

Electron/ion Conductor Double-coated LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Li-ion Battery Cathode Material and Its Electrochemical Performance
Received date: 2021-12-30
Online published: 2022-01-24
Supported by
Xiamen Science and Technology Project(3502Z20201012)
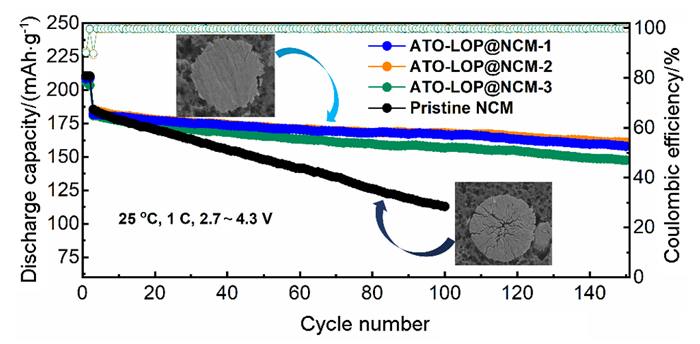
The Ni-rich layered cathode material LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 presents a high specific capacity and relatively low cost, however, the inherent structure instability during the electrochemical cycling process hinders its application widely. Universally, the strategy of surface coating can be used to improve the structural stability of the material and then improve its electrochemical performance. This work combines the high-speed solid-phase coating method and the high-temperature sintering method to coat the electronic conductor antimony tin oxide and lithium-ion conductor lithium metaphosphate on the surface of the LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material, respectively. The electron/ion conductor double coating layer forms a charge conversion and transport channel on the surface of the LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2. The electronic conductivity of the double-coated LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material increased from 2.17×10-3 Ѕ•cm-1 to 1.02×10-2 Ѕ•cm-1, and the diffusion coefficient of lithium-ion also increased from 7.05×10-9 cm2•s-1 to 2.88×10-8 cm2•s-1. At the same time, due to strong P—O bonds and stable metal oxides, the double-coating layer on the surface of the LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material can effectively restrain the irreversible phase transitions, and it also can inhibit the interfacial reactions under high electrode potential. The electrochemical performance test demonstrated that the cyclability and rate performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material improved due to surface modification. The cathode assembled with double-coated LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material can maintain a reversible capacity of 161.1 mAh•g-1 after 150 cycles at 1 C (after being activated at 0.1 C for two cycles, 1 C=180 mA•g-1) during 2.7~4.3 V (vs. Li/Li+), with a capacity retention of 87.1%. This coated LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 material also displays a specific capacity as high as 133 mAh•g-1 at 10 C. In comparison, the pristine LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 delivers a capacity of only 113 mAh•g-1 after 100 cycles and a reversible capacity retention rate of less than 60% (a decay rate of 0.4% per cycle).
Shouxiao Chen , Junke Liu , Weichen Zheng , Guozhen Wei , Yao Zhou , Juntao Li . Electron/ion Conductor Double-coated LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Li-ion Battery Cathode Material and Its Electrochemical Performance[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022 , 80(4) : 485 -493 . DOI: 10.6023/A21120600
| [1] | Chen, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 127. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | (陈军, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 127.) |
| [2] | Goodenough, J. B.; Kim, Y. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 587. |
| [3] | Whittingham, M. S. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4271. |
| [4] | Zhou, H.; Xin, F.; Pei, B.; Whittingham, M. S. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1902. |
| [5] | Xu, P.; Zhang, X.-H.; Ma, E.; Rao, F.; Liu, C-W.; Yao, P.-F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.-W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1073. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | (徐平, 张西华, 马恩, 饶富, 刘春伟, 姚沛帆, 孙峙, 王景伟, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1073.) |
| [6] | Xia, L.; Yu, L.-P.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1183. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | (夏兰, 余林颇, 胡笛, 陈政, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1183.) |
| [7] | Yang, X.; Lin, M.; Zheng, G.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, F.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, N.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004664. |
| [8] | Deng, B.-W.; Sun, D.-M.; Wan, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Zhai, M. Z.; Peng, G.-C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 259. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | (邓邦为, 孙大明, 万琦, 王昊, 陈滔, 李璇, 瞿美臻, 彭工厂, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 259.) |
| [9] | Qiu, K.; Yan, M.-X.; Zhao, S.-W.; An, S.-L.; Wang, W.; Jia, G.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1146. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | (邱凯, 严铭霞, 赵守旺, 安胜利, 王玮, 贾桂霄, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1146.) |
| [10] | Xin, F.; Zhou, H.; Zong, Y.; Zuba, M.; Chen, Y.; Chernova, N. A.; Bai, J.; Pei, B.; Goel, A.; Rana, J.; Wang, F.; An, K.; Piper, L. F. J.; Zhou, G.; Whittingham, M. S. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1377. |
| [11] | Xiao, Y.; Miara, L. J.; Wang, Y.; Ceder, G. Joule 2019, 3, 1252. |
| [12] | Lin, H.-C.; Yang, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 104. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | (林和成, 杨勇, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 104.) |
| [13] | Liu, J.-D.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Liu, J.-X.; Li, J.-H.; Qiu, X.-G.; Cheng, F.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1426. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | (刘九鼎, 张宇栋, 刘俊祥, 李金翰, 邱晓光, 程方益, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1426.) |
| [14] | Ren, X.-Q.; Li, D.-L.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhao, K.; Kong, X.-Z.; Li, T.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1268. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | (任旭强, 李东林, 赵珍珍, 陈光琦, 赵坤, 孔祥泽, 李童心, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1268) |
| [15] | Liu, H.-H.; Zhang, J.; Lou, Y.-W.; Xia, B.-J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1055. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | (刘浩涵, 张建, 娄豫皖, 夏保佳, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1055.) |
| [16] | Kong, J.-Z.; Ren, C.; Tai, G.-A.; Zhang, X.; Li, A.-D.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Zhou, F. J. Power Sources 2014, 266, 433. |
| [17] | Myung, S.-T.; Izumi, K.; Komaba, S.; Yashiro, H.; Bang, H. J.; Sun, Y.-K.; Kumagai, N. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4061. |
| [18] | Lu, Y.; Wang, J.-F.; Xie, H.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1058. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | (陆远, 王继芬, 谢华清, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1058.) |
| [19] | Li, T.-X.; Li, D.-L.; Zhang, Q.-B.; Gao, J.-H.; Kong, X.-Z.; Fan, X.-Y.; Gou, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 678. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | (李童心, 李东林, 张清波, 高建行, 孔祥泽, 樊小勇, 苟蕾, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 678.) |
| [20] | Chang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, H.-Z.; Deng, H.; Zhu, X.-Y.; He, P.; Zhou, H.-S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 139. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | (常智, 乔羽, 杨慧军, 邓瀚, 朱星宇, 何平, 周豪慎, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 139.) |
| [21] | Liang, Q.-M.; Guo, Y.-J.; Guo, J.-M.; Xiang, M.-W.; Liu, X.-F.; Bai, W.; Ning, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1526. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | (梁其梅, 郭昱娇, 郭俊明, 向明武, 刘晓芳, 白玮, 宁平, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1526.) |
| [22] | Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, R.; Yang, L.; Zhu, M. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600256. |
| [23] | Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Sari, H. M. K.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Qin, J.; Cao, B.; Xiao, W.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Kou, L.; Tian, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, C.; Sun, X. Nano Energy, 2020, 77, 105034. |
| [24] | Wang, C.-W.; Zhou, Y.; You, J.-H.; Chen, J.-D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.-J.; Shi, C.-G.; Zhang, W.-D.; Zou, M.-H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.-T.; Zeng, L.-Y.; Huang, L.; Sun, S.-G. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 2593. |
| [25] | Griffith, K. J.; Wiaderek, K. M.; Cibin, G.; Marbella, L. E.; Grey, C. P. Nature 2018, 559, 556. |
| [26] | Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, Q.; Yu, S.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ma, L.; Liu, T.; Li, M.; Lin, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xing, X.; Choi, Y.; Gao, L.; Cho, H. S.; An, K.; Feng, J.; Kostecki, R.; Amine, K.; Wu, T.; Lu, J.; Xin, H. L.; Ong, S. P.; Liu, P. Nature 2020, 585, 63. |
| [27] | Guo, B.; Yu, X.; Sun, X.-G.; Chi, M.; Qiao, Z.-A.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.-S.; Yang, X.-Q.; Goodenoughe, J. B.; Dai, S. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2220. |
| [28] | Ryu, H.-H.; Park, K.-J.; Yoon, D. R.; Aishova, A.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y.-K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902698. |
| [29] | Zhou, A.; Dai, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, M.; Li, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34123. |
| [30] | Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; An, Y.; Song, S.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Su, F.; Chen, C.-M.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z.-S.; Ma, Y. J. Power Sources 2021, 488, 229454. |
| [31] | Li, J.; Manthiram, A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902731. |
| [32] | Zou, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Jia, H.; Zheng, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wang, C. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2433. |
| [33] | Das, H.; Urban, A.; Huang, W.; Ceder, G. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7840. |
| [34] | Liu, W.; Oh, P.; Liu, X.; Lee, M. J.; Cho, W.; Chae, S.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4440. |
| [35] | Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Huq, A.; Misture, S. T.; Zhang, B.; Guo, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K.; Pan, F.; Bai, J.; Wang, F. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601266. |
| [36] | Kim, U. H.; Ryu, H. H.; Kim, J. H.; Mücke, R.; Kaghazchi, P.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y. K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803902. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |