

Unveiling the Synergistic Effect from Key Sensing Regions in Aerolysin-Based Single Oligonucleotide Detection
Received date: 2019-06-08
Online published: 2019-07-11
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21834001);Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(61871183)
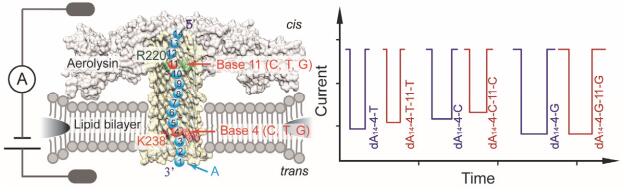
Nanopore technology are being developed for large areas in life science, not only in DNA sequencing and protein sequencing, but also in biomolecule detection, bio-interaction measurement and drug screening. Aerolysin is regarded as new powerful tool for oligonucleotide sensing and peptide sensing due to its high charged pore lumen. Applied a transmembrane potential with a pair of Ag/AgCl electrodes, the negatively charged oligonucleotides are driven into the aerolysin nanopore, inducing a series of ionic current blockages, which could distinguish the oligonucleotides with different length or single base variation. However, due to the lack of high-resolution structure of aerolysin nanopore, the mechanism of its high sensing capability is not clear, limiting the further applications of aerolysin. Recently, we presented two sensing regions inside aerolysin, R1 (near R220) and R2 (near K238), having huge influences on oligonucleotide sensing. Especially, the R1 is responsible for distinguished all 4 bases and 2 modified based in the mixture. However, the detailed mechanism of synergistic effect for these two regions in detection of single nucleotides is still unclear. Here, we use dA14-4-X, dA14-11-X, dA14-4-X-11-X (X=C, T, G) as probes to investigate the effects of base types on the sensing ability of R1 and R2. The results show that the A, C or T in R2 region did not change the sensing ability of R1 region, while G in R2 would hinder the base discrimination in R1 region. This may be caused by the large volume of G that would nearly fully occupy the R2 region and the stronger non-covalent interaction between G and R2 region, resulting in determining the residual current of the whole nanopore. Moreover, we evaluated the interaction between different bases with the sensing region. The results show that the interaction is independent with the volume of the bases, which is ordered by A>G>C>T, suggesting the interaction inside the aerolysin lumen is a considerable factor for its sensing capability. These results would guide us to directly design the mutant Aerolysin nanopore that aims for DNA sequencing and peptide sequencing.
Key words: nanopore; single-molecule interface; electro confinement; aerolysin; oligonucleotide
Mengyin Li, , Yilun Ying, , Yi-Tao Long, . Unveiling the Synergistic Effect from Key Sensing Regions in Aerolysin-Based Single Oligonucleotide Detection[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019 , 77(10) : 984 -988 . DOI: 10.6023/A19060202
| [1] | Kasianowicz, J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 13770. |
| [2] | Bayley, H.; Cremer, P. Nature 2001, 413, 226. |
| [3] | Cao, C.; Long, Y.-T. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 5, 331. |
| [4] | Ying, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, H.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 44. |
| [4] | ( 应佚伦, 张星, 刘钰, 薛梦竹, 李洪林, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 44.) |
| [5] | Gao, P.; Ma, Q.; Ding, D.; Wang, D.; Lou, X.; Zhai, T.; Xia, F. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4557. |
| [6] | Cao, C.; Liao, D.-F.; Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 734. |
| [6] | ( 曹婵, 廖冬芳, 应佚伦, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 734.) |
| [7] | Deamer, D.; Branton, D. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 817. |
| [8] | Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ying, Y.-L.; Liu, S.-C.; Long, Y.-T. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2017, 47, 1445. |
| [8] | ( 李巧, 林瑶, 应佚伦, 刘少创, 龙亿涛 , 中国科学: 化学, 2017, 47, 1445.) |
| [9] | Clarke, J.; Wu, H.-C.; Jayasinghe, L.; Patel, A.; Reid, S.; Bayley, H. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 265. |
| [10] | Manrao, E. A.; Derrington, I. M.; Laszlo, A. H.; Langford, K. W.; Hopper, M. K.; Gillgren, N.; Pavlenok, M.; Niederweis, M.; Gundlach, J. H. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 349. |
| [11] | Garalde, D. R.; Snell, E. A.; Jachimowicz, D.; Sipos, B.; Lloyd, J. H.; Bruce, M.; Pantic, N.; Admassu, T.; James, P.; Warland, A.; Jor-dan, M.; Ciccone, J.; Serra, S.; Keenan, J.; Martin, S.; McNeill, L.; Wallace, E. J.; Jayasinghe, L.; Wright, C.; Blasco, J.; Young, S.; Brocklebank, D.; Juul, S.; Clarke, J.; Heron, A. J.; Turner, D. J. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 201. |
| [12] | Sutherland, T. C.; Long, Y.-T.; Stefureac, R.-I.; Bediako-Amoa, I.; Kraatz, H.-B.; Lee, J. S . Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1273. |
| [13] | Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wu, X.-Y.; Long, Y.-T. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1766. |
| [13] | ( 杨洁, 李爽, 武雪原, 龙亿涛, 分析化学, 2017, 45, 1766.) |
| [14] | Pigue, F.; Ouldali, H.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Manivet, P.; Pelta, J.; Oukhaled, A. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 966. |
| [15] | Li, S.; Cao, C.; Yang, J.; Long, Y.-T. ChemElectroChem 2018, 6, 126. |
| [16] | Si, W.; Aksimentiev, A. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7091. |
| [17] | Hu, Z.; Du, J.; Ying, Y.; Peng, Y.; Cao, C.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1087. |
| [17] | ( 胡正利, 杜冀晖, 应佚伦, 彭岳一, 曹婵, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1087.) |
| [18] | Wanunu, M.; Dadosh, T.; Ray, V.; Jin, J.; McReynolds, L.; Drndi?, M. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 807. |
| [19] | Xi, D.; Shang, J.; Fan, E.; You, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10540. |
| [20] | Uram, J.; Ke, K.; Hunt, A.; Mayer, M. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 2339. |
| [21] | Jiang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Su, J.; Nie, J.; Cao, L.; Mao, L.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18739. |
| [22] | Stoddart, D.; Heron, A. J.; Mikhailova, E.; Maglia, G.; Bayley, H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 7702. |
| [23] | Cao, C.; Li, M.-Y.; Cirauqui, N.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Peraro, M.; Tian, H.; Long, Y.-T. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2823. |
| [24] | Maglia, G.; Restrepo, M.; Mikhailova, E.; Bayley, H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 19720. |
| [25] | Derrington, I.; Butler, T.; Collins, M.; Manrao, E.; Pavlenok, M.; Niederweis, M.; Gundlach, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 16060. |
| [26] | Duan, J.; Zhuo, S.; Yao, F.-J.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Kang, X.-F. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 44, 1801. |
| [26] | ( 段静, 卓莎, 姚付军, 张亚妮, 亢晓峰, 分析化学, 2016, 44, 1801.) |
| [27] | Gao, R.; Ying, Y.-L.; Yan, B.-Y.; Long, Y.-T. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4968. |
| [28] | Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.-C. Small 2019, 15, 1804078. |
| [29] | Ying, Y.-L.; Chao, C.; Hu, Y.-X.; Long, Y.-T. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 450. |
| [30] | Iacovache, I.; Carlo, S.; Cirauqui, N.; Peraro, M.; van der Goot, G.; Zuber, B. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12062. |
| [31] | Stefureac, R.; Long, Y.-T.; Kraatz, H. B.; Howard, P.; Lee, J. S. Biochemistry 2006, 60, 9172. |
| [32] | Cressiot, B.; Braselmann, E.; Oukhaled, A.; Elcock, A. H.; Pelta, J.; Clark, P. L. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9050. |
| [33] | Fennouri, A.; Daniel, R.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Auvray, L.; Pelta, J.; Bacri, L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8488. |
| [34] | Baaken, G.; Halimeh, I.; Bacri, L.; Pelta, J.; Oukhaled, A.; Behrends, J. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6443. |
| [35] | Cao, C.; Ying, Y.-L.; Hu, Z.-L.; Liao, D.-F.; Tian, H.; Long, Y.-T. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 713. |
| [36] | Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, M.-Y.; Qiu, H.; Cao, C.; Wang, M.-B.; Wu, X.-Y.; Huang, J.; Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7790. |
| [37] | Hu, Z.-L.; Li, Z.-Y.; Ying, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C.; Long, Y.-T.; Tian, H. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4268. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |