

Synthesis and Characterizations of 15N Isotope Labeling Metal Nitride Clusterfullerene
Received date: 2022-02-25
Online published: 2022-04-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(51832008); National Natural Science Foundation of China(52022098); National Natural Science Foundation of China(51972309); Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Y201910); Opening Project of PCOSS, Xiamen University(201928); Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province(201901D111109)
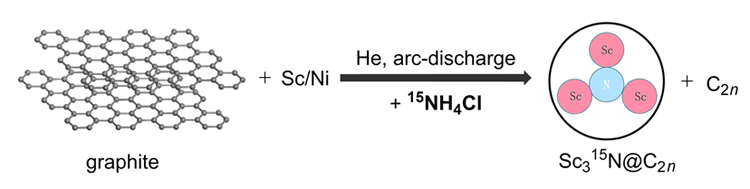
In this work, we prepared the 15N-labeled metal nitride clusterfullerene by arc discharge method. In the synthetic process, scandium metal, graphite powder, and 15NH4Cl were atomized by arc discharge method under helium atmosphere with 15NH4Cl as solid nitrogen source, and finally Sc315N@C80 and Sc315N@C78 were obtained. Sc315N@C80 was isolated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and characterized by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry, UV-Vis absorption spectra, and 13C NMR. These results demonstrate the successful labeling of 15N and also illustrate that the prepared Sc315N@C80 has an Ih-C80 cage. The prepared 15N-labeled metal nitride clusterfullerenes contain more than 98% of the 15N isotope, which will expand the application fields of metallofullerene materials such as isotope tracing. In detail, clusterfullerenes were separated from hollow fullerenes by multistage HPLC. And then pure samples of Sc315N@C80-Ih and Sc315N@C78 were obtained. Mass spectrometry was used to characterize the molecular weight of Sc315N@C80-Ih and Sc315N@C78. According to the isotopic distributions of Sc315N@C80-Ih and Sc315N@C78 in mass spectra, their molecular weight values have increased by 1 compared to those of unlabeled Sc3N@C80-Ih and Sc3N@C78, revealing the successful labeling of isotope 15N on the Sc3N cluster. At the same time, we added Y3N@C80 as an internal standard into Sc315N@C80-Ih and Sc315N@C78 samples to further confirm the labeling of 15N atom on the Sc3N cluster. Moreover, the UV-Vis absorption spectrum showed that the absorption of Sc315N@C80 begins at 820 nm, and the lowest energy transition was observed at 735 nm. Based on the absorption onset, the optical energy gap of Sc315N@C80 can be calculated, which is about 1.51 eV. According to the reported UV-Vis absorption spectra in literature, the carbon cage of the isolated Sc315N@C80 can be characterized as Ih-symmetry. The carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (13C NMR) was executed by dissolving Sc315N@C80 in 1,2-dichlorobenzene-d4 at 293 K. The 13C NMR spectrum consists of only two NMR lines of chemical shifts of 143.60 and 136.37 with an intensity ratio of 3:1. This is a characteristic 13C NMR spectrum of the Ih-symmetric C80 carbon cage.
Ling Qiu , Jiayi Liang , Zhuxia Zhang , Taishan Wang . Synthesis and Characterizations of 15N Isotope Labeling Metal Nitride Clusterfullerene[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022 , 80(7) : 874 -878 . DOI: 10.6023/A22020087
| [1] | Yang, S. F.; Liu, F. P.; Chen, C. B.; Jiao, M. Z.; Wei, T. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11822. |
| [2] | Dong, W.; Nie, M. S.; Lian, Y. F. Acta. Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 453. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | (董薇, 聂梦思, 廉永福, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 453.) |
| [3] | Shi, J. J.; Hu, Z. Q.; Yang, Y. H.; Bu, Y. X.; Shi, Z. J. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin. 2019, 37, 1907077. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | (施俊杰, 胡子琦, 杨逸豪, 步宇翔, 施祖进, 物理化学学报, 2019, 37, 1907077.) |
| [4] | Chaur, M. N.; Melin, F.; Ortiz, A. L.; Echegoyen, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7514. |
| [5] | Dunsch, L.; Yang, S. F. Small 2007, 3, 1298. |
| [6] | Dunsch, L.; Yang, S. F. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 3067. |
| [7] | Lu, X.; Feng, L.; Akasaka, T.; Nagase, S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7723. |
| [8] | Rodriguez-Fortea, A.; Balch, A. L.; Poblet, J. M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3551. |
| [9] | Liu, T. T.; Wang, H. S.; Zhang, M. X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X. Polym. Bull. 2019, (4), 1. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | (刘婷婷, 王华山, 张明秀, 王美, 陈醒, 高分子通报, 2019, (4), 1.) |
| [10] | Ruan, L. F.; Chang, X. L.; Sun, B. Y.; Guo, C. B.; Dong, J. Q.; Yang, S. T.; Gao, X. F.; Zhao, Y. L.; Yang, M. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 905. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | (阮龙飞, 常雪灵, 孙宝云, 郭翠彬, 董金泉, 杨胜韬, 高兴发, 赵宇亮, 杨敏, 科学通报, 2014, 59, 905.) |
| [11] | Bhate, M. P.; Wylie, B. J.; Thompson, A.; Tian, L.; Nimigean, C.; McDermott, A. E. Protein. Expres. Purif. 2013, 91, 119. |
| [12] | Ruhland, K.; Frenzel, R.; Horny, R.; Nizamutdinova, A.; van Wüllen, L.; Moosburger-Will, J.; Horn, S. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 298. |
| [13] | Stevenson, S.; Rice, G.; Glass, T.; Harich, K.; Cromer, F.; Jordan, M. R.; Craft, J.; Hadju, E.; Bible, R.; Olmstead, M. M.; Maitra, K.; Fisher, A. J.; Balch, A. L.; Dorn, H. C. Nature 1999, 401, 55. |
| [14] | Dunsch, L.; Krause, M.; Noack, J.; Georgi, P. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2004, 65, 309. |
| [15] | Jiao, M. Z.; Zhang, W. F.; Xu, Y.; Wei, T.; Chen, C. B.; Liu, F. P.; Yang, S. F. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2666. |
| [16] | Liu, F. P.; Guan, J.; Wei, T.; Wang, S.; Jiao, M. Z.; Yang, S. F. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 3814. |
| [17] | Lu, Y. X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Nie, M. Z.; Wang, C. R.; Wang, T. S. Sci. China. Chem. 2020, 64, 29. |
| [18] | Popov, A. A.; Yang, S. F.; Dunsch, L. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5989. |
| [19] | Popov, A. A.; Avdoshenko, S. M.; Pendás, A. M.; Dunsch, L. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8031. |
| [20] | Krause, M.; Dunsch, L. ChemPhysChem 2004, 5, 1445. |
| [21] | Wang, T. S.; Chen, N.; Xiang, J. F.; Li, B.; Wu, J. Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, L.; Tan, K.; Shu, C. Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16646. |
| [22] | Wang, T. S.; Feng, L.; Wu, J. Y.; Xu, W.; Xiang, J. F.; Tan, K.; Ma, Y. H.; Zheng, J. P.; Jiang, L.; Lu, X.; Shu, C. Y.; Wang, C. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16362. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |