

Surface Chemistry and Phase Transformation of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) in Aquatic Media
Received date: 2018-10-02
Online published: 2018-11-13
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41673096, 41772243, 51578398) and National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX201700172).
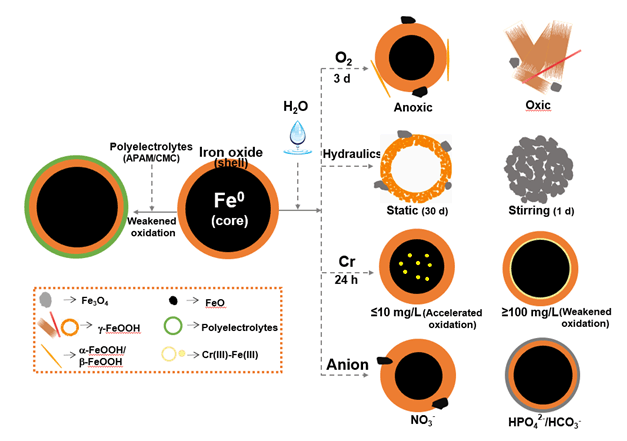
The unique "core-shell" structure endows nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) rich aquatic surface chemistry properties. Transformation of surface chemistry and crystal phase of nZVI affect its reactivity and environmental transport and fate. Recent advances on the surface chemistry and phase transformation of nZVI in aqueous media are highlighted in this paper focusing on a basic theory of nZVI for pollution control and environmental application. Surface chemistry and phase of both fresh and reacted nZVI are presented. The structure, composition and properties of nanoparticles are determined not only by reaction time but also by environmental conditions. Specifically, the influences of dissolved oxygen, hydraulic conditions (static and stirring), types and concentrations of heavy metals (U(VI), Cr(VI), Se(IV)) and anions (NO3-, SO42-, HPO42- and HCO3-) are investigated. In addition, the effect of surface modification with polyelectrolytes, including anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) and carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC), on microstructure, morphology and composition of nanoparticles in aqueous phase was discussed. Results demonstrate that environmental conditions have significant impacts on particles structure, composition and properties, consequently on nZVI performance for pollutant removal. After corrosion under different aqueous conditions, the core-shell structured nZVI are distorted and the metallic iron core is transformed into different iron oxides/hydroxides, such as γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4 and γ-FeOOH. These iron (hydr)oxides exhibit different surface complexation and affinity proprieties, thus eventually affecting the pollutant removal performance and the environmental fate of reaction products. More research on the effect of dynamic structure transformation by different types of pollutants, and a reaction model between the surface chemistry/phase transformation and removal performance are needed to deepen our understanding on nZVI surface chemistry, and develop more effective technologies of environmental applications.
Liu Jing , Liu Jing , Gu Tianhang , Gu Tianhang , Wang Wei , Wang Wei , Liu Ai-rong , Liu Ai-rong , Zhang Wei-xian , Zhang Wei-xian . Surface Chemistry and Phase Transformation of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) in Aquatic Media[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019 , 77(2) : 121 -129 . DOI: 10.6023/A18100412
[1] Alowitz, M. J.; Scherer, M. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 299.
[2] Johnson, T. L.; Scherer, M. M.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2634.
[3] Matheson, L. J.; Tratnyek, P. G. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 2045.
[4] Bang, S.; Korfiatis, G. P.; Meng, X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 61.
[5] Wang, C. B.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2154.
[6] Shu, H. Y.; Chang, M. C.; Chen, C. C.; Chen, P. E. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 499.
[7] Sohn, K.; Kang, S. W.; Ahn, S.; Woo, M.; Yang, S. K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5514.
[8] Huang, X. Y.; Wang, W.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 529(in Chinese). (黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 529.)
[9] Gu, T.; Shi, J.; Hua, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 991(in Chinese). (顾天航, 石君明, 滑熠龙, 刘静, 王伟, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 991.)
[10] Xia, X.; Hua, Y.; Huang, X.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 594(in Chinese). (夏雪芬, 滑熠龙, 黄潇月, 凌岚, 张伟贤, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 594.)
[11] Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, W. X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 129.
[12] Liu, A. R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. X. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1068.
[13] Liu, A. R.; Liu, J.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, W. X. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57377.
[14] Mu, Y.; Jia, F.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 538 (in Chinese). (穆毅, 贾法龙, 艾智慧, 张礼知, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 538.)
[15] Wang, C. Y.; Chen, Z. Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, Y. R.; Liu, H. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1999, 60, 223.
[16] Liu, A. R.; Zhang, W. X. Analyst 2014, 139, 4512.
[17] Wang, C.; Baer, D. R.; Amonette, J. E.; Engelhard, M. H.; Antony, J.; Qiang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8824.
[18] Nurmi, J. T.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Sarathy, V.; Baer, D. R.; Amonette, J. E.; Pecher, K.; Wang, C.; Linehan, J. C.; Matson, D. W.; Penn, R. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1221.
[19] Yan, W.; Herzing, A. A.; Kiely, C. J.; Zhang, W. X. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 118, 96.
[20] Liu, Y.; Majetich, S. A.; Tilton, R. D.; Sholl, D. S.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1338.
[21] Kim, H. S.; Kim, T.; Ahn, J. Y.; Hwang, K. Y.; Park, J. Y.; Lim, T. T.; Hwang, I. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 16.
[22] Kanel, S. R.; Greneche, J. M.; Choi, H. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2045.
[23] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 209.
[24] Yan, W. L.; Herzing, A. A.; Li, X. Q.; Kiely, C. J.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4288.
[25] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33861.
[26] Ling, L.; Huang, X. Y.; Zhang, W. X. Adv. Mater. 2018, 1705703.
[27] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 305.
[28] Kanel, S. R.; Manning, B.; Charlet, L.; Choi, H. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1291.
[29] Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Tang, J.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Y. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1595.
[30] Tang, L.; Feng, H.; Tang, J.; Zeng, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Water Res. 2017, 117, 175.
[31] Ling, L.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, W. X. Water Res. 2015, 71, 274.
[32] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788.
[33] Huang, X. Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 4.
[34] Xia, X. F.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X.. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 52.
[35] Xia, X. F.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1597.
[36] Liu, H. B.; Chen, T. H.; Chang, D. Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; He, H. P.; Yuan, P.; Frost, R. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 133, 205.
[37] Liu, Y.; Phenrat, T.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7881.
[38] Reinsch, B. C.; Forsberg, B.; Penn, R. L.; Kim, C. S.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3455.
[39] Almeelbi, T.; Bezbaruah, A. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 900.
[40] Wen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, C. Colloid. Surface A 2014, 457, 433.
[41] Hua, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Gu, T.; Ding, D.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 603.
[42] Jiemvarangkul, P.; Zhang, W. X.; Lien, H. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 482.
[43] Johnson, R. L.; Nurmi, J. T.; O'Brien Johnson, G. S.; Fan, D.; O'Brien Johnson, R. L.; Shi, Z.; Salter-Blanc, A. J.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Lowry, G. V. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1573.
[44] Liu, J.; Liu, A. R.; Zhang, W. X. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 26832.
[45] Tang, J.; Tang, L.; Feng, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 575(in Chinese). (汤晶, 汤琳, 冯浩朋, 董浩然, 章毅, 刘思诗, 曾光明, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 575.)
[46] Su, Y. M.; Adeleye, A. S.; Keller, A. A.; Huang, Y. X.; Dai, C. M.; Zhou, X. F.; Zhang, Y. L. Water Res. 2015, 74, 47.
[47] Rajajayavel, S. R. C.; Ghoshal, S. Water Res. 2015, 78, 144.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |