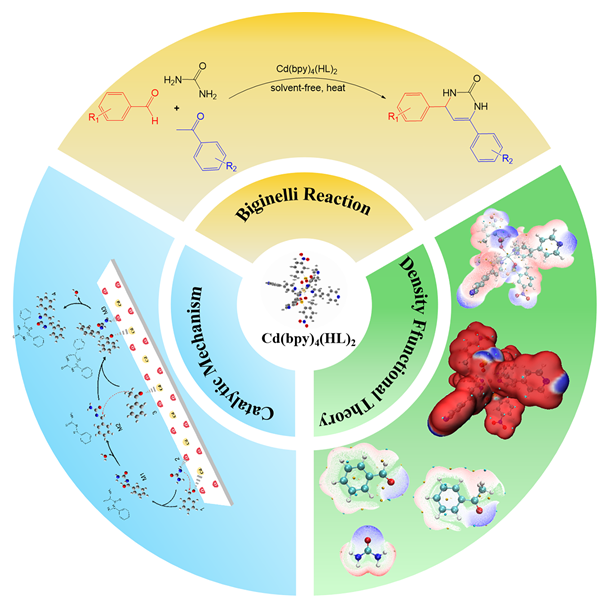
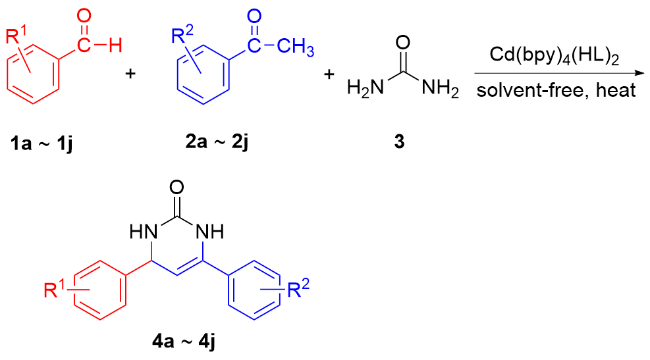
1 引言
2 结果与讨论
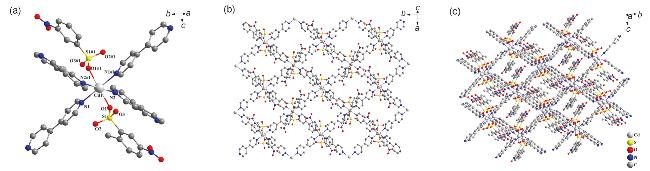
2.1 配合物的晶体结构
表1 Cd(bpy)4(HL)2的晶体学数据a,bTable 1 Crystallographic data for Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 |
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | C34CdN6O10S2 | |
| Formula weight | 828.92 | |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | |
| Space group | P21/n | |
| a/nm | 0.89086(3) | |
| b/nm | 1.61511(5) | |
| c/nm | 1.27040(4) | |
| α/(°) | 90 | |
| β/° | 103.7390(10) | |
| γ/° | 90 | |
| V/nm3 | 1.77560(10) | |
| Z | 2 | |
| Dc/(mg•m-3) | 1.550 | |
| Goodness-of-fit F2 | 1.113 | |
| R1, ωR2 | 0.0338, 0.0986 | |
| R1, ωR2 (all data) | 0.0366, 0.1019 |
ɑ R1=Σ║Fo│-│Fc║/Σ│Fo│. bwR2={Σ[w(Fo2-Fc2)2]/Σ[w(Fo2)2]}1/2. |
表2 Cd(bpy)4(HL)2的部分键长(nm)和键角(°)的实验值和计算值aTable 2 Partial bond length (nm) and bond angle (°) of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 |
| Bond length/nm | Bond angle/(°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | B3LYP | X-ray | B3LYP | ||
| Cd(1)—O(1)#1 | 0.2300(2) | 0.2363 | O(1)#1—Cd(1)—O(1) | 180.0 | 179.35 |
| Cd(1)—O(1) | 0.2300(2) | 0.2363 | N(1)#1—Cd(1)—N(1) | 180.0 | 179.69 |
| Cd(1)—N(1) | 0.2315(2) | 0.2378 | N(2)#1—Cd(1)—N(2) | 180.0 | 179.44 |
| Cd(1)—N(1)#1 | 0.2315(2) | 0.2378 | O(1)#1—Cd(1)—N(2)#1 | 85.24(9) | 86.93 |
| Cd(1)—N(2) | 0.2411(2) | 0.2457 | O(1)#1—Cd(1)—N(1) | 90.32(9) | 92.80 |
| Cd(1)—N(2)#1 | 0.2411(2) | 0.2457 | N(1)—Cd(1)—N(2)#1 | 88.20(9) | 89.16 |
a Symmetry tansformations used to generate equivalent atoms: #1 -x+1, -y+1, -z; #2 x+1/2, -y+3/2, z-1/2; #3 -x+1/2, y-1/2, -z+1/2; #4 -x+1/2, y+1/2, -z+1/2. |
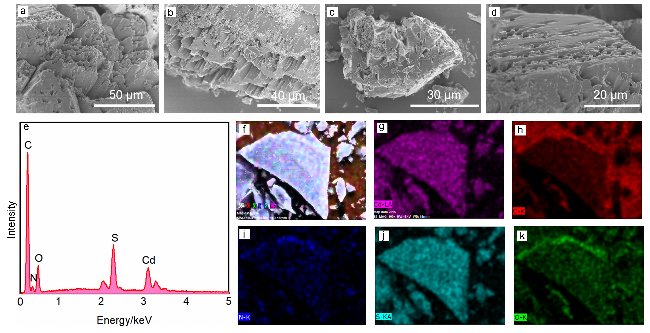
2.2 扫描电镜和能量色散光谱分析
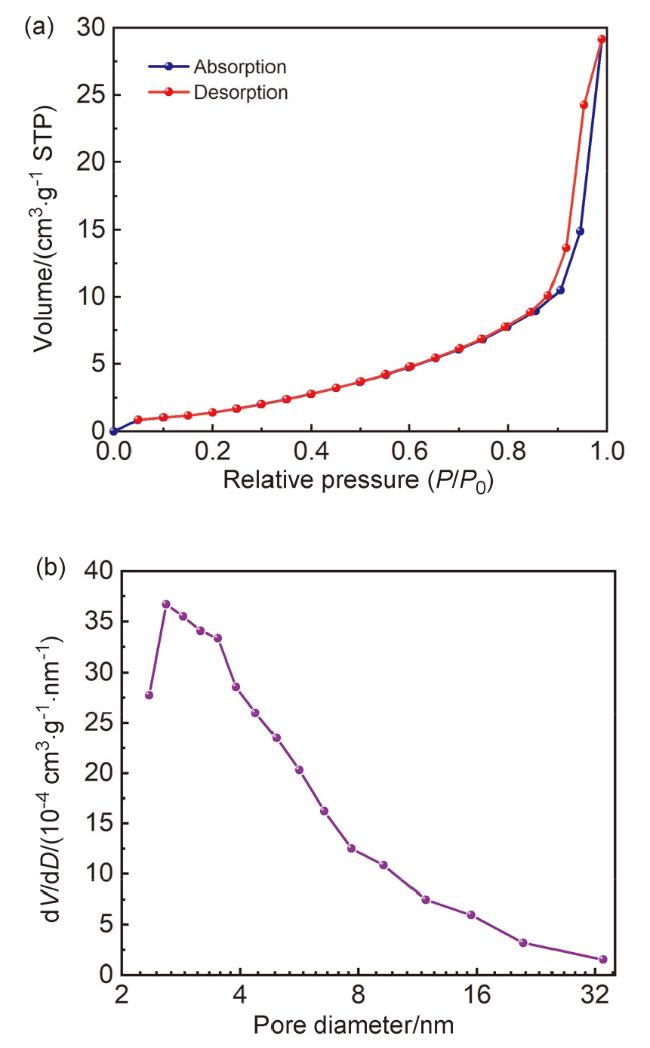
2.3 氮气吸附/脱附分析
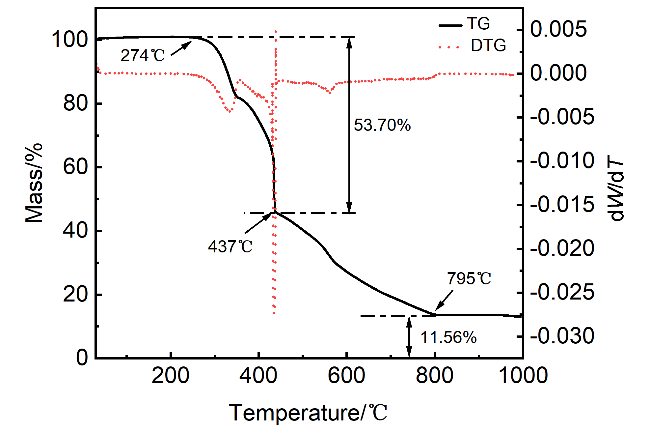
2.4 热重分析
2.5 催化性能考察
2.5.1 反应条件优化
表3 原料配比、反应温度和Cd(bpy)4(HL)2用量优化Table 3 Optimization of raw material ratio, reaction temperature and the amount of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 |
| Entry | nbenzaldehyde∶ nacetophenone∶nurea | Temp./ ℃ | Catal. amount/ mmol | Time/min | Yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.0 | 90 | 0.3 | 46 | 74.6 |
| 2 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 | 0.3 | 16 | 88.2 |
| 3 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.2 | 90 | 0.3 | 29 | 84.2 |
| 4 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.3 | 90 | 0.3 | 37 | 82.8 |
| 5 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 50 | 0.3 | 41 | 67.6 |
| 6 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 70 | 0.3 | 28 | 80.7 |
| 7 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 110 | 0.3 | 20 | 84.4 |
| 8 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 | 0.1 | 18 | 83.3 |
| 9 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 | 0.2 | 18 | 84.3 |
| 10 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 | 0.4 | 16 | 86.2 |
| 11 | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 | 0.5 | 16 | 86.1 |
2.5.2 普适性考察
表4 Cd(bpy)4(HL)2催化合成4,6-二芳基-3,4-二氢嘧啶-2(1H)-酮aTable 4 Synthesis of 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-ones catalyzed by Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 |
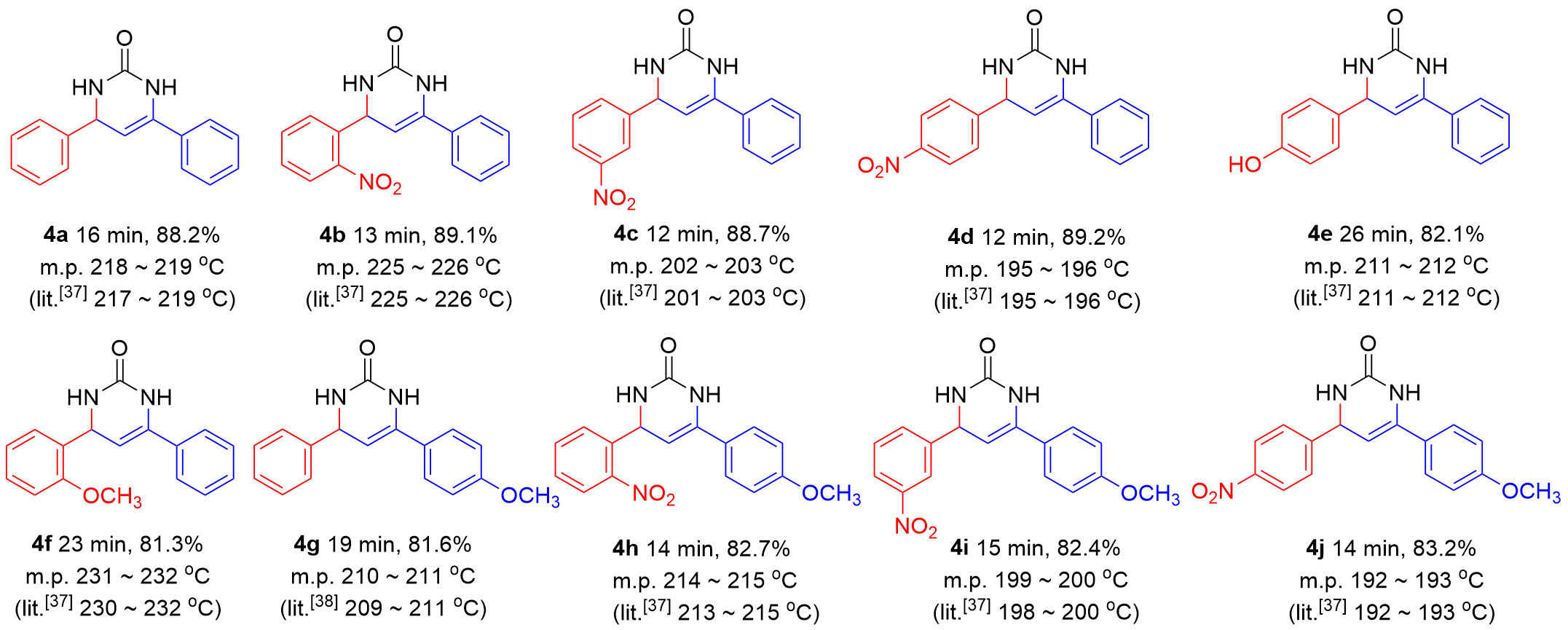 |
a Reaction conditions: aromatic aldehyde (10 mmol), aromatic ketone (10 mmol) and urea (11 mmol), Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 (0.3 mmol), 90 ℃, solvent-free. |
2.5.3 催化剂重复使用考察
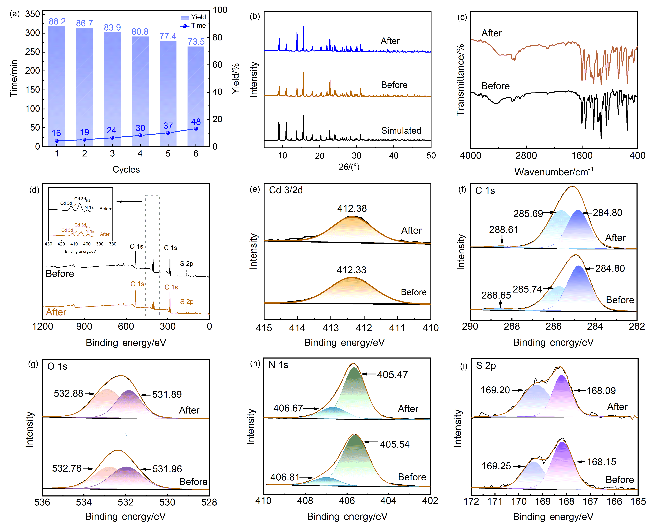
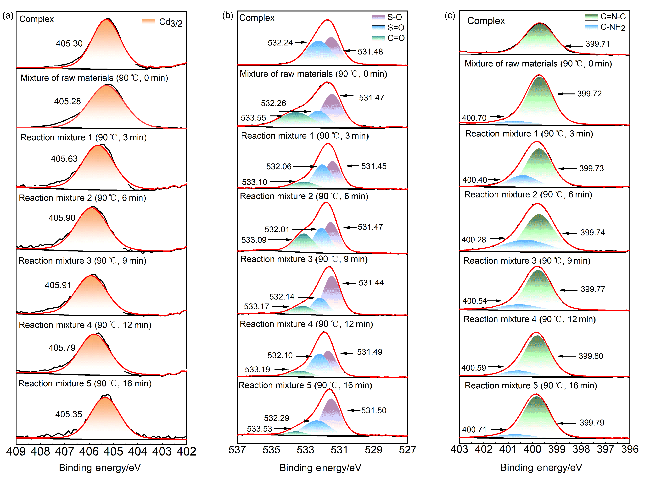
图6 (a) Cd(bpy)4(HL)2的重复使用情况以及Cd(bpy)4(HL)2催化6次前后的(b)粉末X射线衍射图、(c)红外光谱图、(d) X射线光电子能谱总谱和(e~i) Cd3/2d, C1s, O1s, N1s和S2p的X射线光电子能谱Figure 6 (a) Reuse of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2, and (b) powder X-ray diffraction pattern, (c) infrared spectra, XPS spectra of (d) total spectrum and (e~i) Cd3/2d, C1s, O1s, N1s and S2p of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 before and after six catalytic times |
2.5.4 催化剂比较
表5 催化剂比较Table 5 Comparison of catalysts |
| Entry | Catalyst (ncatalyst∶nbenzaldehyde) | Raw material ratioa | Condition | Time/min | Yield/% | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NiFe2O4@SiO2nPr@glucose amine (10%) | 1.0∶1.0∶1.0 | 25 ℃ (H2O) | 120 | 90.0 | [39] | |
| 2 | Ƴ-Fe2O3-SO3H (5%) | 1.0∶1.0∶1.5 | 80 ℃ (solvent free) | 100 | 90.0 | [40] | |
| 3 | [TSPi][CF3SO3]2 (2.5%) | 1.0∶1.0∶1.2 | r.t. (CH2Cl2, grind) | 16 | 89.0 | [41] | |
| 4 | PPh3 (20%)/I2 (15%) | 1.2∶1.0∶1.5 | 80 ℃ (1,4-dioxane) | 120 | 82.0 | [42] | |
| 5 | LDA (20%) | 1.2∶1.5∶1.5 | 0 ℃ (THF) | 60 | 81.0 | [43] | |
| 6 | Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 (3%) | 1.0∶1.0∶1.1 | 90 ℃ (solvent free) | 16 | 88.2 | This work |
a Reactants (benzaldehyde/etthylacetoacetate/urea) ratio in mmol. |
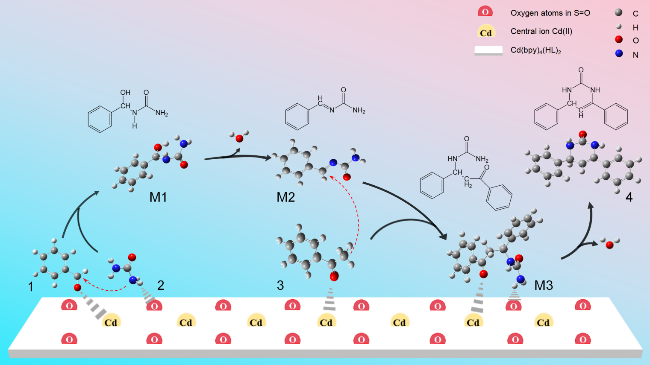
2.6 基于DFT理论分析配合物的催化机理
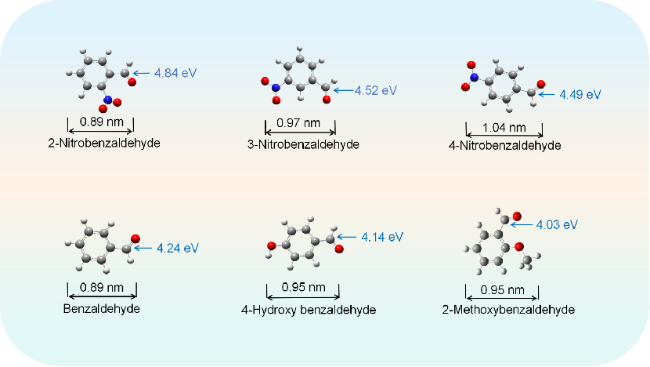
2.6.1 配合物活性位点预测
表6 Cd(bpy)4(HL)2部分原子的Mulliken电荷Table 6 Mulliken charge of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2 part atom |
| Atom | Charge/eV | Atom | Charge/eV | Atom | Charge/eV | Atom | Charge/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(1) | 25.80 | C(11) | 0.74 | N(79) | -9.71 | H(106) | 4.14 |
| C(2) | 1.77 | C(12) | -3.27 | O(83) | -14.61 | H(107) | 5.28 |
| C(3) | 1.82 | C(13) | -3.27 | O(86) | -16.98 | C(118) | -13.63 |
| C(4) | -3.89 | C(14) | -0.19 | O(87) | -16.95 | H(119) | 5.20 |
| H(5) | 5.82 | H(15) | 3.92 | C(99) | -9.80 | H(121) | 3.95 |
| C(6) | -3.92 | C(16) | 0.19 | C(100) | -2.29 | H(120) | 5.77 |
| H(7) | 6.01 | H(17) | 4.19 | C(101) | 4.41 | N(109) | 1.42 |
| C(8) | 0.93 | H(18) | 4.11 | C(102) | 8.38 | O(112) | -7.84 |
| H(9) | -4.03 | H(19) | 4.19 | H(103) | 6.67 | O(113) | -7.76 |
| H(10) | 4.38 | N(78) | -14.59 | C(104) | -4.68 | C(105) | -2.34 |
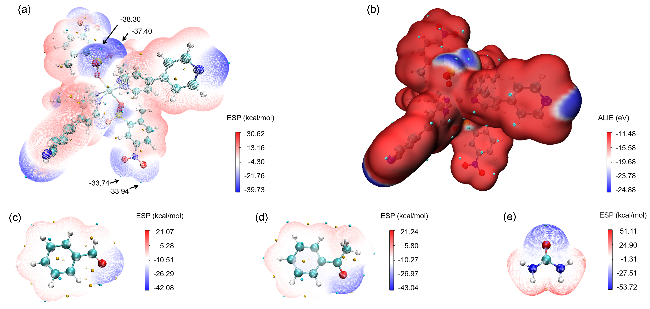
图8 Cd(bpy)4(HL)2的(a)表面静电势填色图、(b)表面平均局部离子化能填色图及(c~e)苯甲醛、苯乙酮和脲的表面静电势填色图Figure 8 (a) Surface electrostatic potential coloring diagram, (b) surface average local ionization energy coloring diagram of Cd(bpy)4(HL)2, and (c~e) Surface electrostatic potential coloring diagram of benzaldehyde, acetophenone and urea |