

Acid Strength Controlled Reaction Pathways for the Catalytic Cracking of 1-Heptene over ZSM-5
Received date: 2024-07-15
Online published: 2024-09-02
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22072044); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21673076); Research Funds of Happiness Flower ECNU(2020ST2203)
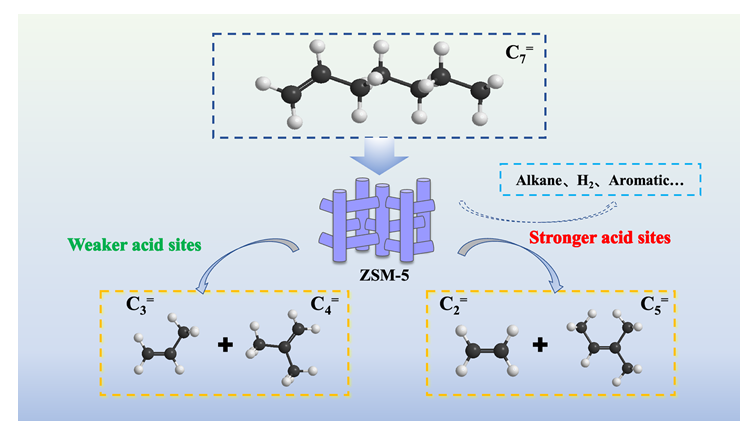
Heptene (C7=) is an important chemical intermediate. The C7= catalytic cracking to ethylene/propylene (C2=/C3=) represents an effective approach for the high-value utilization of carbon resources. However, the reaction pathways involved in the catalytic cracking of C7= and the principles governing their modulation remain to be thoroughly analyzed and clarified. In this study, we established a reaction network for C7= catalytic cracking based on the carbenium ion mechanism and β-scission mechanism. We investigated the catalytic performance of various zeolite catalysts with different topological structures and found that ZSM-5 zeolite, characterized by its unique pore structure, served as an efficient catalyst for C7= catalytic cracking. On this basis, a series of ZSM-5 zeolites (ZSM-5(I) to ZSM-5(V)) with comparable acid density and varying acid strength were synthesized via hydrothermal processes using phosphorus-modified and ammonium fluorosilicate-modified methods.The effects of the acidity (acid amount and acid strength) of the ZSM-5 zeolites on the catalytic cracking reaction of C7= were systematically investigated under 550 ℃. The results indicated that the C7= catalytic cracking primarily involved unimolecular cracking, hydrogen transfer, dehydrogenative aromatization, and decarbonylation reactions. The reduction of both acid amount and acid strength in ZSM-5 suppressed the reaction pathways for generating non-olefinic products, such as hydrogen transfer and aromatization, while enhancing the cracking pathways that produce olefins, thereby increasing the carbon resource utilization efficiency. Specifically, the acid strength of ZSM-5 played a crucial role in controlling the unimolecular cracking reaction pathways: pathway I (C7=→C3=+C4=) and pathway II (C7=→C2=+C5=). An increase in strong acid sites within ZSM-5 enhanced pathway II, leading to increased ethylene yields. Conversely, a higher number of weak acid sites promoted pathway I, resulting in greater propylene production. This research provides new insights into the design of catalysts for the efficient utilization of carbon resources in the catalytic cracking of C7= to C2=/C3=.
Key words: catalytic cracking; heptene; ZSM-5; acid strength; reaction pathway
Qin Zhao , Fang Li , Penghe Zhang , Yueming Liu . Acid Strength Controlled Reaction Pathways for the Catalytic Cracking of 1-Heptene over ZSM-5[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024 , 82(10) : 1013 -1021 . DOI: 10.6023/A24070216
| [1] | Lavrenov, A. V.; Saifulina, L. F.; Buluchevskii, E. A.; Bogdanets, E. N. Catal. Ind. 2015, 7 175. |
| [2] | Li, J.; Li, W.; Wang, C. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2013, 31 1134 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | (李继文, 李薇, 王川, 色谱, 2013, 31 1134.) |
| [3] | Alotibi, M. F.; Alshammari, B. A.; Alotaibi, M. H.; Alotaibi, F. M.; Alshihri, S.; Navarro, R. M.; Fierro, J. L. G. Catal. Surv. Asia 2020, 24 1. |
| [4] | Yang, M.; Fan, D.; Wei, Y. X.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z. M. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31 1902181. |
| [5] | Almuqati, N. S.; Aldawsari, A. M.; Alharbi, K. N.; González-Cortés, S.; Alotibi, M. F.; Alzaidi, F.; Dilworth, J. R.; Edwards, P. P. Fuel 2023, 366 131270. |
| [6] | Jiao, F.; Bai, B.; Li, G.; Pan, X. L.; Ye, Y. H.; Qu, S. C.; Xu, C. Q.; Xiao, J. P.; Jia, Z. H.; Liu, W. Science 2023, 380 727. |
| [7] | Zhang, Y.; Shen, K. X.; Teng, J. W. Chem. React. Eng. Technol. 2021, 37 181 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | (张燕, 沈凯旭, 滕加伟, 化学反应工程与工艺, 2021, 37 181.) |
| [8] | Huang, X.; Aihemaitijiang, D.; Xiao, W. D. Chem. Eng. J. (Loughborough, Engl). 2015, 280 222. |
| [9] | Lin, L. F.; Qiu, C. F.; Zhuo, Z. X.; Zhang, D. W.; Zhao, S. F.; Wu, H. H.; Liu, Y. M.; He, M. Y. J. Catal. 2014, 309 136. |
| [10] | Lin, L. F.; Zhao, S. F.; Zhang, D. W.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y. M.; He, M. Y. ACS Catal. 2015, 5 4048. |
| [11] | Sun, H. L.; Cao, L. Y.; Zhang, Y. H.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J. S.; Xu, C. M. Energy Fuels 2021, 35 3295. |
| [12] | Chen, C. J.; Rangarajan, S.; Hill, I. M.; Bhan, A. ACS Catal. 2014, 4 2319. |
| [13] | Zhao, G. L.; Teng, J. W.; Xie, Z. K.; Jin, W. Q.; Yang, W. M.; Chen, Q. L.; Tang, Y. J. Catal. 2007, 248 29. |
| [14] | Liu, Q.; Chen, Z. K.; Piao, Y.; Xiao, P.; Ge, Y. F.; Gong, Y. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2024, 75 120 (in Chinese). |
| [14] | (刘琦, 陈子康, 朴宇, 肖鹏, 葛亚粉, 巩雁军, 化工学报. 2024, 75 120.) |
| [15] | Jiang, L.; Yang, X. Y.; Huang, X. Y.; Wen, M. F. Refin. Chem. Ind. 2022, 33 22. |
| [16] | Li, L.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Z. G.; Zhu, Y. F. CN 202111073921.7. 2021 (in Chinese). |
| [16] | (李丽, 黄鑫, 郑志刚, 朱豫飞, CN202111073921.7. 2021.) |
| [17] | Abbot, J.; Wojciechowski, B. W. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1985, 63 462. |
| [18] | Buchanan, J. S.; Santiesteban, J. G.; Haag, W. O. J. Catal. 1996, 158 279. |
| [19] | Wu, W. Z.; Guo, W. Y.; Xiao, W. D.; Luo, M. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66 4722. |
| [20] | Ji, H.; Li, Z.; Hou, S.; Long, J. Acta Pet. Sin., Pet. Process Sect. 2009, 25 14. |
| [21] | Zhou, W. Z.; Lin, D. C.; Zhong, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, T.; Long, Y. C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62 833 (in Chinese). |
| [21] | (周伟正, 林德昌, 钟鹰, 郭娟, 王梯, 龙英才, 化学学报. 2004, 62 833.) |
| [22] | Gong, J. H.; Yang, Y. N.; Xu, Y. H.; Zhang, J. S.; Long, J. Petrochem. Technol. 2006, 22 27 (in Chinese). |
| [22] | (龚剑洪, 杨轶男, 许友好, 张久顺, 龙军, 石油学报(石油加工), 2006, 22 27.) |
| [23] | Li, J.; Li, T.; Ma, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, C.; Ying, W.; Fang, D. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346 397. |
| [24] | Ying, L.; Zhu, J. J.; Cheng, Y. W.; Wang, L. J.; Li, X. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33 80. |
| [25] | Zhu, X. X.; Liu, S. L.; Song, Y. Q.; Xu, L. Y. Appl. Catal., A 2005, 288 134. |
| [26] | Sun, H.; Zhang, B.; Wei, C.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J.; Xu, C. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60 17469. |
| [27] | Pal?i?, A.; Valtchev, V. Appl. Catal., A 2020, 606 117795. |
| [28] | Li, F.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, B. H.; Huang, X.; Ding, C. J.; Liu, Y. M.; He, M. Y. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 373 113. |
| [29] | Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, M. Fuel 2024, 371 132077. |
| [30] | Bai, Y. E.; Zhang, B. R.; Liu, D. Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J. S.; Xu, C. M. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2023, 74 438 (in Chinese). |
| [30] | (白宇恩, 张彬瑞, 刘东阳, 赵亮, 高金森, 徐春明, 化工学报 2023, 74 438.) |
| [31] | Chen, Z. P.; Meng, Y. L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W. W.; Yang, Z. Y.; Zhou, A. N. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81 14 (in Chinese). |
| [31] | (陈治平, 孟永乐, 芦静, 周文武, 杨志远, 周安宁, 化学学报 2023, 81 14.) |
| [32] | Yang, W. J.; Xu, Y. H.; Shu, X. T.; Wang, X.; Bai, X. H.; Zuo, Y. F.; Luo, Y. B.; Ouyang, Y. Appl. Energy. 2023, 349 121665. |
| [33] | He, L.; Yao, Q. X.; Sun, M.; Ma, X. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80 180 (in Chinese). |
| [33] | (何磊, 么秋香, 孙鸣, 马晓迅, 化学学报, 2022, 80 180.) |
| [34] | Zhao, G. L.; Teng, J. W.; Xie, Z. K.; Tang, Y.; Yang, W. M.; Chen, Q. L. Chin. J. Catal. 2005, 26 1083 (in Chinese). |
| [34] | (赵国良, 滕加伟, 谢在库, 唐颐, 杨为民, 陈庆龄, 催化学报, 2005, 26 1083.) |
| [35] | Zhao, G. L.; Teng, J. W.; Jin, W. Q.; Yang, W. M.; Xie, Z. K.; Chen, Q. L. Chin. J. Catal. 2004, 25 3 (in Chinese). |
| [35] | (赵国良, 滕加伟, 金文清, 杨为民, 谢在库, 陈庆龄, 催化学报, 2004, 25 3.) |
| [36] | Li, X. L.; Hou, S. M.; Duan, H. C.; Lu, R. L.; Zhang, Y. T. Pet. Process. Petrochem. 2023, 54 74 (in Chinese). |
| [36] | (李雪礼, 侯硕旻, 段宏昌, 路瑞玲, 张琰图, 石油炼制与化工, 2023, 54 74.) |
| [37] | Li, H.; Li, X. G.; Xiao, W. D. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151 955. |
| [38] | Reddy, J. K.; Motokura, K.; Koyama, T.; Miyaji, A.; Baba, T. J. Catal. 2012, 289 53. |
| [39] | Al-Dughaither, A. S.; de Lasa, H. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53 15303. |
| [40] | Stach, H.; J?nchen, J. Zeolites 1992, 12 152. |
| [41] | Li, B.; Long, J.; Hou, S. D. Comput. Appl. Chem. 2009, 26 129 (in Chinese). |
| [41] | (李博, 龙军, 侯栓弟, 计算机与应用化学, 2009, 26 129.) |
| [42] | Zhu, X. X.; Liu, S. L.; Song, Y. Q.; Xu, L. Y. Catal. Lett. 2005, 103 201. |
| [43] | Leydier, F.; Chizallet, C.; Costa, D.; Raybaud, P. J. Catal. 2015, 325 35. |
| [44] | Wang, B.; Gao, Q.; Gao, J. D.; Ji, D.; Wang, X. L.; Suo, J. S. Appl. Catal., A 2004, 274 167. |
| [45] | Bortnovsky, O.; Sazama, P.; Wichterlova, B. Appl. Catal., A 2005, 287 203. |
| [46] | Liu, J. T.; Zhong, S. Q.; Xu, C. M.; Xie, Z. K.; Yang, W. M. Petrochem. Technol. 2005, 34 5 (in Chinese). |
| [46] | (刘俊涛, 钟思青, 徐春明, 谢在库, 杨为民, 石油化工, 2005, 34 5.) |
| [47] | Potapenko, O. V.; Doronin, V. P.; Sorokina, T. P.; Likholobov, V. A. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128 251. |
| [48] | Schailmoser, S.; Haller, G. L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; Lercher, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139 8646. |
| [49] | Corma, A.; Miguel, P. J.; Orchilles, A. V. J. Catal. 1994, 145 171. |
| [50] | Corma, A.; Miguel, P. J.; Orchillés, A. V. J. Catal. 1997, 172 355. |
| [51] | Liang, C. C.; Xu, R. F.; Chang, X. S.; Liu, G. D.; Liu, J. X.; Guo, H. C. J. Mol. Catal. 2011, 25 69 (in Chinese). |
| [51] | (梁翠翠, 徐瑞芳, 常旭升, 刘国东, 刘家旭, 郭洪臣, 分子催化, 2011, 25 69.) |
| [52] | Rigby, A. M.; Kramer, G. J.; van Santen, R. A. J. Catal. 1997, 170 1. |
| [53] | Arudra, P.; Bhuiyan, T. I.; Akhtar, M. N.; Aitani, A. M.; Al-Khattaf, S. S.; Hattori, H. ACS Catal. 2014, 4 4205. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |