

CsPbI3 Perovskite Quantum Dots: Fine Purification and Highly Efficient Light-emitting Diodes
Received date: 2020-08-21
Online published: 2020-10-17
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51922049); the National Key Research and Development Program of China(2016YFB0401701); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(BK20180020); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(30920032102); the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
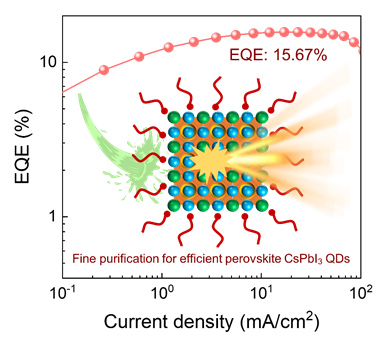
Perovskite quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) possess the characteristics of high color purity, precise color control, wide gamut, and solution processibility, which shows great prospects in displays and lightings. However, red CsPbI3 quantum dots (QDs) are prone to luminescence degradation due to the thermal non-equilibrium-induced phase transition and ligand loss during the purification process. The purification of CsPbI3 QDs is more difficult than that of CsPbBr3 QDs. Because the ligands on the surface of the quantum dots will be lost continuously during the purification process, resulting in aggregation and transformation toδ-CsPbI3 phase. Aiming at this problem, We prepared the CsPbI3 QDs through a hot-injection method at 180 ℃. The original solution of the perovskite QD also contains impurities such as octadecene solvent, oleic amine, and oleic acid ligand, which will seriously affect the photoelectric properties and destroy the film. So we used different flocculation solvents and dispersion solvents to collaboratively purify the QDs. At last, our work developed a mixed-solvent purification strategy with toluene and ethyl acetate, which can avoid the phase transition during the purification process and lead to pure cubic CsPbI3 QDs. But when we do not add the additional ligands in purification process, the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of QDs will be far less than 100%. In order to enhance the PLQY, a ligand compensation strategy of using oleylammonium iodide (OAmI) to control the surface state of QDs was proposed, which reduced the surface defects and solved the problem of luminescence quenching caused by ligand loss. We found that 400 μL OAmI enabled quantum dots to have both high PLQY of 70% and excellent electrical properties. Under electrically driven, the exciton recombination probability was significantly increased, and the CsPbI3- based QLED achieved a maximum luminance of 3090 cd/m2 and a maximum external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 15.67%. The proposed fine purification strategy of CsPbI3 QDs has an important guiding significance for the development of high-efficiency QD materials and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
Yan Li , Jinhang Li , Leimeng Xu , Jiawei Chen , Jizhong Song . CsPbI3 Perovskite Quantum Dots: Fine Purification and Highly Efficient Light-emitting Diodes[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021 , 79(1) : 126 -132 . DOI: 10.6023/A20080386
| [1] | Protesescu, L.; Yakunin, S.; Bodnarchuk, M.I.; Krieg, F.; Caputo, R.; Hendon, C.H.; Yang, R.X.; Walsh, A.; Kovalenko, M.V. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692. |
| [2] | Zhang, F.; Zhong, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.-G.; Hu, X.; Huang, H.; Han, J.; Zou, B.; Dong, Y. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4533. |
| [3] | Xu, L.; Li, J.; Cai, B.; Song, J.; Zhang, F.; Fang, T.; Zeng, H. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3902. |
| [4] | Fang, T.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, H.; Song, J. InfoMat 2019, 1, 211. |
| [5] | Xu, L.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, H.; Song, J. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 6, 100036. |
| [6] | Song, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Han, B.; Shan, Q.; Zeng, H. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800764. |
| [7] | Yang, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhu, C.; Chen, T.; Ma, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, L.; Guo, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 217 . (in Chinese) |
| [7] | 杨英, 林飞宇, 朱从潭, 陈甜, 马书鹏, 罗媛, 朱刘, 郭学益, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 217. |
| [8] | Song, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Xue, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, H. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4861. |
| [9] | Song, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Dong, Y.; Zeng, H. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7162. |
| [10] | Song, J.; Fang, T.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, F.; Han, B.; Shan, Q.; Zeng, H. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1805409. |
| [11] | Chiba, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ebe, H.; Hoshi, K.; Sato, J.; Sato, S.; Pu, Y.-J.; Ohisa, S.; Kido, J. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 681. |
| [12] | Fang, T.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Bai, S.; Song, J. Sci. Bull. 2020, |
| [13] | Pan, J.; Quan, L.N.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Murali, B.; Sarmah, S.P.; Yuan, M.; Sinatra, L.; Alyami, N.M.; Liu, J. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8718. |
| [14] | Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.-K.; Yuan, F.; Johnston, A.; Liu, Y.; Ma, D.; Choi, M.-J.; Chen, B.; Chekini, M.; Baek, S.-W. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 668. |
| [15] | Li, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Chen, J.; Xue, J.; Dong, Y.; Cai, B.; Shan, Q.; Han, B.; Zeng, H. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603885. |
| [16] | Hoshi, K.; Chiba, T.; Sato, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Ebe, H.; Ohisa, S.; Kido, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24607. |
| [17] | Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kan, M.; Zhao, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12345. |
| [18] | Steele, J.A.; Jin, H.; Dovgaliuk, I.; Berger, R.F.; Braeckevelt, T.; Yuan, H.; Martin, C.; Solano, E.; Lejaeghere, K.; Rogge, S.M. Science 2019, 365, 679. |
| [19] | Wang, Y.; Dar, M.I.; Ono, L.K.; Zhang, T.; Kan, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gao, X. Science 2019, 365, 591. |
| [20] | Swarnkar, A.; Marshall, A.R.; Sanehira, E.M.; Chernomordik, B.D.; Moore, D.T.; Christians, J.A.; Chakrabarti, T.; Luther, J.M. Science 2016, 354, 92. |
| [21] | Ling, X.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, J.; Shi, J.; Qian, Y.; Larson, B.W.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, C.; Li, F.; Shi, G. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900721. |
| [22] | Pan, J.; Shang, Y.; Yin, J.; De Bastiani, M.; Peng, W.; Dursun, I.; Sinatra, L.; El-Zohry, A.M.; Hedhili, M.N.; Emwas, A.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 140, 562. |
| [23] | Li, X.-L.; Cai, X.; Ali, M.U.; Su, S.-J.; Meng, H. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8063. |
| [24] | Acharya, K.P.; Titov, A.; Hyvonen, J.; Wang, C.; Tokarz, J.; Holloway, P.H. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14451. |
| [25] | Tang, Z.; Tanaka, S.; Ito, S.; Ikeda, S.; Taguchi, K.; Minemoto, T. Nano Energy 2016, 21, 51. |
| [26] | Ikhmayies, S.J.; Ahmad-Bitar, R.N. Renew. Energ. 2013, 49, 143. |
| [27] | Li, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Lan, S.; Li, X.; Song, J. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 1444. |
| [28] | Lu, M.; Guo, J.; Sun, S.; Lu, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Kershaw, S.V.; Yu, W.W.; Rogach, A.L.; Zhang, Y. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2829. |
| [29] | Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kershaw, S.V.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1552. |
| [30] | Zou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Bai, S.; Gao, F.; Sun, B. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 5, 100028. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |