

Detection of Single c-di-AMP by an Aerolysin Nanopore
Received date: 2019-06-24
Online published: 2019-08-13
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21922405);Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(61871183);Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21834001);the National Ten Thousand Talent Program for Young Top-notch Talent
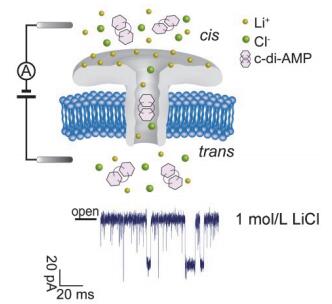
Cyclic di-AMP (c-di-AMP) is a ubiquitous second messenger in prokaryotic cells. c-di-AMP can not only effectively regulate various physiological processes such as cell growth, ion transport and cell wall metabolism balance, but also trigger type I interferon response to inspire the body's immune response. Nanopore-based single molecule detection technology is an emerging single molecule detection method which is currently applied to various fields since it has many advantages such as high speed, label-free, high sensitivity and low cost. Aerolysin is a robust biological nanopore with high temporal resolution and high current resolution, which has achieved single oligonucleotide detection, polysaccharide analysis and the studies of enzymolysis kinetics. Aerolysin nanopore is negatively-charged protein nanopore which has numerous negatively charged amino acid residues around its cis entrances. The electrostatic repulsion between the negatively charged c-di-AMP and negatively charged amino acid residues around the cis entrances prevents c-di-AMP entering the nanopore. In this study, 1.0 mol/L LiCl was used as electrolyte solution to facilitate aerolysin analysis of single c-di-AMP molecule. Each event can be characterized by two parameters, the current blockade, I/I0, and the blockade time, τoff. The blockades are classified into two populations as PI and PII. The PI events are assigned to c-di-AMP that bump into the pore and then diffuse away. PII events are assigned to traversing of c-di-AMP through the nanopore. Compared with potassium ions, lithium ion can be more effectively to associate with the negative charges on the aerolysin nanopore surface and reduce the electrostatic repulsion between the c-di-AMP molecule and the Aerolysin. The results showed that number of PI events in per minute was significantly increased in 1.0 mol/L LiCl. The number of PI events in per minute in LiCl is 30 times than that in KCl at 90 mV. Hence, Aerolysin nanopore can be used as an ultrasensitive single molecule sensor for cyclic dinucleotides.
Hongyan Niu, , Zhengli Hu, , Yilun Ying, , Yi-Tao Long, . Detection of Single c-di-AMP by an Aerolysin Nanopore[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019 , 77(10) : 989 -992 . DOI: 10.6023/A19060230
| [1] | Maelfait, J.; Rehwinkel, J. Immunity 2017, 46, 337. |
| [2] | Dey, B.; Dey, R. J.; Cheung, L. S.; Pokkali, S.; Guo, H.; Lee, J. H.; Bishai, W. R. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 401. |
| [3] | Corrigan, R. M.; Campeotto, I.; Jeganathan, T.; Roelofs, K. G.; Lee, V. T.; Gru?ndling, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 9084. |
| [4] | Underwood, A. J.; Zhang, Y.; Metzger, D. W.; Bai, G. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2014, 107, 58. |
| [5] | Bai, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Ding, X.; Eisele, L. E.; Bai, G. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35206. |
| [6] | Barker, J. R.; Koestler, B. J.; Carpenter, V. K.; Burdette, D. L.; Waters, C. M.; Vance, R. E.; Valdivia, R. H . mBio. 2013,e00018. |
| [7] | Kellenberger, C. A.; Wilson, S. C.; Sales-Lee, J.; Hammond, M. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4906. |
| [8] | Underwood, A. J.; Zhang, Y.; Metzger, D. W.; Bai, G. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 58. |
| [9] | Cao, C.; Long, Y.-T. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 5, 331. |
| [10] | Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ying, Y.-L.; Liu, S.-C.; Long, Y.-T. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2017, 47, 1445 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | ( 李巧, 林瑶, 应佚伦, 刘少创, 龙亿涛, 中国科学, 2017, 47, 1445.) |
| [11] | Jiang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Su, J.; Nie, J.; Cao, L.; Mao, L.; Jiang, L.; Guo, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18739. |
| [12] | Qiu, H.; Sarathy, A.; Schulten, K.; Leburton, J. P . npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2017, 1, 3. |
| [13] | Sha, J. J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. ACS Sensors 2017, 2, 506. |
| [14] | Kasianowicz, J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 13770. |
| [15] | Ying, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, H.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 44 (in Chinese). |
| [15] | ( 应佚伦, 张星, 刘钰, 薛梦竹, 李洪林, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 44.) |
| [16] | Ying, Y.-L.; Chao, C.; Hu, Y.-X.; Long, Y.-T. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 450. |
| [17] | Sha, J. J.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y. F.; Yang, Y. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1121 (in Chinese). |
| [17] | ( 沙菁絜, 徐冰, 陈云飞, 杨颜菁, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1121.) |
| [18] | Qiu, H.; Girdhar, A.; Schulten, K.; Leburton, J. P. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4482. |
| [19] | Parker, M. W.; Buckley, J. T.; Postma, J. P. M.; Tucker, A. D.; Leonard, K.; Pattus, F.; Tsernoglou, D . Nature 1994, 367, 292. |
| [20] | Cao, C.; Liao, D. F.; Ying, Y. L.; Long, Y. T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 734 (in Chinese). |
| [20] | ( 曹婵, 廖冬芳, 应佚伦, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 734.) |
| [21] | Cao, C.; Ying, Y. L.; Hu, Z. L.; Liao, D. F.; Tian, H.; Long, Y. T. Nat. Nanotech. 2016, 11, 713. |
| [22] | Fennouri, A.; Przybylski, C.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Bacri, L.; Auvray, L.; Daniel, R. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9672. |
| [23] | Hu, Z.; Du, J.; Ying, Y.; Peng, Y.; Cao, C.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1087 (in Chinese). |
| [23] | ( 胡正利, 杜冀晖, 应佚伦, 彭岳一, 曹婵, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1087.) |
| [24] | Xi, D.; Shang, J.; Fan, E.; You, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10540. |
| [25] | Cressiot, B.; Braselmann, E.; Oukhaled, A.; Elcock, A. H.; Pelta, J.; Clark, P. L. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9050. |
| [26] | Hu, Z. L.; Li, M. Y.; Liu, S. C.; Ying, Y. L.; Long, Y. T. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 354. |
| [27] | Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wu, X.-Y.; Long, Y.-T. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1766. |
| [28] | Iacovache, I.; De Carlo, S.; Cirauqui, N.; Dal Peraro, M.; Van Der Goot, F. G.; Zuber, B. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12062. |
| [29] | Kowalczyk, S. W.; Wells, D. B.; Aksimentiev, A.; Dekker, C. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1038. |
| [30] | Boukhet, M.; Piguet, F.; Ouldali, H.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Pelta, J.; Oukhaled, A. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18352. |
| [31] | Bhattacharya, S.; Muzard, J.; Payet, L.; Mathé, J.; Bockelmann, U.; Aksimentiev, A.; Viasnoff, V . J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4255. |
| [32] | Sutherland, T. C.; Long, Y. T.; Stefureac, R. I.; Bediako-Amoa, I.; Kraatz, H. B.; Lee, J. S. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1273. |
| [33] | Stefureac, R.; Long, Y. T.; Kraatz, H. B.; Howard, P.; Lee, J. S. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 9172. |
| [34] | Kasianowicz, J. J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. W. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 13770. |
| [35] | Corrigan, R. M.; Abbott, J. C.; Burhenne, H.; Kaever, V.; Gründling, A. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002217. |
| [36] | Corrigan, R. M.; Bowman, L.; Willis, A. R.; Kaever, V.; Gründling, A. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5826. |
| [37] | Dengler, V.; McCallum, N.; Kiefer, P.; Christen, P.; Patrignani, A.; Vorholt, J. A.; BergerB?chi, B.; Senn, M. M. PLoS One 2013, 8, e73512. |
| [38] | Cao, C.; Liao, D. F.; Yu, J.; Tian, H.; Long, Y. T . Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1901. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |