

A Lithium Polyacrylate-based High-performance Composite Binder for Graphite Anode
Received date: 2024-05-16
Online published: 2024-07-02
Supported by
National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFB2502103); Xiamen Science and Technology Project(3502Z20231057); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22309153); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22288102); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(20720230039)
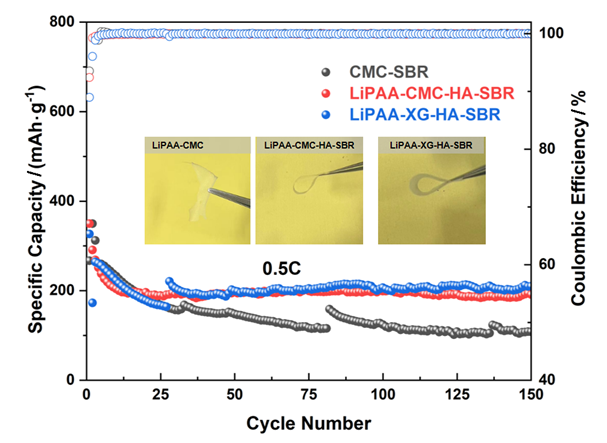
Lithium polyacrylate (LiPAA) is widely used as a binder for lithium-ion battery anodes due to its high ionic conductivity and good chemical stability. However, LiPAA has disadvantages such as low viscosity and high hardness, resulting in the adhesive performance, flexibility and processability of the anode becoming an issue when LiPAA is used as a binder. In this paper, a composite formula was developed by integrating LiPAA with other polymers, including carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or Xanthan gum (XG) to tune the viscosity, sodium hyaluronate (HA) to reduce the brittleness, and benzene butadiene rubber (SBR) to improve the stripping strength. On this basis, two LiPAA-based composite binders (LiPAA-CMC-HA-SBR and LiPAA-XG-HA-SBR) were developed. Compared with the commercial anode binder (CMC-SBR), the two LiPAA-based composite binders both demonstrate well-tuned bonding strength and flexibility; more importantly, they also can significantly improve the interfacial affinity between the graphite particles, the conductive agent and the electrolyte, which hence promotes the diffusion kinetics of lithium ions at the electrode/electrolyte interface and thus improves the electrochemical performance of the graphite anode. At the current density of 0.5 C, after 150 cycles, the graphite anode prepared with our two composite binders displayed a capacity of 209 mAh•g−1 and 191 mAh•g−1, respectively, which was much higher than the graphite anode prepared with the commercial CMC-SBR binder (which is 108 mAh•g−1). The graphite anode prepared with our binder also demonstrates much higher rate capability and better cycling stability compared to the control. Characterizations of the cycled anode reveal that, in the anode prepared with our binders, a much more homogeneous distribution of the conductive carbon and the graphite particles was observed, and a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) with a higher fraction of LiF was formed. In addition, in the commercial CMC-SBR formula, a mass fraction of SBR up to 50% is required; in comparison, in our two LiPAA-based formulations, only a small fraction of SBR is employed yet which can still maintain the integrity of the anode sheet. It is worth noting that, at a low binder content (≈3%) and high active material load (≈95%), the graphite anode elec trode prepared by these two composite binders can still maintain remarkable mechanical strength, and it also demonstrates excellent electrochemical performance, showing the promising industrialization potential of such LiPAA-based composite binders.
Kungui Zheng , Junke Liu , Yiyang Hu , Zuwei Yin , Yao Zhou , Juntao Li , Shigang Sun . A Lithium Polyacrylate-based High-performance Composite Binder for Graphite Anode[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024 , 82(8) : 833 -842 . DOI: 10.6023/A24050160
| [1] | Boudet, H. S. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 446. |
| [2] | Wang, X.; Li, Y. B.; Du, L. Y.; Gao, F. J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L. J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 627 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | (王啸, 李有彬, 杜玲玉, 高福杰, 吴强, 杨立军, 陈强, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 627.) |
| [3] | Wu, M. Y.; Xiao, X. C.; Vukmirovic, N.; Xun, S. D.; Das, P. K.; Song, X. Y.; Olalde-Velasco, P.; Wang, D. D.; Weber, A. Z.; Wang, L. W.; Battaglia, V. S.; Yang, W. L.; Liu, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12048. |
| [4] | Kovalenko, I.; Zdyrko, B.; Magasinski, A.; Hertzberg, B.; Milicev, Z.; Burtovyy, R.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. Science 2011, 334, 75. |
| [5] | Agubra, V. A.; Fergus, J. W. J. Power Sources 2014, 268, 153. |
| [6] | Xu, T.; Sun, W.; Kong, T. C.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. T. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2024, 40, 85 (in Chinese). |
| [6] | (许涛, 孙伟, 孔天赐, 周杰, 钱逸泰, 物理化学学报, 2024, 40, 85.) |
| [7] | Tang, S. Y.; Lu, G. T.; Su, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Z.; Zhang, G. Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y. G. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sinica 2022, 38, 33 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | (唐诗怡, 鹿高甜, 苏毅, 王广, 李炫璋, 张广琦, 魏洋, 张跃钢, 物理化学学报, 2022, 38, 33.) |
| [8] | Park, T. S.; Oh, E. S.; Lee, S. M. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 1191. |
| [9] | Hofmann, K.; Hegde, A. D.; Liu-Theato, X.; Gordon, R.; Smith, A.; Willenbacher, N. J. Power Sources 2024, 593, 233996. |
| [10] | Wang, X. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wei, L. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 24 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | (王晓钰, 张渝, 马磊, 魏良明, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 24.) |
| [11] | Lee, J. H.; Paik, U.; Hackley, V. A.; Choi, Y. M. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 612. |
| [12] | Magasinski, A.; Zdyrko, B.; Kovalenko, I.; Hertzberg, B.; Burtovyy, R.; Huebner, C. F.; Fuller, T. F.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3004. |
| [13] | Li, Z. H.; Tang, W. T.; Yang, Y. J.; Lai, G. Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, H. Y.; Qiu, J. C.; Wei, X. J.; Wu, S. X.; Lin, Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206615. |
| [14] | Dang, D. Y.; Wang, Y. K.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Z.; Ban, C. M.; Cheng, Y. T. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10940. |
| [15] | Guo, M. J.; Xiang, C. C.; Hu, Y. Y.; Deng, L.; Pan, S. Y.; Lv, C.; Chen, S. X.; Deng, H. T.; Sun, C. D.; Li, J. T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, S. G. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 425, 140704. |
| [16] | Wei, L. M.; Chen, C. X.; Hou, Z. Y.; Wei, H. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19583. |
| [17] | Luo, C.; Wu, X. F.; Zhang, T.; Chi, S. S.; Liu, Z. Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Y.; Deng, Y. H. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 306, 2000525. |
| [18] | Lee, H. A.; Shin, M. Y.; Kim, J. M.; Choi, J. W.; Lee, H. S. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007460. |
| [19] | Li, Y.; Jin, B. Y.; Wang, K. Y.; Song, L. N.; Ren, L. H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhan, X. L.; Zhang, Q. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132235. |
| [20] | Hu, L. L.; Jin, M. H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. X.; Ajdari, F. B.; Song, J. X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111560. |
| [21] | Wang, R.; Liu, Z. K.; Yan, C.; Jia, L.; Huang, Y. H. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2023, 39, 81 (in Chinese). |
| [21] | (汪茹, 刘志康, 严超, 伽龙, 黄云辉, 物理化学学报, 2023, 39, 81.) |
| [22] | Pieczonka, N. P. W.; Borgel, V.; Ziv, B.; Leifer, N.; Dargel, V.; Aurbach, D.; Kim, J. H.; Liu, Z. Y.; Huang, X. S.; Krachkovskiy, S. A.; Goward, G. R.; Halalay, I.; Powell, B. R.; Manthiram, A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501008. |
| [23] | Wang, Y. Q.; Ma, Z.; Cao, Z.; Cai, T.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H. R.; Zhao, F.; Cavallo, L.; Li, Q.; Ming, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305974. |
| [24] | Lee, Y. S.; Ryu, K. S. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16617. |
| [25] | Rahim, S.; Naveed, A.; Amir, A. R.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. J.; Hu, J. P.; Zhao, X. H.; Peng, Y.; Deng, Z. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2019, 35, 1382 (in Chinese). |
| [25] | (拉希姆?沙阿, 纳维德?阿拉姆, 阿米尔?拉扎克, 杨成, 陈宇杰, 胡加鹏, 赵晓辉, 彭扬, 邓昭, 物理化学学报, 2019, 35, 1382.) |
| [26] | Weisenberger, C.; Harrison, D. K.; Zhou, C. K.; Knoblauch, V. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 461, 142629. |
| [27] | Pan, S. Y.; Yang, X. R.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, C.; Deng, H, T.; Guo, M. J.; Chen, S. X.; Hu, Y. Y.; Deng, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J. T.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S. G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55700. |
| [28] | Huang, Y. S.; Wang, C. A.; Lv, H. F.; Xie, Y. S.; Zhou, S. Y.; Ye, Y. D.; Zhou, E.; Zhu, T. Y.; Xie, H. Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X. J.; Kong, X. H.; Jin, H. C.; Ji, H. X. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308675. |
| [29] | Yang, Y. Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H. L. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7666. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |