L.; Li, S. L.; Yan, W. L.; Zhang, W. X. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 79.
[26] Li, S. L.; Wang, W.; Liang, F. P.; Zhang, W. X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 163.
[27] Wang, W.; Li, S. L.; Lei, H.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, W. X. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 616.
[28] Shi, Z. Q.; Nurmi, T. J.; Tratnyek, G. P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1586.
[29] Sverdrup, H.; Koca, D.; Ragnarsdottir, V. K. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2014, 83, 121.
[30] Liang, L. P.; Yang, W. J.; Guan, X. H.; Li, J. L.; Xu, Z. J.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y. Y.; Zhang, X. Z. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5846.
[31] Guan, X. H.; Sun, Y. K.; Qin, H. J.; Li, J. X.; Lo, I. M. C.; He, D.; Dong, H. R. Water Res. 2015, 75, 224.
[32] Liang, L. P.; Sun, W.; Guan, X. H.; Huang, Y. Y.; Choi, W. Y.; Bao, H. L.; Li, L. N.; Jiang, Z. Water Res. 2014, 49, 371.
[33] Nitayaphat, W.; Jintakosol, T. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 850.
[34] Wang, Y.; Ma, X. J.; Li, Y. F.; Li, X. L.; Yang, L. Q.; Ji, L.; He, Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 394.
[35] Ju, S. H.; Zhang, Y. F.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, P. Y.; Wang, Y. H. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 554.
[36] Yin, Y. G.; Shen, M. H.; Tan, Z. Q.; Yu, S. J.; Liu, J. F.; Jiang, G. B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6581.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |