

Accelerator Production of the Medical Isotope 211At and Monoclonal Antibody Labeling
Received date: 2021-06-11
Online published: 2021-08-17
Supported by
Special Fund for Scientific and Technological Innovation and Development of Gansu Province of China
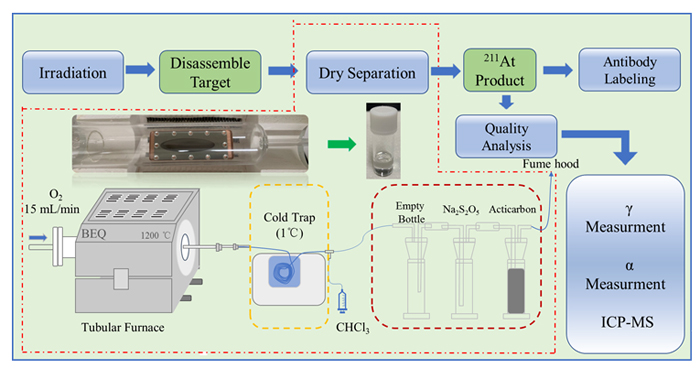
211At, with a half-life of 7.2 h, is an excellent radionuclide being investigated for use in targeted alpha therapy as the result of very high linear energy transfer. However, the production of 211At is limited by 210At, because 210At decays to produce long half-life (138.4 d) extremely toxic daughter 210Po. The production of 211At via 209Bi(α,2n) nuclear reaction and 210At via 209Bi(α,3n) nuclear reaction, as the energy of incident α-particle increases, the ratio of N(210At)/N(211At) increases. In this research, the α-particle is provided by the Chinese Accelerator Driven Sub-critical System (ADS) Front-end Demo Linac at Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The technical process of 211At produced was studied systematically, including accelerator irradiation, separation by dry distillation method, quality analysis, and monoclonal antibody labeling. The bismuth targets were irradiated with α-particle by 28.18, 28.34, 28.48 28.92 MeV, and the target chamber adopts an inclined target with water cooling to improve the cooling effect. The dry distillation separation was carried out at a high temperature of 850 ℃, oxygen as the carrier gas, chloroform and ethanol as eluent, and the chloroform solution containing 211At was blow dry with nitrogen. The results showed that the total recovery of dry distillation separation of 211At reached 78.53%. After separation, the quality analysis of 211At was performed using a high-purity Ge-detector, alpha energy spectrometer, and mass spectrometer. The obtained solid 211At had high specific activity, radionuclide purity and chemical purity, where the content of impurity elements Bi, Cu, Zn, and Al was less than 100 ng/GBq, and the ratio of N(210At)/N(211At) was less than 10–5 when the incident particle energy is below 28.2 MeV. Finally, the labeling of 211At-nimotuzumab was realized through N-succinimidyl-3-(trimethylstannyl)benzoate, and the labeling rate was 94.86%. Based on this research, a set of simple and efficient separation methods was established, which laid a good foundation for the subsequent production and application of 211At in China.
Key words: accelerator; medical isotope; dry distillation method; 211At; labeling
Desheng Chen , Weihao Liu , Qinggang Huang , Shiwei Cao , Wei Tian , Xiaojie Yin , Cunmin Tan , Jieru Wang , Jian Chu , Zimeng Jia , Nianwei Cheng , Ruiqin Gao , Xiaolei Wu , Zhi Qin , Fangli Fan , Jing Bai , Feize Li , Jiali Liao , Yuanyou Yang , Ning Liu . Accelerator Production of the Medical Isotope 211At and Monoclonal Antibody Labeling[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021 , 79(11) : 1376 -1384 . DOI: 10.6023/A21060266
| [1] | Nefedov V. D.; Norseev Y. V.; Toropova M. A.; Khalkin V. A. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1968, 37, 193. |
| [2] | Corson D. R.; Mackenzie K. R.; Segrè E. J. Phys. Rev. 1940, 58. |
| [3] | Yanokura M.; Kudo H.; Nakahara H.; Miyano K.; Ohya S.; Nitoh O. Nucl. Phys. A 1978, 299, 92. |
| [4] | Bäck T.,Alpha-radioimmunotherapy with At-211: Evaluations and Imaging on Normal Tissues and Tumors, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, 2011, pp. 8-12. |
| [5] | Bakr H. H. M.S. Thesis, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, 2014. |
| [6] | Brown I., Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part A 1986, 37, 789. |
| [7] | Morzenti S.; Bonardi M. L.; Groppi F.; Zona C.; Persico E.; Menapace E.; Alfassi Z. B. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2008, 276, 843. |
| [8] | Gagnon K.; Risler R.; Pal S.; Hamlin D.; Orzechowski J.; Pavan R.; Zeisler S.; Wilbur D. S. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2012, 55, 436. |
| [9] | Bochvarova M.; Do Kim T.; Dudova I.; Norseev Y. V.; Khalkin V. Radiokhimiya 1972, 14, 858. |
| [10] | Wang F. C.; Kang M. H.; Khalkin V. A. Radiokhimiya 1962, 4, 94. |
| [11] | Meyer G.-J.; Lambrecht R. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 1981, 18, 233. |
| [12] | Meyer G.; Lambrecht R. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1980, 31, 351. |
| [13] | Dasgupta M.; Hinde D.; Hagino K.; Moraes S.; Gomes P.; Anjos R.; Butt R.; Berriman A.; Carlin N.; Morton C. Phys. Rev. C 2002, 66, 041602. |
| [14] | Lindegren S.; Bäck T.; Jensen H. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2001, 55, 157. |
| [15] | Martin T. M., Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, 2018. |
| [16] | Wang Y.; Sato N.; Komori Y.; Yokokita T.; Mori D.; Usuda S.; Haba H. RIKEN Accel. Prog. Rep, 2017, 50, 262. |
| [17] | Zona C.; Bonardi M. L.; Groppi F.; Morzenti S.; Canella L.; Persico E.; Menapace E.; Alfassi Z. B.; Abbas K.; Holzwarth U. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2008, 276, 819. |
| [18] | Yordanov A.; Pozzi O.; Carlin S.; Akabani G.; Wieland B.; Zalutsky M. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2004, 262, 593. |
| [19] | O’hara M. J.; Krzysko A. J.; Niver C. M.; Morrison S. S.; Owsley S. L.; Hamlin D. K.; Dorman E. F.; Scott Wilbur D. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 122, 202. |
| [20] | Sundberg Å. L.; Almqvist Y.; Tolmachev V.; Carlsson J. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 727. |
| [21] | Willhauck M. J.; Samani B.-R. S.; Wolf I.; Senekowitsch- Schmidtke R.; Stark H.-J.; Meyer G. J.; Knapp W. H.; Göke B.; Morris J. C.; Spitzweg C. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1272. |
| [22] | Petrich T.; Korkmaz Z.; Krull D.; Frömke C.; Meyer G. J.; Knapp W. H. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 851. |
| [23] | Robinson M. K.; Shaller C.; Garmestani K.; Plascjak P. S.; Hodge K. M.; Yuan Q.-A.; Marks J. D.; Waldmann T. A.; Brechbiel M. W.; Adams G. P. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 875. |
| [24] | Aurlien E.; Larsen R.; Kvalheim G.; Bruland O. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1375. |
| [25] | Andersson H.; Elgqvist J.; Horvath G.; Hultborn R.; Jacobsson L.; Jensen H.; Karlsson B.; Lindegren S.; Palm S. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3914s. |
| [26] | Zalutsky M. R.; Pruszynski M. Curr. Radiopharm. 2011, 4, 177. |
| [27] | Makvandi M.; Dupis E.; Engle J. W.; Nortier F. M.; Fassbender M. E.; Simon S.; Birnbaum E. R.; Atcher R. W.; John K. D.; Rixe O. Targeted Oncol. 2018, 13, 189. |
| [28] | Kiess A.; Minn I.; Vaidyanathan G.; Hobbs R. F.; Josefsson A.; Shen C.; Brummet M.; Chen Y.; Choi J.; Koumarianou E. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1569. |
| [29] | Dziawer L.; Komiński P.; Mczyńska-Wielgosz S.; Pruszyński M.; Yczko M.; Ws B.; Celichowski G.; Grobelny J.; Jastrzbski J.; Bilewicz A. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41024. |
| [30] | Zalutsky M. R.; Reardon D. A.; Akabani G.; Coleman R. E.; Friedman A. H.; Friedman H. S.; Mclendon R. E.; Wong T. Z.; Bigner D. D. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 30. |
| [31] | Andersson H.; Cederkrantz E.; Bäck T.; Divgi C.; Elgqvist J.; Himmelman J.; Horvath G.; Jacobsson L.; Jensen H.; Lindegren S. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1153. |
| [32] | Liu N.; Jin J.; Zhang S.; Mo S.; Yang Y.; Wang J.; Zhou M. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2001, 247, 129. |
| [33] | Liu N.; Jin J.; Mo S.; Chen H.; Yu Y. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1998, 227, 187. |
| [34] | Liu N.; Jin J.; Zhang S.; Luo D.; Wang J.; Zhou M.; Luo L.; Wang F. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 1995, 36, 1105. |
| [35] | Tarasov O. B.; Bazin D. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2008, 266, 4657. |
| [36] | http://lise.nscl.msu.edu/lise.html. |
| [37] | Otuka N.; Takács S. Radiochim. Acta 2015, 103, 1. |
| [38] | Serov A.; Aksenov N.; Bozhikov G.; Eichler R.; Dressler R.; Lebedev V. Y.; Petrushkin O.; Piguet D.; Shishkin S.; Tereshatov E. Radiochim. Acta 2011, 99, 593. |
| [39] | Shinohara A.; Toyoshima A.; Yoshimura T.; Kanda A.CN 201880078835. 5, 2020. |
| [39] | ( 篠原厚, 丰岛厚史, 吉村崇, 神田晃充,CN 201880078835. 5, 2020.) |
| [40] | Demidov Y.; Zaitsevskii A. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 691, 126. |
| [41] | Sun R.; Kang X.; Wang L.; Xu Y. J. Univ. South China (Sci. Technol.), 2017, 31, 37. (in Chinese) |
| [41] | ( 孙荣忠, 康玺, 王郦彬, 许艳婷, 南华大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 31, 37.) |
| [42] | Vennart J. J. Radiol. Prot. 1991, 11, 199. |
| [43] | Liu W.; Ma H.; Tang Y.; Chen Q.; Peng S.; Yang J.; Liao J.; Yang Y.; Li Q.; Liu N. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 316, 451. |
| [44] | Liu N.; Jin J.; Zhang S.; Mo Shang.; Yang Y.; Wang J.; Zhou M.; J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2001, 247, 129. |
| [45] | Ning L.; Yang Y.; Zan L.; Liao J.; Jin J. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2007, 272, 85. |
| [46] | Yang Y.; Lin R.; Ning L.; Liao J.; Jin J. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 288. |
| [47] | Glockler G. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 828. |
| [48] | Lin J. L.; Bent B. E. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 8529. |
| [49] | Li J. L., Laboratory γ Measurement and Analysis of Lenergy Spectrum, China Communications Press, Beijing, 2014, pp. 88-93. (in Chinese) |
| [49] | ( 李君利, 实验室γ能谱测量与分析, 人民交通出版社, 北京, 2014, pp. 88-93.) |
| [50] | Zvara I. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1996, 204, 123. |
| [51] | Zvára I., The Inorganic Radiochemistry of Heavy Elements: Methods for Studying Gaseous Compounds, Springer Science & Business Media, Heidelberg, 2008, pp. 87-118. |
| [52] | Zvára I. Radiochim. Acta 1985, 38, 95. |
| [53] | Lin M.; Qin Z.; Guo J.; Zhang L.; Ding H.; Fan F.; Bai J.; Lei F.; Wu X.; Li X. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2009, 31, 28. (in Chinese) |
| [53] | ( 林茂盛, 秦芝, 郭俊盛, 张丽娜, 丁华杰, 范芳丽, 白静, 雷富安, 吴晓蕾, 李小飞, 核化学与放射化学, 2009, 31, 28.) |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |