1 引言
2 结果与讨论
2.1 熔盐温度对SrTiO3:Al光催化性能的影响
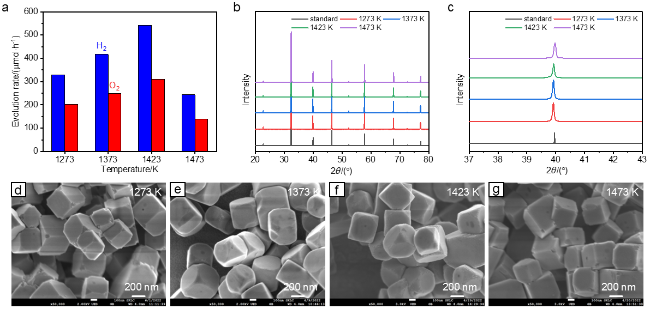
图1 (a)未添加Al2O3时不同温度下熔盐制备SrTiO3:Al的光催化活性图; (b)对应样品的XRD图; (c)是(b)中部分区域的放大XRD图; (d~g)是该组SrTiO3:Al样品对应的SEM图; 光催化活性测试条件: 100 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOHFigure 1 (a) Photocatalytic overall water splitting activities of SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method at various temperatures without Al2O3 addition. (b) XRD patterns of the corresponding samples. (c) Enlarged XRD patterns in (b). (d~g) SEM images of the corresponding SrTiO3:Al samples. Photocatalytic reaction conditions: 100 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water |
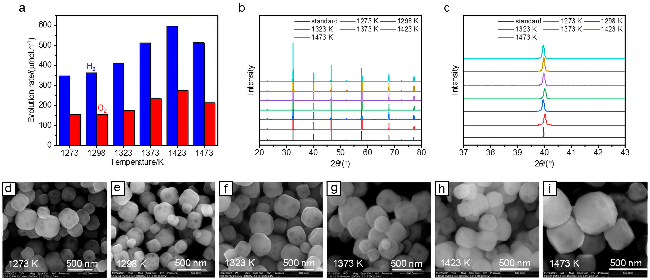
图2 (a)添加1 mol%的γ-Al2O3时不同温度下熔盐制备1%-SrTiO3:Al的光催化全分解水活性(a)和对应的XRD衍射图(b); (c)是图(b)部分区域的放大XRD图; (d~i)不同熔盐温度下制备1%-SrTiO3:Al的SEM图; 光催化活性测试条件: 100 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOHFigure 2 (a) Photocatalytic overall water splitting activities of 1%-SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method at various temperatures with the addition of 1 mol% γ-Al2O3. (b) XRD patterns of the corresponding samples in (a). (c) Enlarged XRD patterns in (b). (d~i) SEM images of 1%-SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method at various temperatures with the addition of 1 mol% γ-Al2O3. Photocatalytic reaction conditions: 100 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water |
2.2 Al2O3的类型对SrTiO3:Al光催化性能的影响
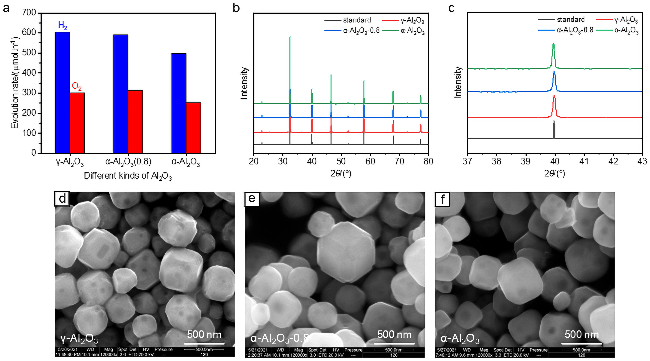
图3 添加量为1 mol%, Al源分别为γ-Al2O3、α-Al2O3(0.8)和α-Al2O3合成1%-SrTiO3:Al的光催化活性(a)与对应的XRD衍射图(b); (c)是图(b)部分区域的放大XRD图; (d~f)是对应1%-SrTiO3:Al的SEM图; 光催化活性测试条件: 100 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOHFigure 3 (a) Photocatalytic overall water splitting activities of 1%-SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method with the addition of 1 mol% γ-Al2O3, α-Al2O3(0.8) and α-Al2O3, respectively. (b) XRD patterns of the 1%-SrTiO3:Al in (a). (c) Enlarged XRD patterns in (b). (d~f) SEM images of the corresponding 1%-SrTiO3:Al samples. Photocatalytic reaction conditions: 100 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water |
2.3 Al2O3的添加量对SrTiO3:Al光催化性能的影响
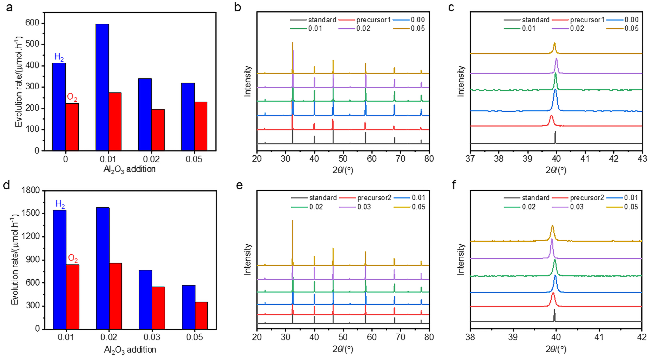
图4 以十八面体SrTiO3为前驱体调节γ-Al2O3的添加量合成SrTiO3:Al的光催化活性(a)与XRD衍射图(b); (c)是图(b)部分区域的放大XRD图; (a)中的光催化活性测试条件: 100 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOH; 以固相合成的SrTiO3为前驱体调节γ-Al2O3的添加量合成SrTiO3:Al的光催化活性(d)与XRD衍射图(e); (f)是图(e)部分区域的放大XRD图; (d)中的光催化活性测试条件: 130 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOHFigure 4 (a) Photocatalytic overall water splitting activities of SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method with varying addition amounts of γ-Al2O3 using 18-facet SrTiO3 as the precursor. (b) XRD patterns of SrTiO3:Al samples in (a). (c) Enlarged XRD patterns in (b). Photocatalytic reaction conditions in (a): 100 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water. (d) Photocatalytic overall water splitting activities of SrTiO3:Al synthesized via the flux method with varying addition amounts of γ-Al2O3 using solid-state-derived SrTiO3 as the precursor. (e) XRD patterns of SrTiO3:Al samples in (d). (f) Enlarged XRD patterns in (e). Photocatalytic reaction conditions in (d): 130 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water |
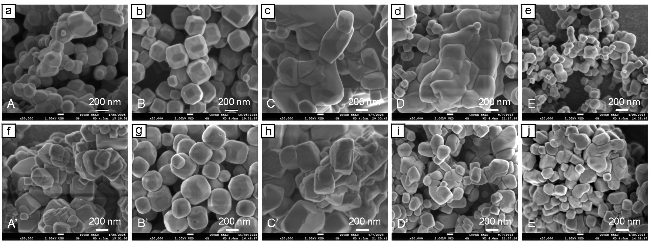
图5 (a~e)十八面体SrTiO3与以其为前驱体在对应Al2O3添加量下合成的SrTiO3:Al的SEM图; (f~j)固相合成的SrTiO3与以其为前驱体在对应Al2O3添加量下合成的SrTiO3:Al的SEM图Figure 5 (a~e) SEM images of 18-facet SrTiO3 and the corresponding SrTiO3:Al samples with various Al2O3 additions. (f~j) SEM images of SrTiO3 prepared via solid-state reaction and the corresponding SrTiO3:Al samples synthesized with various Al2O3 additions |
2.4 前驱体的形貌与结晶性对SrTiO3:Al光催化性能的影响
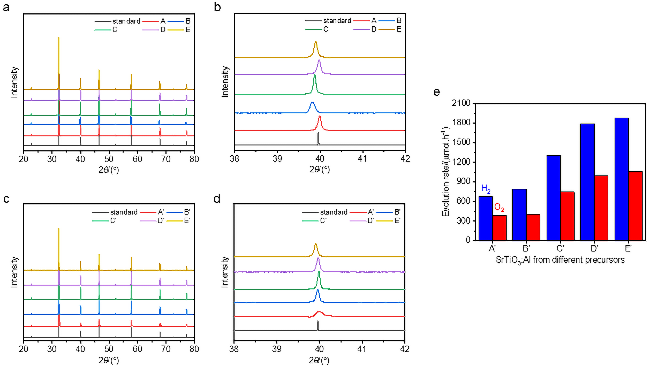
图7 前驱体SrTiO3的XRD衍射图(a); (b)是图(a)部分区域的放大XRD图; 各类2%-SrTiO3:Al的XRD衍射图(c)和光催化全分解水活性(e); (d)是图(c)部分区域的放大XRD图; 光催化活性测试条件: 130 mg光催化剂分散于100 mL去离子水中, 助催化剂的负载为0.1% (w) Rh-0.05% (w) Cr2O3-0.05% (w) CoOOHFigure 7 (a) XRD patterns of the SrTiO3 precursors. (b) Enlarged XRD patterns in (a). XRD patterns (c) and photocatalytic overall water splitting activities (e) of the corresponding 2%-SrTiO3:Al samples. (d) Enlarged XRD patterns in (c). Photocatalytic reaction conditions: 130 mg of photocatalyst loaded with 0.1% (w) Rh, 0.05% (w) Cr2O3, 0.05% (w) CoOOH, dispersed in 100 mL deionized water |