

Small Molecule Degraders Targeting the SHP2E76A Mutant Effectively Inhibiting the Proliferation of Wild-type and Mutant SHP2 Dependent Tumor Cells
Received date: 2023-05-16
Online published: 2023-06-07
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(81761128022); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21772214); National Science & Technology Major Project “Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program”, China(2018ZX09711002-006-004)
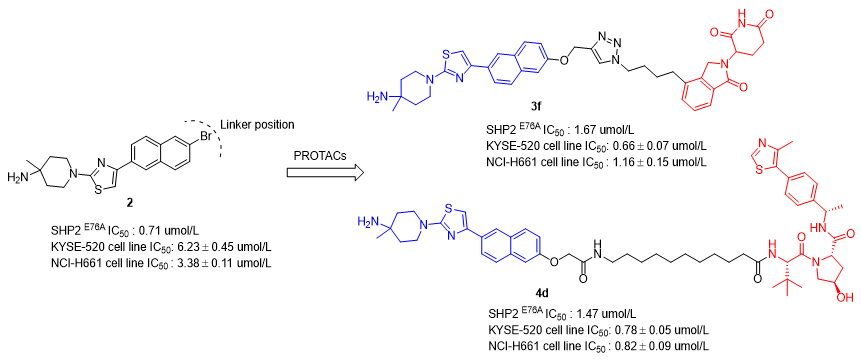
Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP2) is a non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase encoded by the Ptpn11 gene. SHP2 regulates cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis via modulating various signaling pathways, such as RAS/ERK signaling pathway, and participates in the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway governing immune surveillance, thus has been recognized as a breakthrough antitumor therapeutic target. By stabilizing the inactive closed conformation of SHP2, allosteric inhibitors have overcome the druggability issues and advanced to clinical trials. However, the gain-of-function mutation (GOF) of the Ptpn11 gene renders SHP2 in a pathological active conformation, causing a range of developmental disorders and tumors. Overactivated SHP2 mutants undergo structural and functional changes, conferring resistance to SHP2 wild-type allosteric inhibitors. Therefore, developing novel therapeutic modality that effectively inhibits pathogenic SHP2 mutants has become an urgent need for the treatment of SHP2 related diseases. Herein, we report the design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel SHP2 small molecule degraders based on PROTACs (proteolysis-targeting chimeras) technology by employing an allosteric inhibitor 2 targeting SHP2-activated mutant as the warhead. These SHP2E76A PROTACs have shown strong inhibitory activities in both enzyme and cell proliferation. Notably, the lead compounds 3f and 4d exhibit potent antiproliferative activities against both the wild-type SHP2 dependent human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell line KYSE-520 and the mutant SHP2N58S human large-cell lung carcinoma cell line NCI-H661, with an improvement by 5 to 10-fold compared to the positive control 2. This study provides a new therapeutic intervention strategy for treating developmental disorders and tumors caused by SHP2 mutation or activation.
Jiao Kong , Lin Du , Xiangyang Li , Jidong Zhu , Ya-Qiu Long . Small Molecule Degraders Targeting the SHP2E76A Mutant Effectively Inhibiting the Proliferation of Wild-type and Mutant SHP2 Dependent Tumor Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023 , 81(9) : 1120 -1128 . DOI: 10.6023/A23050229
| [1] | Hof, P.; Pluskey, S.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Eck, M. J.; Shoelson, S. E. Cell 1998, 92, 441. |
| [2] | Grossmann, K. S.; Rosário, M.; Birchmeier, C.; Birchmeier, W. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 106, 53. |
| [3] | (a) Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2015, 19, 2075; |
| [3] | (b) Shi, Z. Q.; Yu, D. H.; Park, M.; Marshall, M.; Feng, G. S. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1526; |
| [3] | (c) You, M.; Yu, D. H.; Feng, G. S. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 2416; |
| [3] | (d) Wu, C. J.; O'Rourke, D. M.; Feng, G. S.; Johnson, G. R.; Wang, Q.; Greene, M. I. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6018; |
| [3] | (e) Tartaglia, M.; Gelb, B. D. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 48, 81; |
| [3] | (f) Kong, J.; Long, Y. Q. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 246. |
| [4] | Mullard, A. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 847. |
| [5] | (a) Araki, T.; Mohi, M. G.; Ismat, F. A.; Bronson, R. T.; Williams, I. R.; Kutok, J. L.; Yang, W.; Pao, L. I.; Gilliland, D. G.; Epstein, J. A.; Neel, B. G. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 849; |
| [5] | (b) Chan, R. J.; Leedy, M. B.; Munugalavadla, V.; Voorhorst, C. S.; Li, Y.; Yu, M.; Kapur, R. Blood 2005, 105, 3737; |
| [5] | (c) Tartaglia, M.; Niemeyer, C. M.; Fragale, A.; Song, X.; Buechner, J.; Jung, A.; Hahlen, K.; Hasle, H.; Licht, J. D.; Gelb, B. D. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 148. |
| [6] | Mohi, M. G.; Neel, B. G. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007, 17, 23. |
| [7] | Chan, G.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Neel, B. G. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2008, 27, 179. |
| [8] | (a) Chen, L.; Sung, S. S.; Yip, M. L.; Lawrence, H. R.; Ren, Y.; Guida, W. C.; Sebti, S. M.; Lawrence, N. J.; Wu, J. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 562; |
| [8] | (b) Hellmuth, K.; Grosskopf, S.; Lum, C. T.; Wurtele, M.; Roder, N.; von Kries, J. P.; Rosario, M.; Rademann, J.; Birchmeier, W. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7275; |
| [8] | (c) Liu, W.; Yu, B.; Xu, G.; Xu, W. R.; Loh, M. L.; Tang, L. D.; Qu, C. K. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7212; |
| [8] | (d) Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, Z. X.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Nabinger, S. C.; Wu, L.; Gunawan, A. M.; Wang, L.; Chan, R. J.; Zhang, Z. Y. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2482. |
| [9] | Chen, Y.-N. P.; LaMarche, M. J.; Chan, H. M.; Fekkes, P.; Garcia- Fortanet, J.; Acker, M. G.; Antonakos, B.; Chen, C. H.-T.; Chen, Z.; Cooke, V. G.; Dobson, J. R.; Deng, Z.; Fei, F.; Firestone, B.; Fodor, M.; Fridrich, C.; Gao, H.; Grunenfelder, D.; Hao, H.-X.; Jacob, J.; Ho, S.; Hsiao, K.; Kang, Z. B.; Karki, R.; Kato, M.; Larrow, J.; La Bonte, L. R.; Lenoir, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Majumdar, D.; Meyer, M. J.; Palermo, M.; Perez, L.; Pu, M.; Price, E.; Quinn, C.; Shakya, S.; Shultz, M. D.; Slisz, J.; Venkatesan, K.; Wang, P.; Warmuth, M.; Williams, S.; Yang, G.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Zhu, P.; Ramsey, T.; Keen, N. J.; Sellers, W. R.; Stams, T.; Fortin, P. D. Nature 2016, 535, 148. |
| [10] | LaMarche, M. J.; Acker, M.; Argintaru, A.; Bauer, D.; Boisclair, J.; Chan, H.; Chen, C. H.-T.; Chen, Y.-N.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Z.; Dore, M.; Dunstan, D.; Fan, J.; Fekkes, P.; Firestone, B.; Fodor, M.; Garcia-Fortanet, J.; Fortin, P. D.; Fridrich, C.; Giraldes, J.; Glick, M.; Grunenfelder, D.; Hao, H.-X.; Hentemann, M.; Ho, S.; Jouk, A.; Kang, Z. B.; Karki, R.; Kato, M.; Keen, N.; Koenig, R.; LaBonte, L. R.; Larrow, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Majumdar, D.; Mathieu, S.; Meyer, M. J.; Mohseni, M.; Ntaganda, R.; Palermo, M.; Perez, L.; Pu, M.; Ramsey, T.; Reilly, J.; Sarver, P.; Sellers, W. R.; Sendzik, M.; Shultz, M. D.; Slisz, J.; Slocum, K.; Smith, T.; Spence, S.; Stams, T.; Straub, C.; Tamez, V.,Jr.; Toure, B.-B.; Towler, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Williams, S. L.; Yang, F.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J.-H.; Zhu, S. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13578. |
| [11] | Dose Finding Study of TNO155 in Adult Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03114319?cond=SHP2 |
| [12] | Huang, X.; Dixit, V. M. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 484. |
| [13] | Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, C. Y.; Wang, S. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7510. |
| [14] | Song, Y. H.; Yang, X. Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Yu, B. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1781. |
| [15] | Xie, J.; Si, X.; Gu, S.; Wang, M.; Shen, J.; Li, H.; Shen, J.; Li, D.; Fang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 10205. |
| [16] | Ishoey, M.; Chorn, S.; Singh, N.; Jaeger, M. G.; Brand, M.; Paulk, J.; Bauer, S.; Erb, M. A.; Parapatics, K.; Müller, A. C.; Bennett, K. L.; Ecker, G. F.; Bradner, J. E.; Winter, G. E. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 553. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |