

Colorimetric Sensing of Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Based on Gold Nanoparticles
Received date: 2019-01-09
Online published: 2019-03-26
Supported by
Project supported by the Doctoral Research Start-up Fund of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (No. 2014BL19).
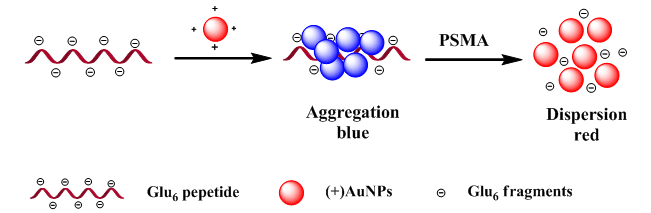
Cancer is a major cause of death and its early diagnosis has been a research goal for many decades. For males, prostatic carcinoma has become the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) has been widely recognized as a prostate cancer marker. Thus, measurement of PSMA would be more valuable for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Nanomaterials have the characteristics of small size effect, quantum size effect, macroscopic quantum tunneling effect and surface effect, and have been widely used in various fields, such as cell imaging, analysis and detection, drug release and treatment. Gold nanoparticles have been widely used in biosensing and medical diagnosis due to their simple preparation, high stability and unique photoelectric properties. In this paper, a new colorimetric approach is proposed for simple detection of PSMA based on gold nanoparticles. In the experiment, we synthesized gold nanoparticles with positive charges, and the polyanionic peptide as the substrate of PSMA. The detection of PSMA was based on the property that different aggregation states of gold nanoparticles can lead to the change of color and the specific recognition of PSMA for its substrate. The positively charged gold nanoparticles interact electrostatically with polyanionic peptide, resulting in aggregation of gold nanoparticles. In the presence of PSMA, however, the polyanionic peptide are hydrolyzed into glutamic acid fragment due to the reaction between the PSMA and the polyanionic peptide, resulting in the dispersion of gold nanoparticles. This behaviour leads to the development of a rapid and simple colorimetric method for assaying PSMA activity, with a detection limit of 0.5 nmol/L and the linear range of 2~10 nmol/L. This approach is simple compared to the existing ones since the gold nanoparticles-peptide based sensor is easy to be assembled and the detection can be achieved without the involvement of complicated procedures. Moreover, the applicability of the method has been demonstrated by detecting PSMA spiked into urine samples.
Feng Tingting , Gao Shouqin , Wang Kun . Colorimetric Sensing of Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Based on Gold Nanoparticles[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019 , 77(5) : 422 -426 . DOI: 10.6023/A19010018
[1] Juzgado, A.; Soldà, A.; Ostric, A.; Criado, A.; Valenti, G.; Rapino, S.; Conti, G.; Fracasso, G.; Paolucci, F.; Prato, M. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6681.
[2] Huang, W. F.; Chang, C. L.; Brault, N. D.; Gur, O.; Wang, Z.; Jalal, S. I.; Low, P. S.; Ratliff, T. L.; Pili, R.; Savran, C. A. Lab Chip. 2017, 17, 415.
[3] Ferraris, D. V.; Shukla, K.; Tsukamoto, T. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1282.
[4] Yang, H. W.; Hua, M. Y.; Liu, H. L.; Tsai, R. Y.; Chuang, C. K.; Chu, P. C.; Wu, P. Y.; Chang, Y. H.; Chuang, H. C.; Yu, K. J.; Pang, S. T. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1795.
[5] Pu, F.; Salarian, M.; Xue, S. H.; Qiao, J. J.; Feng, J.; Tan, S. S.; Patel, A.; Li, X.; Mamouni, K.; Hekmatyar, K.; Zou, J.; Wu, D. Q.; Yang, J. J. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12668.
[6] Min, K.; Song, K. M.; Cho, M.; Chun, Y. S.; Shim, Y. B.; Ku, J. K.; Ban, C. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5566.
[7] Carter, R. E.; Feldman, A. R.; Coyle, J. T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 749.
[8] Kamga, I.; Ng, R.; Hosaka, M.; Berkman, C. E. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 310, 125.
[9] Wang, H. S.; Lin, P. T.; Zhao, S. L.; Li, S. T.; Lu, X.; Liang, H. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 943.
[10] Yang, L. M.; Liu, B.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1047. (杨立敏, 刘波, 李娜, 唐波, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1047.)
[11] Li, M. B.; Tian, S. K.; Wu, Z. K. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 567.
[12] Li, S. S.; Wang, F. Z. R.; Liu, Y. M.; Cao, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 591.
[13] Zhu, A.W.; Qu, Q.; Shao, X. L.; Kong, B.; Tian, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7185.
[14] Zhang, Y. Y.; Wu, M. H.; Wu, M. J.; Guo, L. P.; Cao, L., Wu, H. Y.; Zhang, X. N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 709. (张燕燕, 武明豪, 武明杰, 国林沛, 曹琳, 吴虹仪, 张雪宁, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 709.)
[15] Ji, G.; Yan, L. L.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, B.; Tian, W. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 917. (纪光, 闫路林, 王慧, 马莲, 徐斌, 田文晶, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 917.)
[16] Men, J. Y.; Gao, B. J.; Chen, Z. P.; Yao, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 2273. (门吉英, 高保娇, 陈志萍, 么兰, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 2273.)
[17] Wen, Q. S.; Tang, H. W.; Yang, G. M.; Liu, L. B.; Lv, F. T.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 2137. (温泉山, 唐红伟, 杨高买, 刘礼兵, 吕凤婷, 杨琼, 王树, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 2137.)
[18] Elghanian, R.; Storhoff, J. J.; Mucic, R. C.; Letsinger, R. L.; Mirkin, C. A. Science 1997, 277, 1078.
[19] Taton, T. A.; Mirkin, C. A.; Letsinger, R. L. Science 2000, 289, 1757.
[20] Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Cametti, C.; Russo, M. V. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4204.
[21] Obare, S. O.; Hollowell, R. E.; Murphy, C. J. Langmuir 2002, 18, 10407.
[22] Kim, Y.; Johnson, R. C.; Hupp, J. T. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 165.
[23] Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7454.
[24] Anderson, M. O.; Wu, L. Y.; Santiago, N. M. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6678.
[25] Feng, D.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Feng, T. T.; Shi, W.; Li, X. H.; Ma, H. M. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10680.
[26] Miao, X. M.; Cheng, Z. Y.; Li, Z. B.; Wang, P. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 21.
[27] Sun, C. D.; Shi, W.; Song, Y. C.; Chen, W.; Ma, H. M. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8638.
[28] Mohan, K. M.; Donavan, K. C.; Arter, J. A.; Penner, R. M.; Weiss, G. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7761.
[29] Li, C. M.; Li, Y. F.; Wang, J.; Huang, C. Z. Talanta 2010, 81, 1339.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |