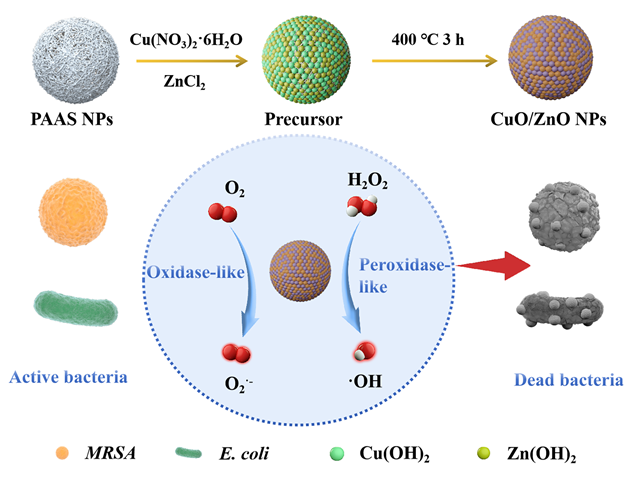
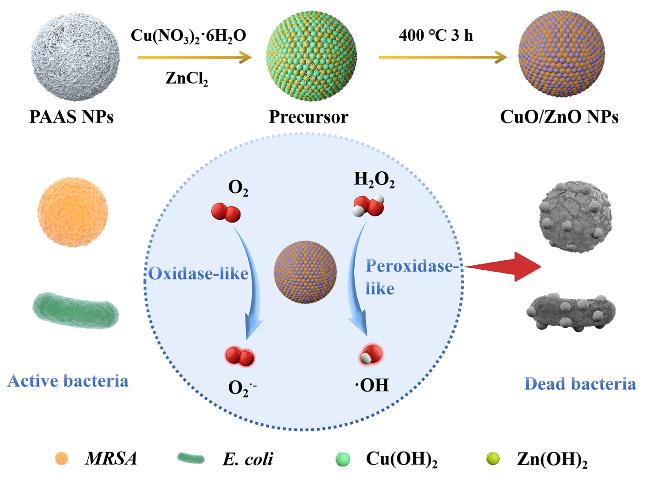
1 引言
2 结果与讨论
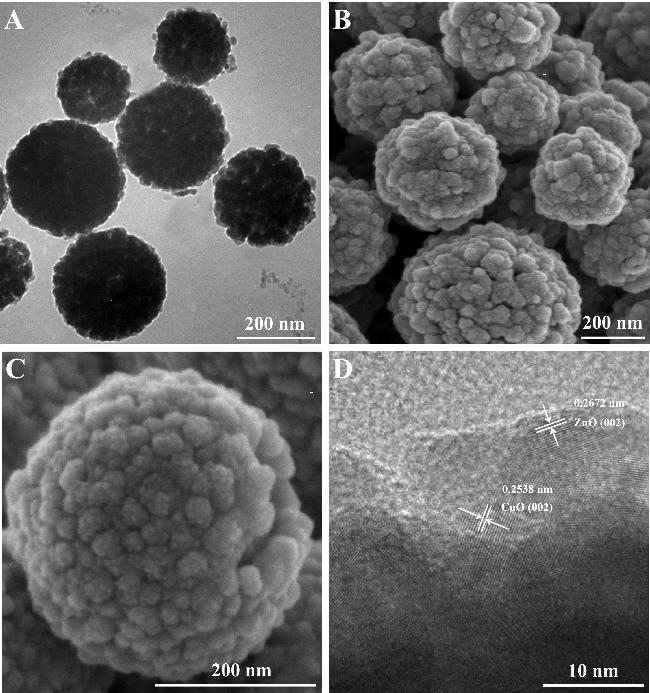
2.1 CuO/ZnO复合纳米球的表征
图2 (A) CuO/ZnO纳米球的傅里叶红外光谱图、(B) CuO/ZnO纳米球的X射线光电子能谱图(XPS)和(C, D) CuO/ZnO纳米球的高分辨XPS能谱图[Cu 2p (C), Zn 2p (D)]Figure 2 (A) Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectrum of CuO/ZnO nanospheres, (B) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectrum of CuO/ZnO nanospheres and (C, D) High-resolution XPS spectra of CuO/ZnO nanospheres [Cu 2p (C), Zn 2p (D)] |
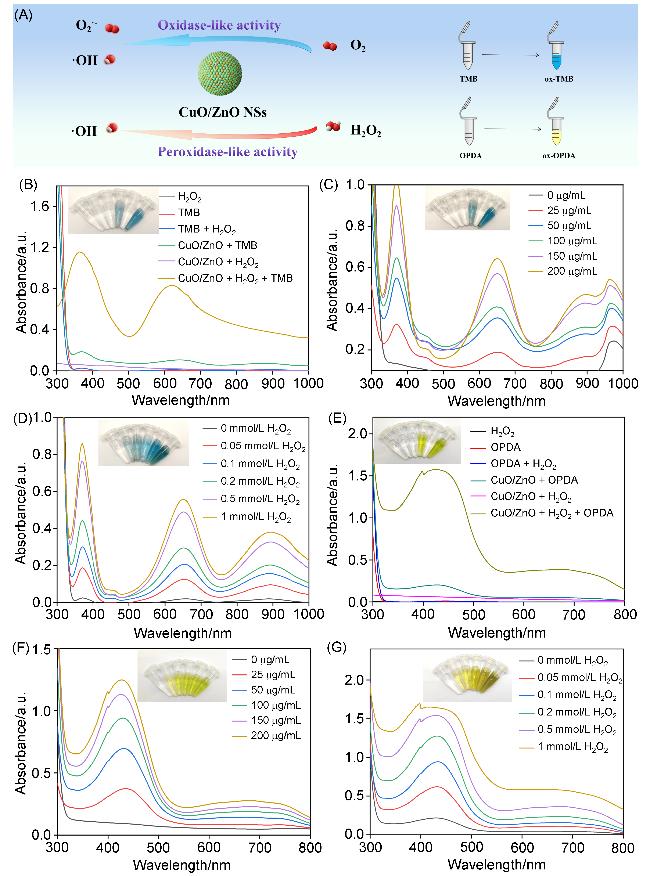
2.2 CuO/ZnO复合纳米球的类酶活性评估
图3 (A) CuO/ZnO纳米球的类氧化酶活性(OXD-like)和类过氧化物酶(POD-like)活性示意图、使用TMB探针得到的不同组合(B)、不同浓度(C)及不同H2O2浓度(D)下的CuO/ZnO纳米球的类酶催化活性以及使用OPDA探针得到的不同组合(E)、不同浓度(F)及不同H2O2浓度(G)下的CuO/ZnO纳米球的类酶催化活性Figure 3 (A) Schematic representation of the OXD-like and POD-like enzymatic activities of CuO/ZnO nanospheres, enzyme-like catalytic activity of CuO/ZnO nanospheres obtained under different combinations (B), concentrations (C) and H2O2 concentrations (D) using TMB probe, and enzyme-like catalytic activity of CuO/ZnO nanospheres obtained under different combinations (E), concentrations (F) and H2O2 concentrations (G) using OPDA prob |
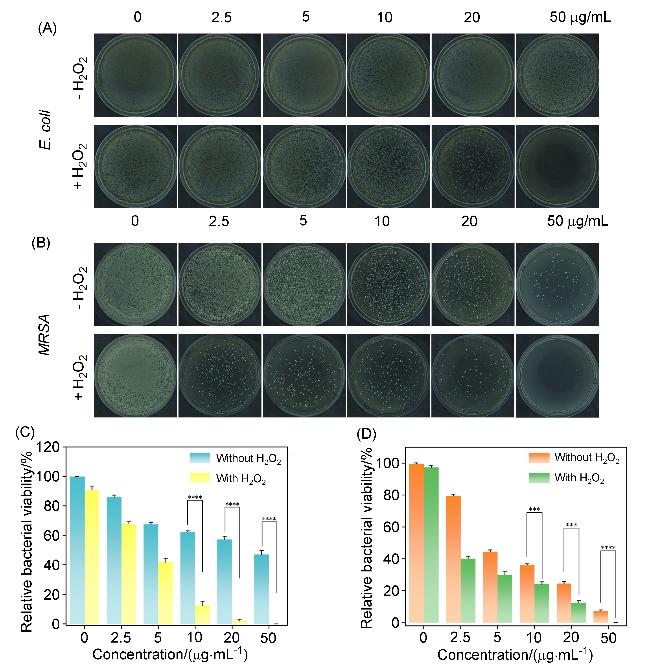
2.3 CuO/ZnO复合纳米球的抗菌性能研究
图4 有无H2O2存在时不同浓度的CuO/ZnO纳米球处理后(A) E. coli和(B) MRSA在平板上的菌落数以及(C) E. coli和(D) MRSA的细菌存活率统计图Figure 4 (A) Number of colonies of E. coli (A) and MRSA (B) on plates and statistical graph of the lower bacterial survival rate of (C) E. coli and (D) MRSA after CuO/ZnO nanosphere treatment after treatment with CuO/ZnO nanospheres at different concentrations, with and without the presence of H2O |
2.4 CuO/ZnO复合纳米球的抗菌机制研究
图5 有无H2O2存在时不同浓度的CuO/ZnO纳米球处理后(A) E. coli和(B) MRSA的扫描电镜(SEM)图像(箭头为细菌破损处)及(C) E. coli和(D) MRSA的蛋白泄露统计图Figure 5 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of E. coli (A) and MRSA (B) (arrows indicate bacterial damage sites) and protein leakage statistics of E. coli (C) and MRSA (D) after treatment with CuO/ZnO nanoparticles of different concentrations, with or without the presence of H2O2 |