

Recent Progress on the Detection of Dioxins Based on Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Received date: 2019-04-22
Online published: 2019-06-05
Supported by
Project supported by the 13th five-year development plan of China by the National Key Research and Development Program(2017YFC1600301);the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(1610072017006)
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), represented by dioxins and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls have the property of teratogenic, carcinogenic and mutagenic, which have been classified as Group A human carcinogen by the international agency for research on cancer (IARC) and put into the initial list of Stockholm Convention managed by the United Nations Environment Program. POPs have posed a threat and impact on food security through the food chain from environment. The conventional detection methods, such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, high resolution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry are sufficiently accurate, but fail to meet the requirements of on-site detection. Meanwhile, the rapid testing technologies for PCBs mainly included fluorescence detection, electrochemical sensors, and so on. As a new type of rapid detection technology, Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) has attracted significant attention as a promising analytical technique. With its ultra-sensitivity, high speed detection, ease of operation, SERS is particularly well-suited for the rapid detection of POPs. However, the multiple molecules in matrices may generate interfering Raman signals via competitive adsorption with the target compound on the substrate surface in the SERS detection of real samples. In addition, reproducibility represents a major bottleneck for the widespread application of SERS. Metal nanoparticle colloids are widely used as SERS substrates due to the hot spots formed between the nanoparticles. However, metal nanoparticle aggregation in colloidal solutions is difficult to control, leading to the random formation of hot spots. When the target POPs exist near the hot spots, the intensities of the enhanced Raman signals were unstable. Other factors influenced by the chemical adsorption such as vibration, charge transfer, and the deformation or distortion of molecules also affect the Raman signals. In the review, we provide an overview of the recent advances in SERS for POPs determination, especially the different types of enhanced substrates. And several key technical points of SERS detection including sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility have been summarized. Finally, the development of SERS for POPs detection in the future are proposed.
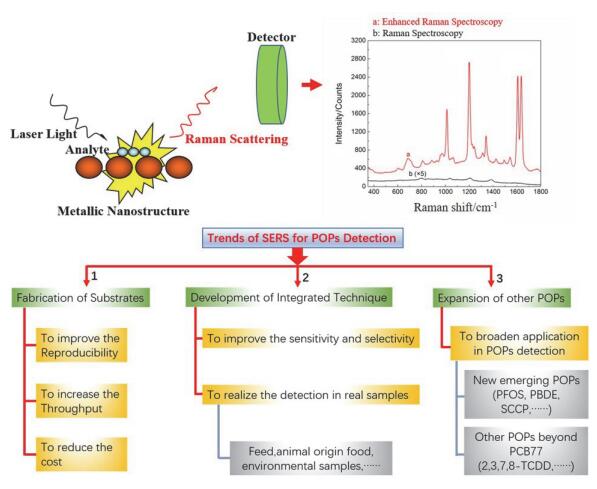
Jie Cheng, , Peilong Wang, , Xiaoou Su, . Recent Progress on the Detection of Dioxins Based on Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019 , 77(10) : 977 -983 . DOI: 10.6023/A19040139
| [1] | Cammilleri, G.; Calvaruso, E.; Pantano, L.; Cascio, G. L.; Randisi, B.; Macaluso, A.; Vazzana, M.; Caracappa, G.; Giangrosso, G.; Vella, A.; Ferrantelli, V . Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2997. |
| [2] | Adam, T. S. G.; Christoph, A.; Craig, A. B.; Barry, C. P . Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 414. |
| [3] | Jamieson, A. J.; Malkocs, T.; Piertney, S.; Fujii, T.; Zhang, Z. L . Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017,0051. |
| [4] | Matuszak, M.; Minorczyk, M.; Góralczyk, K.; Hernik, A.; Struciński, P.; Liszewska, M.; Czaja, K.; Korcz, W.; ?yczewska, M.; Ludwicki, J. K . Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2016, 67, 113. |
| [5] | Lv, F.; Gan, N.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Dong, Y . J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1525, 42. |
| [6] | United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2010, Method 1678C. |
| [7] | Xia, D.; Gao, L.; Zheng, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, G . Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 937, 160. |
| [8] | Dam, G. T.; Pussente, I. C.; Scholl, G.; Eppe, G.; Schaechtele, A.; Leeuwen, S. V . J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1477, 76. |
| [9] | Li, W.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Z. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 813. |
| [10] | Nebert, D. W. G.; Goujon, F.; Gielen, J. Nature 1972, 236, 107. |
| [11] | Commission Directive 2002/69/EC. Official J. Eur . Communities 2002a. |
| [12] | Levy, W.; Brena, B. M.; Henkelmann, B.; Bernh?ft, S.; Pirez, M.; González-Sapienza, G.; Schramm, K. W. Toxicol. in Vitro 2014, 28, 1036. |
| [13] | Crump, D.; Farhat, A.; Chiu, S.; Williams, K. L.; Jones, S. P.; Langlois, V. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3265. |
| [14] | Urbaniak, M.; Tygielska, A.; Krauze, K. Plos One 2016, 11, e0151756. |
| [15] | Ching, L.; Eric, B.; James, L.; Zhang, W. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1095. |
| [16] | Babikian, S.; Li, G. P.; Bachman, M. IEEE Transactions on Components 2017, 7, 846. |
| [17] | Yang, G.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, H.; Ping, X.; Bu, D. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 214, 152. |
| [18] | Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Xia, F.; Tian, D.; Hua, X.; Qiao, X.; Zhou, C . Electrochim. Acta 2016, 194, 413. |
| [19] | Moskovits, M. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 4408. |
| [20] | Ruchita, S.; Agrawal, Y. K. Vib. Spectrosc. 2011, 57, 163. |
| [21] | Liang, H. Y.; Li, Z. P.; Wang, W. Z.; Wu, Y. S.; Xu, H. X. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4614. |
| [22] | Wang, X. S.; Yang, D. P.; Huang, P.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Cui, D. X. Nanoscale 2012, 24, 7766. |
| [23] | Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Lu, Z. C.; Li, Q.; Yin, W. M.; Ding, F.; Han, H. Y. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2424. |
| [24] | Zhang, B.; Xu, P.; Xie, X. M.; Wei, H.; Li, Z. P.; Mack, N. H.; Han, X. J.; Xu, H. X.; Wang, H. L. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2495. |
| [25] | Panneerselvam, R.; Liu, G. K.; Wang, Y. H.; Liu, J. Y.; Ding, S. Y.; Li, J. F.; Wu, D. Y.; Tian, Z. Q. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10. |
| [26] | Xu, W. G.; Mao, N. N.; Zhang, J. Small 2013, 8, 1206. |
| [27] | Cheng, J.; Su, X. O.; Han, C. Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. L.; Zhang, S.; Xie, J. C . Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 2329. |
| [28] | Cheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. L.; Su, X. O.; Xie, J. C. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 157. |
| [29] | Yao, Y.; Wang, W.; Tian, K. Z.; Ingram, W. M.; Cheng, J.; Qu, L. L.; Li, H. T.; Han, C. Q. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 195, 165. |
| [30] | Cheng, J.; Su, X. O.; Yao, Y.; Han, C. Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. P . Plos one 2016, 11, e0154402. |
| [31] | Han, C. Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, X. M.; Huang, Y. W . Talanta 2014, 128, 293. |
| [32] | Patricia, T. B.; Niklaas, J. B.; Laura, R. L.; Jorge, P. J.; Luis, M. L. M.; Pablo, H. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16880. |
| [33] | Bonyár, A.; Csarnovics, I.; Veres, M.; Himics, L.; Csik, A.; Kámán, J.; Balázs, L.; K?kényesi, S. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 433. |
| [34] | Feng, J. Y.; Hu, Y. X.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 816. |
| [35] | Zhao, B. W.; Feng, S. L.; Hu, Y. X.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. N. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 366. |
| [36] | Fu, C. C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, L. Y.; Xu, S. P.; Xu, W. Q. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9555. |
| [37] | Sun, K.; Huang, Q.; Meng, G. W.; Lu, Y. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5723. |
| [38] | Lopez, A.; Lovato, F.; Oh, S. H.; Lai, Y. H.; Filbrun, S.; Driskell, E. A.; Driskell, J. D . Talanta 2016, 146, 388. |
| [39] | Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, J. Talanta 2016, 158, 322. |
| [40] | Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, Q.; Alfranca, G.; De la Fuente, J. M.; Chen, D.; Cui, D. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8169. |
| [41] | Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, J. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 923, 66. |
| [42] | Fang, F.; Qi, Y.; Lu, F.; Yang, L . Talanta 2016, 146, 351. |
| [43] | Tang, H. B.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z. L.; Zhu, C. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 218. |
| [44] | Li, Z. B.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Hu, X. Y.; He, X.; Tang, H. B.; Wang, Z. W.; Li, F. D. Small 2015, 40, 5452 |
| [45] | Bantz, K. C.; Haynes, C. L. Vib. Spectrosc. 2009, 50, 29. |
| [46] | Lu, Y. L.; Yao, G. H.; Sun, K. X.; Huang, Q. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21149. |
| [47] | Zhu, C.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z. B.; Huang, Z. L.; Wang, M. L.; Yuan, J. P. J. Mater Chem. 2012, 22, 2271. |
| [48] | Arocikia, J. D.; Parimaladevi, R.; Vasant, S. G.; Umadevi, M. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 29, 281. |
| [49] | Shanta, P. V.; Cheng, Q . ACS Sensors 2017, 6, 817. |
| [50] | Jency, D. A.; Umadevi, M.; Sathe, G. V. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 377. |
| [51] | Xu, W.; Meng, G. W., Huang, Q.; Hu, X. Y.; Huang, Z. L.; Tang, H. B.; Zhang, J. X. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 271, 125. |
| [52] | Lu, Y. L.; Huang, Q.; Meng, G. W.; Wu, L. J.; Zhang, J. J. Analyst 2014, 139, 3083. |
| [53] | Zhang, C. Y.; Hao, R.; Fu, Y. Z.; Zhang, H.; Moeendarbari, J. S.; Peckering, C. S.; Hao, Y. W.; Liu, Y. Q. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 49. |
| [54] | Rindzevicius, T.; Barten, J.; Vorobiev, M.; Schmidt, M. S.; Castillo, J. J.; Boisen, A. Vib. Spectrosc. 2017, 90, 1. |
| [55] | Jiao, C. L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y. X.; Xu, M. M.; Yao, J. L . Acta Chim. Sinica2018, 76, 526. |
| [55] | ( 焦岑蕾, 王炜, 刘娇, 袁亚仙, 徐敏敏, 姚建林, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 526. ) |
| [56] | Liu, J.; Sun, H. L.; Yin, L.; Yuan, Y. X.; Xu, M. M.; Yao, J. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 257. |
| [56] | ( 刘娇, 孙海龙, 印璐, 袁亚仙, 徐敏敏, 姚建林, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 257.) |
| [57] | Jia, F. L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Z . Acta Chim. Sinica2017, 75, 602. |
| [57] | ( 贾法龙, 刘娟, 张礼知, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 602.) |
| [58] | Commission Directive 277/2012/EC Official J. Eur . Communities 2012. |
| [59] | National standards of the People's Republic of China GB/T, 2762-2017. |
| [59] | ( 中华人民共和国国家标准 GB/T, 2762-2017.) |
| [60] | National standards of the People's Republic of China GB/T, 13078-2017. |
| [60] | ( 中华人民共和国国家标准 GB/T, 13078-2017.) |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |