

Progresses in the Study of Low-Energy Ion-molecule Reaction Dynamics※
Received date: 2021-12-25
Online published: 2022-02-24
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22003062); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21625301)
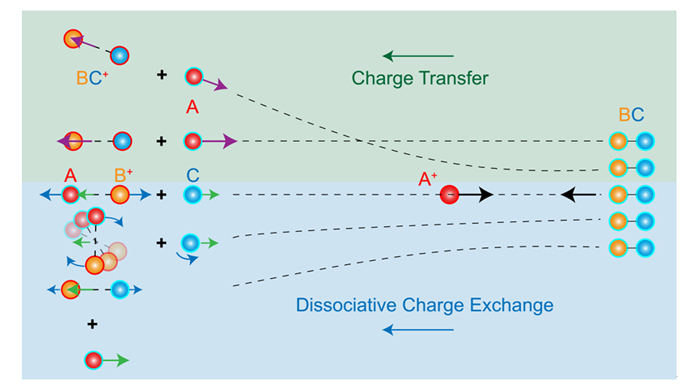
Ion-molecule reaction is one of the most fundamental processes in the Earth and other planets' atmosphere, interstellar space and combustion. Basic physical chemistry processes such as charge transfer and energy transfer are frequently involved in the low-energy (several eV) ion-molecule reactions. In recent decades, the experimental study of low-energy ion-molecule reaction dynamics is highly benefit from the introduction of velocity map imaging method, but some dynamics mechanisms remain to be validated. Based on our own cross-beam ion velocity imaging apparatus, we have recently realized an efficient measurement of three-dimensional ion velocity images for multiple products by using a delay line anode detector, indicating the much higher efficiency. Upon above technique improvement, more details about the charge transfer reactions between Ar+ and small molecules have been revealed. Here we summarize and emphasize the dynamics differences among this process, photoionization and Marcus theoretical model. Meanwhile, we obtained stereodynamic characteristics of the dissociative charge transfer reactions of Ar+ with O2 and CO. Moreover, comparison between the charge transfer only and dissociative charge transfer reaction indicates that the latter is not a subsequent even of the former, namely, these two processes may have completely different pathways. We also present a perspective about the experimental techniques those are potentially applicable and some interesting topics in the future.
Jie Hu , Shanxi Tian . Progresses in the Study of Low-Energy Ion-molecule Reaction Dynamics※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022 , 80(4) : 535 -541 . DOI: 10.6023/A21120584
| [1] | Larsson, M.; Geppert, W. D.; Nyman, G. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 066901. |
| [2] | Semo, N. M.; Koski, W. S. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5320. |
| [3] | Williams, K. L.; Martin, I. T.; Fisher, E. R. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 13, 518. |
| [4] | Ng, C.-Y.; Baer, M. State-selected and State-to-State Ion-Molecule Reaction Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1992. |
| [5] | Marcus, R.; Sutin, N. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 811, 265. |
| [6] | McDaniel, E. W.; Barnes, W. S.; Martin, D. W. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1962, 33, 2. |
| [7] | Baldeschwieler, J. D.; Woodgate, S. S. Acc. Chem. Res. 1971, 4, 114. |
| [8] | Teloy, E.; Gerlich, D. Chem. Phys. 1974, 4, 417. |
| [9] | Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Xie, J. C.; He, M. M.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1346. |
| [10] | Hu, J.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Xie, J. C.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 7127. |
| [11] | Xie, J.; Otto, R.; Mikosch, J.; Zhang, J.; Wester, R.; Hase, W. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2960. |
| [12] | Meyer, J.; Wester, R. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2017, 68, 333. |
| [13] | Wester, R. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 1. |
| [14] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 6122. |
| [15] | Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Ma, Y. S.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 9171. |
| [16] | Wu, C. X.; Hu, J.; He, M. M.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 8536. |
| [17] | Wu, C. X.; Hu, J.; He, M. M.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Tian, S. X. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4640. |
| [18] | He, M. M.; Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 3358. |
| [19] | Hu, J.; Xie, J. C.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 234303. |
| [20] | Zhi, Y. Y.; Hu, J.; Xie, J. C.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 2573. |
| [21] | Trippel, S.; Stei, M.; Cox, J. A.; Wester, R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 163201 |
| [22] | Michaelsen, T.; Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Meyer, J.; Parker, D. H.; Wester, R. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 013940. |
| [23] | Michaelsen, T.; Gstir, T.; Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Ayasli, A.; Meyer, J.; Wester, R. Mol. Phys. 2021, 119, e1815885. |
| [24] | Carrascosa, E.; Kainz, M. A.; Stei, M.; Wester, R. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2742. |
| [25] | Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Kaiser, A.; Meyer, J.; Michaelsen, T.; Czakó, G.; Hase, W. L.; Wester, R. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 438, 175. |
| [26] | Vera, M. H.; Wester, R.; Gianturco, F. A. J. Phys. B 2017, 51, 014004. |
| [27] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 204305. |
| [28] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 154312. |
| [29] | Pei, L. S.; Carrascosa, E.; Yang, N.; Falcinelli, S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1684. |
| [30] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 377, 93. |
| [31] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 084304. |
| [32] | Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 227. |
| [33] | Herman, Z. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 212, 413. |
| [34] | Reichert, E. L.; Thurau, G.; Weisshaar, J. C. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 653. |
| [35] | Mikosch, J.; Fruhling, U.; Trippel, S.; Schwalm, D.; Weidemuller, M.; Wester, R. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 2990. |
| [36] | Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 066104. |
| [37] | Azriel, V. M.; Rusin, L.Y.; Sevryuk, M. B. Theor. Chim. Acta 1993, 87, 195. |
| [38] | Filsinger, F.; Meijer, G.; Stapelfeldt, H.; Chapman, H. N.; Küpper, J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2076. |
| [39] | Zhang, G.; Guan, L.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, M.; Gao, H. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 34, 71. |
| [40] | Kilaj, A.; Wang, J.; Straňák, P.; Schwilk, M.; Rivero, U.; Xu, L.; Lilienfeld, O. A.; Küpper, J.; Willitsch, S. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6047. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |