

PEGylated Mesoporous Silica Coated Conjugated Polymer for NIR Phototheranostics
Received date: 2024-09-23
Online published: 2024-11-14
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(52373142); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21605088); Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications(NY223100)
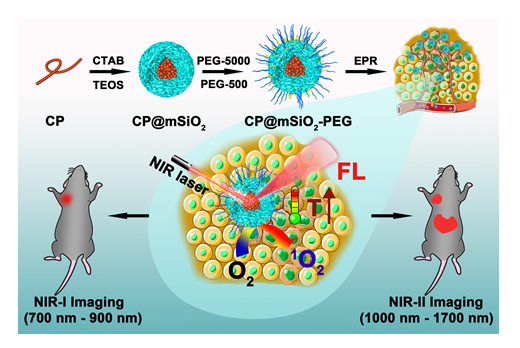
The near-infrared fluorescence imaging and phototherapy technologies have garnered increasing attention in the biomedical field, providing novel approaches for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. In recent years, the development of high-performance phototheranostic agents has become a research focus in the related fields. This study encapsulated conjugated polymers (CP) within highly polyethylene glycol (PEG)-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles (CP@mSiO2-PEG), resulting in a highly efficient near-infrared phototheranostic agent with high stability, brightness, and biocompatibility. The obtained material exhibited strong fluorescence emission in both the first (NIR-I, 700~900 nm) and the second (NIR-II, 1000~1700 nm) near-infrared regions, along with a high photothermal conversion efficiency (40.5%) and a singlet oxygen quantum yield (5.2%) under 730 nm laser irradiation. Taking advantage of the strong and broad fluorescence emission, simultaneous NIR-I and NIR-II imaging in one living mouse can be achieved to compare the advantages and disadvantages of the two NIR fluorescence imaging modalities. This approach eliminated individual differences and random errors, which can provide a more accurate and reliable result. Through subcutaneous tumor models, it was observed that these highly PEGylated nanoparticles can be efficiently accumulated at the tumor sites after intravenous injection. Performing NIR-I and NIR-II fluorescence imaging with the same tumor-bearing mouse, it was found that NIR-I imaging can provide a higher tumor-to-liver signal ratio, which facilitates the early diagnosis and preliminary localization of subcutaneous tumors. In contrast, NIR-II imaging offers a higher signal-to-background ratio and a higher resolution, which enables clearer delineation of the tumor contour, thus demonstrating greater advantages in fluorescence imaging-guided surgical resection. Additionally, NIR-II imaging can eliminate the interference from the spontaneous fluorescence of the animal fur. Furthermore, the obtained nanoparticles, which integrate photothermal and photodynamic therapy modalities, also exhibiting high phototherapy efficacy for in vivo tumor therapy. The conjugated polymer used here can also be replaced with other desired polymers to achieve other optical applications.
Yuqi Zhang , Chen Zhan , Yi Gong , Feng Lu , Quli Fan . PEGylated Mesoporous Silica Coated Conjugated Polymer for NIR Phototheranostics[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024 , 82(12) : 1226 -1233 . DOI: 10.6023/A24090286
| [1] | Rowe, S. P.; Pomper, M. G. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 333. |
| [1] | Si, G. X.; Du, Y.; Tang, P.; Ma, G.; Jia, Z. C.; Zhou, X. Y.; Mu, D.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, N. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae057. |
| [2] | Chen, S. F.; Zhuang, D. P.; Jia, Q. Y.; Guo, B.; Hu, G. W. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 0042. |
| [3] | Hong, G. S.; Antaris, A. L.; Dai, H. J. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0010. |
| [4] | Wang, F. F.; Zhong, Y. T.; Bruns, O.; Liang, Y. Y.; Dai, H. J. Nat. Photonics 2024, 18, 535. |
| [5] | Liu, J. W.; Tang, Y. G.; Wang, R. Q.; Wang, X. Y.; Fu, M. X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, F.; Fan, Q. L.; Wang, Q. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2024, 414, 135951. |
| [6] | Chen, Y. F.; Spinelli, S.; Pan, Z. W. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7542. |
| [7] | Lu, F.; Li, L. L.; Zhao, T.; Ding, B. Q.; Liu, J. W.; Wang, Q.; Xie, C.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 200, 110124. |
| [8] | Antaris, A. L.; Chen, H.; Diao, S.; Ma, Z. R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, S. J.; Wang, J.; Lozano, A. X.; Fan, Q. L.; Chew, L. L.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, K.; Hong, X. C.; Dai, H. J.; Cheng, Z. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15269. |
| [9] | Wang, S.; Fan, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, C.; Lei, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, F. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1058. |
| [10] | Zhu, S. J.; Hu, Z. B.; Tian, R.; Yung, B. C.; Yang, Q. L.; Zhao, S.; Kiesewetter, D. O.; Niu, G.; Sun, H. T.; Antaris, A. L.; Chen, X. Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802546. |
| [11] | Cai, Z. C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M. Q.; Roe, A. W.; Xi, W.; Qian, J. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4265. |
| [12] | Wu, Z. F.; Ke, J. X.; Liu, Y. S.; Sun, P. M.; Hong, M. C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 542. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | (吴志芬, 柯建熙, 刘永升, 孙蓬明, 洪茂椿, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 542.) |
| [13] | MacFarlane, L. R.; Shaikh, H.; Garcia-Hernandez, J. D.; Vespa, M.; Fukui, T.; Manners, I. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 7. |
| [14] | Qian, C. G.; Chen, Y. L.; Feng, P. J.; Xiao, X. Z.; Dong, M.; Yu, J. C.; Hu, Q. Y.; Shen, Q. D.; Gu, Z. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 764. |
| [15] | Liu, Y.; Liu, J. F.; Chen, D. D.; Wang, X. S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. C.; Jiang, L. H.; Qi, W. Z.; Ye, Z. Y.; He, S. Q.; Liu, Q. Y.; Xi, L.; Zou, Y. P.; Wu, C. F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21049. |
| [16] | Yan, C. X.; Guo, Z. Q.; Chi, W. J.; Fu, W.; Abedi, S. A. A.; Liu, X. G.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W. H. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3869. |
| [17] | Jia, H. Y.; Yu, Y. W.; Feng, G. X.; Tang, B. Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 2530. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | (贾涵羽, 俞岳文, 冯光雪, 唐本忠, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 2530.) |
| [18] | Lu, F.; Li, L. L.; Zhang, M.; Yu, C. W.; Pan, Y. H.; Cheng, F. F.; Hu, W. B.; Lu, X. M.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Q. L. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 12086. |
| [19] | Sun, B.; Ju, W. W.; Wang, T.; Sun, X. J.; Zhao, T.; Lu, X. M.; Lu, F.; Fan, Q. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 757. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | (孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 757.) |
| [20] | Jiang, Y. Y.; Li, J. C.; Zhen, X.; Xie, C.; Pu, K. Y. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705980. |
| [21] | Li, L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Ren, Y. X.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y. Z.; Bao, B. K.; Li, M. Q.; Tang, Y. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5927. |
| [22] | Zhu, H.; Fang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Wei, N.; Gao, Y.; Luo, K. Q.; Xu, C.; Duan, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, P.; Pu, K. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5118. |
| [23] | Zhu, H. J.; Li, J. C.; Qi, X. Y.; Chen, P.; Pu, K. Y. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 586. |
| [24] | Lu, F.; Wang, J. F.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J. J. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9447. |
| [25] | Tan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. X.; Zhang, X. H.; Yong, A. M.; Wong, S. Y.; Chang, A. Y. C.; Chen, Z. K.; Li, X.; Choolani, M.; Wang, J. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 237. |
| [26] | Lu, F.; Zhan, C.; Gong, Y.; Tang, Y. F.; Xie, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W. J.; Fan, Q. L.; Huang, W. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 1900483. |
| [27] | Yang, Y. Q.; Fan, X. X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y. M.; Nuernisha, A.; Xue, D. W.; He, C.; Qian, J.; Hu, Q. L.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, W. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2509. |
| [28] | Hu, Z. H.; Fang, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Cao, C. G.; Cai, M. S.; Su, S.; Sun, X. W.; Shi, X. J.; Li, C.; Zhou, T. J.; Zhang, Y. X.; Chi, C. W.; He, P.; Xia, X. M.; Chen, Y.; Gambhir, S. S.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, J. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 259. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |