

Temperature-Responsive Nanofibrous Membranes Fabricated by Subsurface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Controllable Oil/Water Separation
Received date: 2020-09-27
Online published: 2021-01-05
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(52065061); National Natural Science Foundation of China(51805514); National Natural Science Foundation of China(51705507); Bureau of International Cooperation, Chinese Academy of Sciences(121B62KYSB2017009); Key Research Projects of Frontier Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences(QYZDY-SSW-JSC013)
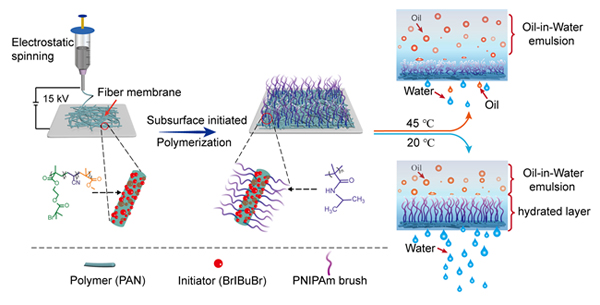
Subsurface-initiated polymerization is a novel modification strategy for the preparation of covalently embedded polymer brushes. It shows great advantages in the development of polymer brush-functionalized surface with high stability. In this work, the electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) based nanofibrous membrane was modified by subsurface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (sSI-ATRP). Covalently embedded poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) brushes were grafted from nanofibrous membranes to prepare temperature-responsive oil/water separation membrane (PAN-sg-PNIPAM). When the temperature is lower than the lower critical solution temperature (LCST), strong hydrogen bond interaction between PNIPAM chains and water molecules makes polymer chains fully extended. The membranes are hydrophilic and show very low underwater oil adhesion, resulting in a very high separation efficiency for oil-water emulsions (up to 98.7%). While the temperature is higher than LCST, PNIPAM chains dehydrate and collapse, the membranes become more hydrophobic and the underwater oil adhesion increases significantly. Thus, the separation efficiency dramatically decreases to as low as 9.1%. In addition, due to the high stability and durability of covalently embedded polymer brushes, the membrane can maintain a very stable permeation flux after reversible switch between 20 ℃ and 45 ℃ for 10 cycles under a pressure of 4 kPa. This study provides a novel method for the development of highly stable, durable and smart oi/water separation membranes.
Lele Li , Yangyang Xiang , Huan Liu , Shuanhong Ma , Bin Li , Zhengfeng Ma , Qiangbing Wei , Bo Yu , Feng Zhou . Temperature-Responsive Nanofibrous Membranes Fabricated by Subsurface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Controllable Oil/Water Separation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021 , 79(3) : 353 -360 . DOI: 10.6023/A20090449
| [1] | Stokstad, E. Science 2010, 328,1618. |
| [2] | Schnoor, J. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44,4833. |
| [3] | Wang, B.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44,336. |
| [4] | Shannon, M. A.; Bohn, P. W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J. G.; Marinas, B. J.; Mayes, A. M. Nature 2008, 452,301. |
| [5] | Pezeshki, S. R.; Hester, M. W.; Lin, Q.; Nyman, J. A. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 108,129. |
| [6] | Belkacem, M.; Matamoros, H.; Cabassud, C.; Aurelle, Y.; Cotteret, J. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 106,195. |
| [7] | Ma, Q.; Cheng, H.; Fane, A. G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Small 2016, 12,2186. |
| [8] | Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6,e101. |
| [9] | Li, W. T.; Yong, J. L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Fang, Y.; Hou, X. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sinica 2018, 34,456. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | ( 李文涛, 雍佳乐, 杨青, 陈烽, 方瑶, 侯洵, 物理化学学报, 2018, 34,456.) |
| [10] | Wu, F.; Pickett, K.; Panchal, A.; Liu, M.; Lvov, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11,25445. |
| [11] | Liang, B.; Zhang, G. Y.; Zhong, Z. X.; Tomoya, S.; Atsushi, H.; Su, Z. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362,126. |
| [12] | Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Fu, C.; Li, K.; Tao, L.; Feng, L.; Wei, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6,2026. |
| [13] | Parnell, A. J.; Martin, S. J.; Dang, C. C.; Geoghegan, M.; Jones, R. A. L.; Crook, C. J.; Howse, J. R.; Ryan, A. J. Polymer 2009, 50,1005. 7fcaa455-fafb-4d69-bee2-bb0ee2380bd6 |
| [14] | Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4,e8. |
| [15] | Zhou, Y. N.; Li, J. J.; Luo, Z. H. AIChE J. 2016, 62,1758. |
| [16] | Qu, D. H.; Wang, Q. C.; Zhang, Q. W.; Ma, X.; Tian, H. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115,7543. |
| [17] | Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22,19652. |
| [18] | Zhu, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3,1500683. |
| [19] | Xue, B.; Gao, L.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25,273. |
| [20] | Zhou, Y. N.; Li, J. J.; Luo, Z. H. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54,10714. |
| [21] | Kwon, G.; Kota, A. K.; Li, Y.; Sohani, A.; Mabry, J. M.; Tuteja, A. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24,3666. |
| [22] | Zheng, X.; Guo, Z.; Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3,1600461. |
| [23] | Kota, A. K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J. M.; Tuteja, A. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3,1025. |
| [24] | Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54,4527. |
| [25] | Li, B.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F. Acta Polym. Sinica 2016, 10, 1312. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | ( 李斌, 于波, 周峰, 高分子学报, 2016, 10, 1312.). |
| [26] | Li, B.; Yu, B.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, F. Prog. Chem. 2015, 27,146. (in Chinese) 81cf855d-0604-4ebb-a38c-81f9e75c9fce |
| [26] | ( 李斌, 于波, 叶谦, 周峰, 化学进展, 2015, 27,146.) 81cf855d-0604-4ebb-a38c-81f9e75c9fce |
| [27] | Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Fu, C.; Li, K.; Tao, L.; Feng, L.; Wei, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6,2026. |
| [28] | Yu, Q.; Cho, J.; Phanindhar, S.; Linnea, K. I.; Gabriel, P. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5,9295. |
| [29] | Wei, T.; Zhan, W. J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9,25767. |
| [30] | Wei, Q. B.; Cai, M. R.; Zhou, F. Acta Polym. Sinica 2012, 10,1103. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | ( 魏强兵, 蔡美荣, 周峰, 高分子学报, 2012, 10, 1103.). |
| [31] | Wu, Y.; Wei, Q. B.; Cai, M. R.; Zhou, F. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2,1400392. |
| [32] | Wei, Q. B.; Cai, M. R.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. M. Macromolecules 2013, 46,9368. |
| [33] | Zhang, L. B.; Zhang, Z. H.; Wang, P. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4,e8. |
| [34] | Tang, Z.; Akiyama, Y.; Okano, T. J. Polym. Sci.: Polym. Phys. 2014, 52,917. |
| [35] | Kim, Y. J.; Matsunaga, Y. T. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5,4307. |
| [36] | Jean, B.; Lee, L. T. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109,5162. |
| [37] | Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Yang, H.; Yao, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, R. Macromolecules 2011, 44,6227. |
| [38] | Sun, T.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43,357. |
| [39] | Li, J.; Zhu, L. T.; Luo, Z. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287,474. |
| [40] | Yu, Q.; Shivapooja, P.; Johnson, L. M.; Tizazu, G.; Leggett, G. J.; Lopez, G. P. Nanoscale 2013, 5,3632. |
| [41] | Xue, B. L.; Gao, L. C.; Hou, Y. P.; Liu, Z. W.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25,273. |
| [42] | Liu, Y.; Tas, S.; Zhang, K. H.; De Vos, W. M.; Ma, J. H.; Vancso, G. J. Macromolecules 2018, 51,8435. |
| [43] | Ma, Z. F.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, B.; Liu, Q. Z.; Zhou, F. Sci. Sinica Chim. 2018, 48,1611. (in Chinese) |
| [43] | ( 马正峰, 刘强, 吴杨, 李斌, 于波, 刘钦泽, 周峰, 中国科学:化学, 2018, 48, 1611.). |
| [44] | Liu, H.; Ma, Z. F.; Yang, W. F.; Pei, X. W.; Zhou, F. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112,146. |
| [45] | Li, L. L.; Xiang, Y. Y.; Yang, W. F.; Liu, Z. L.; Cai, M. R.; Ma, Z. F.; Wei, Q. B.; Pei, X. W.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 575,388. |
| [46] | Feng, H. Y.; Ma, Z. F.; Zhang, Y. J.; Liu, F. Z.; Ma, S. H.; Zhang, R.; Cai, M. R.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305,2000135. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |