

Superhalogen Substitutions in Cubic Halide Perovskite Materials for Solar Cells:A First-principles Investigation
Received date: 2017-09-04
Online published: 2017-10-20
Supported by
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFB0601904), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11404395), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2013QJ01) and the National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (No. C201604020).
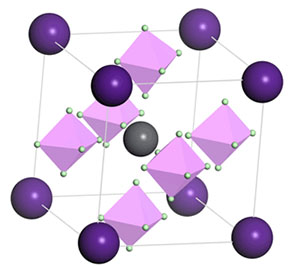
Halide perovskite (ABC3) solar cell has received a lot of attentions due to its excellent photoelectronic properties. It has been proven to be an effective way to modify halide perovskite materials' bandgap by replacing A or B ions with other equivalent ions. However, C ions have much fewer choices and are limited to halogen anions or pseudohalides anions. We designed a series of new cubic perovskite structures through substituting C anions by superhalogen clusters anions (BeX3-, MgX3-, BX4-, AlX4-, SiX5-, PX6-, X=F, Cl), and studied their structures and properties in first-principles way. Calculations were performed by using the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) based on density functional theory. The DOS (Density of States) and bandgaps were calculated to analyze properties of the new perovskite structures. The results show that BeX3-, MgX3- (X=F, Cl) and SiCl5- could not remain its structure which means these three clusters are not superhalogen anions anymore after doping. The size and symmetry of superhalogen anions have influences on the structures of doped perovskites. The superhalogen anion whose symmetry is higher and size is closed to I- ion induces less distortions to doped perovskite structures. Comparing to the VBM (Valence Band Maximum) and CBM (Conduction Band Minimum) of CsPbI3, superhalogen anions substitutions could change the compositions of CBM and VBM and bandgaps. The bandgaps of superhalogen anions partial substitutions in halide perovskite become smaller compared to structures with superhalogen anions substituting completely. We demonstrate that the CsPb(PCl6)3, with a direct-bandgap of 1.58 eV located at M(0,0.5,0.5) point, could be a potential candidate material for solar cells. Its CBM mainly is dominated by Cl 3p states, P 3s states and Pb 6p states. The other doped perovskites with wide bandgaps may have potential applications in transistors or memristors. We hope that these results could provide theoretical guidance for synthesis of new perovskite materials for solar cells.
Key words: halide perovskite; solar cell; superhalogen; substitutions; first-principles
Wu Miao Miao , Liu Shiqiang , Chen Hao , Wei Xuehu , Li Mingyang , Yang Zhibin , Ma Xiangdong . Superhalogen Substitutions in Cubic Halide Perovskite Materials for Solar Cells:A First-principles Investigation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2018 , 76(1) : 49 -54 . DOI: 10.6023/A17090406
[1] Guo, X. D.; Niu, G. D.; Wang, L. D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 211. (郭旭东, 牛广达, 王立铎, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 211.)
[2] Wang, N. N.; Si, J. J.; Jin, Y. Z.; Wang, J. P.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 171. (王娜娜, 司俊杰, 金一政, 王建浦, 黄维, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 171.)
[3] Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050.
[4] Green, M. A.; Ho-Baillie, A.; Snaith, H. J. Nat. Photon. 2014, 8, 506.
[5] Jeon, N. J.; Noh, J. H.; Kim, Y. C.; Yang, W. S.; Ryu, S. C.; Seok, S, I. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 897.
[6] Kim, H. S.; Lee, C. R.; Im, J. H.; Lee, K. B.; Moehl, T.; Marchioro, A.; Moon, S. J.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Yum, J. H.; Moser, J. E.; Gr ätzel, M.; Park, N. G. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 591.
[7] Tang, H.; He, S. S.; Peng, C. W. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 410.
[8] Ganose, A. M.; Savory, C. N.; Scanlon, D. O. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4594.
[9] Jiang, Q. L.; Rebollar, D.; Gong, J.; Piacentino, E. L.; Zheng, C.; Xu, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7617.
[10] Umeyama, D.; Lin, Y.; Karunadasa, H. I. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3241.
[11] Xiao, Z. W.; Meng, W. W.; Saparov, B.; Duan, H. S.; Wang, C. L.; Feng, C. B.; Liao, W. Q.; Ke, W, J.; Zhao, D. W.; Wang, J. B.; Mitzi, D. B.; Yan, Y. F. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1213.
[12] Hendon, C. H.; Yang, R. X.; Burton, L. A.; Walsh, A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9067.
[13] Nagane, S.; Bansode, U.; Game, O.; Chhatre, S.; Ogale, S. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9741.
[14] Yao, Q. S.; Fang, H.; Deng, K. M; Kan, E.; Jena, P. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17836.
[15] Fang, H.; Jena, P. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1596.
[16] Andersen, T.; Haugen, H. K.; Hotop, H. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 1999, 28, 1511.
[17] Gutsev, G. L. Chem. Phys. 1981, 56, 277.
[18] Gutsev, G. L.; Boldyrev, A. I. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1987, 56, 519.
[19] Prigogine, I.; Rice, S. A. The Theoretical Investigation of the Electron Affinity of Chemical Compounds, Vol. 61, John Wiley Sons, Inc., New York, 2007, pp. 169~221.
[20] Gutsev, G. L.; Boldyrev, A. I. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 2256.
[21] Gutsev, G. L.; Boldyrev, A. I. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 108, 250.
[22] Marchaj, M.; Freza, S.; Skurski, P. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 1966.
[23] Marchaj, M.; Freza, S.; Skurski, P. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 612, 172.
[24] Srivastava, A. K.; Misra, N. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 8, 866.
[25] Srivastava, A. K.; Misra, N. Polyhedron 2015, 102, 711.
[26] Anusiewicz, I.; Sobczyk, M.; Dabkowska, I.; Skurski, P. Chem. Phys. 2003, 291, 171.
[27] Sikorska, C.; Smuczynska, S.; Skurski, P.; Anusiewicz, I. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 7348.
[28] Furuhashi, K.; Habasaki, J.; Okada, I. Mol. Phys. 1986, 59, 1329.
[29] Stadler, R.; Wolf, W.; Podloucky, R.; Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J.; Hafner, J. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 1729.
[30] Paier, J.; Marsman, M.; Hummer, K.; Kresse, G.; Gerber, I. C.; Ángyán, J. G. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 154709.
[31] Liu, G.; Liu, S. B.; Xu, B.; Ouyang, C. Y.; Song, H. Y. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 112, 666.
[32] Even, J.; Pedesseau, L.; Jancu, J. M.; Katan, C. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2999.
[33] Mosconi, E.; Amat, A.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Grätzel, M.; De Angelis, F. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 13902.
[34] Zhao, Z. G.; Lu, X. Q.; Li, K.; Wei, S. X.; Liu, X. F.; Niu, K.; Guo, W. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 1003. (赵兹罡, 鲁效庆, 李可, 魏淑贤, 刘学锋, 牛恺, 郭文跃, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 1003.)
[35] Zhao, Z. G.; Niu, Y. Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q. H.; Xin, L.; Lu, X. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 689. (赵兹罡, 牛永强, 赵洋, 宋清华, 忻灵, 鲁效庆, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 689.)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |