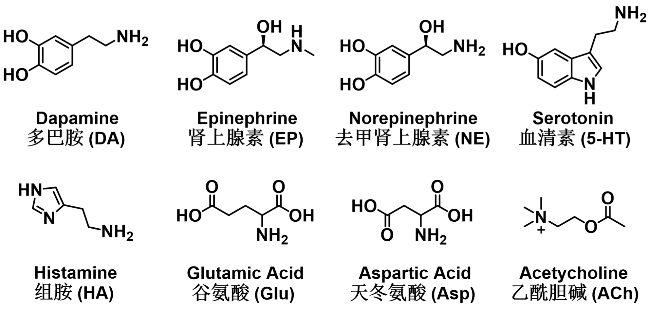
1 引言
2 有机荧光探针用于神经递质检测与生物成像的研究进展
2.1 单胺类
2.1.1 多巴胺(DA)
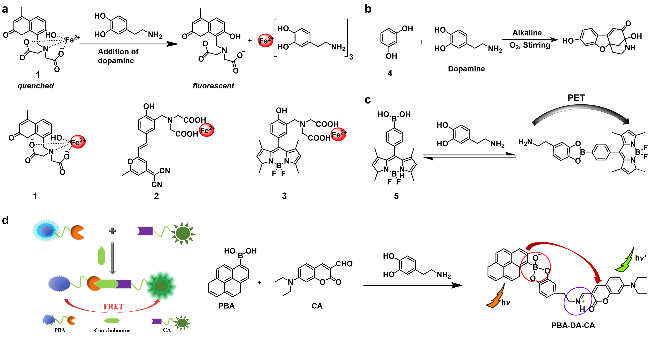
图2 (a)探针1~3的化学结构和探针1对多巴胺的检测机制示意图; 探针4 (b), 5 (c)和PBA-CA (d)用于多巴胺识别的机制示意图Figure 2 (a) Chemical structure of probes 1~3 and schematic diagram of the detection mechanism of probe 1 toward DA; schematic diagram of the mechanism of probes 4 (b), (c) 5 and (d) PBA-CA for the recognition of DA |
2.1.2 去甲肾上腺素(NE)
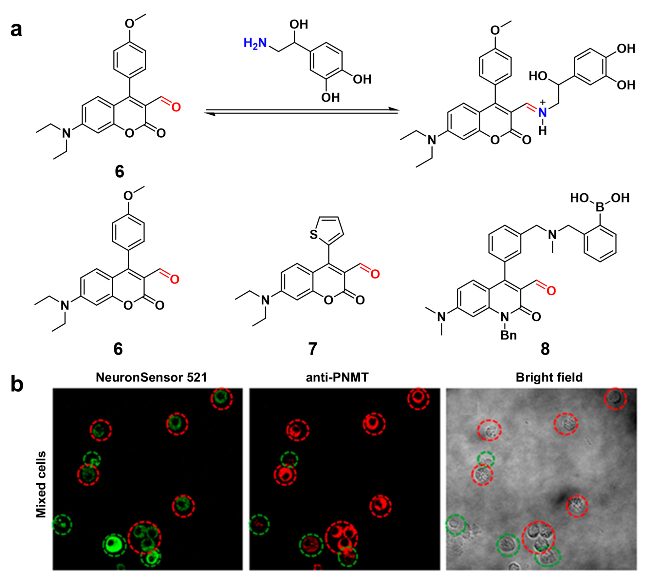
图3 (a)探针6对去甲肾上腺素的检测机制示意图及传感器6~8的化学结构; (b)用探针6和PNMT抗体染色富含去甲肾上腺素和肾上腺素的混合嗜铬细胞图(绿色圆圈内的细胞表示NE富集细胞, 红色圆圈内的细胞表示EP富集细胞)[61]Figure 3 (a) Schematic diagram of the detection mechanism of probe 6 toward NE, and chemical structures of probes 6~8; (b) stain mixed chromaffin cells rich in norepinephrine and adrenaline with probe 6 and PNMT antibody (cells circled in green indicate NE-enriched cells, and cells circled in red indicate EP-enriched cells)[61], Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society |
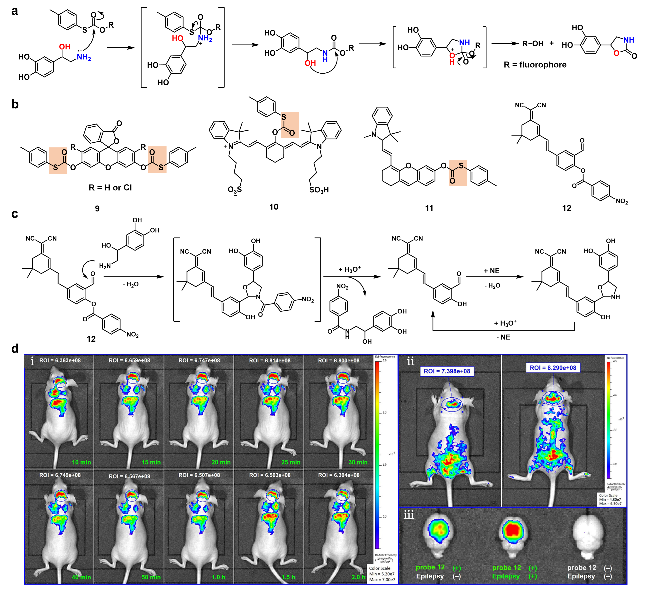
图4 (a)探针检测去甲肾上腺素的级联亲核取代机制; (b)探针9~12的化学结构; (c)探针检测去甲肾上腺素的“狩猎-射击”策略; (d)小鼠脑荧光变化: (ⅰ)经尾静脉注射探针12后监测, (ⅱ)经尾血管注射探针12前(左)和后(右)监测, (ⅲ)通过解剖实验观察癫痫发作和非癫痫发作小鼠脑的荧光强度[68]Figure 4 (a) Cascade nucleophilic substitution mechanism for probe detection of norepinephrine; (b) chemical structures of probes 9~12; (c) the "hunting-shooting" strategy for probe detection of norepinephrine; (d) changes in mice brain fluorescence (ⅰ) monitored after the injection of probe 12 via the tail vein, (ⅱ) before (left) and after (right) epileptic injection of probe 12 via tail vein, (ⅲ) fluorescence intensity of the mice brains with and without epileptic seizure by anatomical experiment[68], Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society |
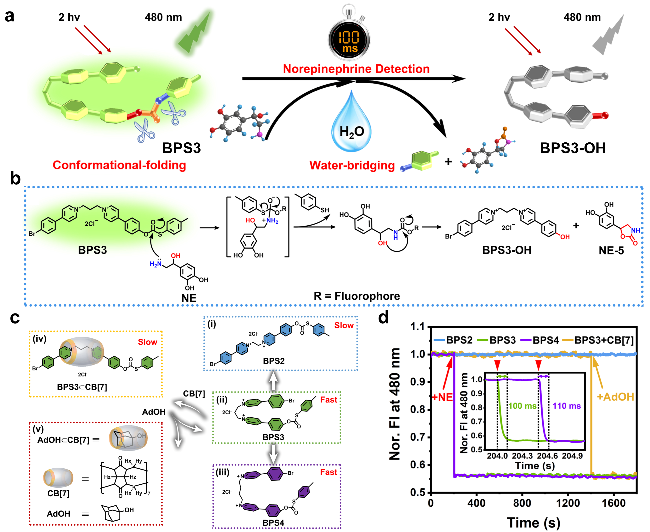
图5 (a)探针BPS3通过构象折叠和水桥的双重加速增强对去甲肾上腺素的超快传感机制示意图[69]; (b)探针BPS3对去甲肾上腺素的检测机制示意图[69]; (c)用共价或超分子方法进行分子构象调节的示意图. 探针BPS3的化学结构[69]; (d) BPS2、BPS3、BPS4和BPS3+CB[7]水溶液的归一化荧光响应动力学, 插图: BPS3和BPS4对NE的响应的部分曲线的放大图[69]Figure 5 (a) Schematic diagram of the ultrafast sensing mechanism of probe BPS3 for norepinephrine through dual acceleration of conformational folding and water bridging[69]; (b) schematic diagram of the detection mechanism of probe BPS3 toward NE[69]; (c) schematic of molecular conformational regulations by covalent or supramolecular approaches[69]; (d) normalized fluorescence response dynamics of aqueous solution of BPS2, BPS3, BPS4, and BPS3+CB[7], Inset: enlarged view of the partial curve for the response of BPS3 and BPS4 toward NE[69], reproduced under a CC BY license |
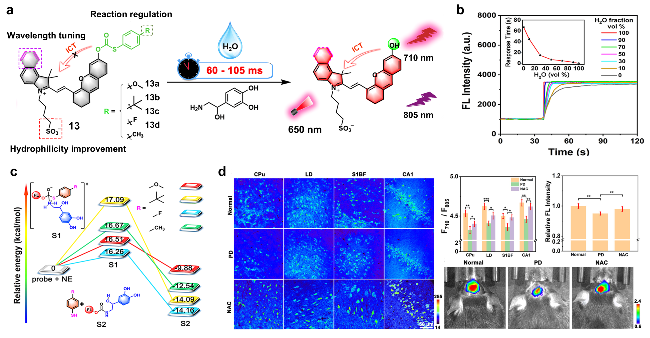
图6 (a)探针13的化学结构及其传感示意图[70]; (b)探针13a在含水量不同的乙腈-水混合溶剂中的反应动力学[70]; (c)通过计算得出在探针13a~13d和NE之间的亲核取代过程中, 可能反应坐标的相对能量[70]; (d)探针13a在正常小鼠、帕金森病(PD)模型小鼠以及经N-乙酰半胱氨酸(NAC)处理的PD模型小鼠的四个大脑区域组织切片荧光图像、体内成像以及相应的荧光变化柱状图[70]Figure 6 (a) Chemical structures of probe 13 and its sensing schematic diagram[70]; (b) Reaction kinetics of probe 13a in acetonitrile-water mixed solvents with different water contents[70]; (c) Calculate the relative energy of possible reaction coordinates during the nucleophilic substitution process between probes 13a~13d and NE[70]; (d) Fluorescence images of tissue sections from four brain regions, in vivo imaging, and corresponding fluorescence change histograms of probe 13a in normal mice, Parkinson's disease (PD) model mice, and PD model mice treated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) [70]. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society |
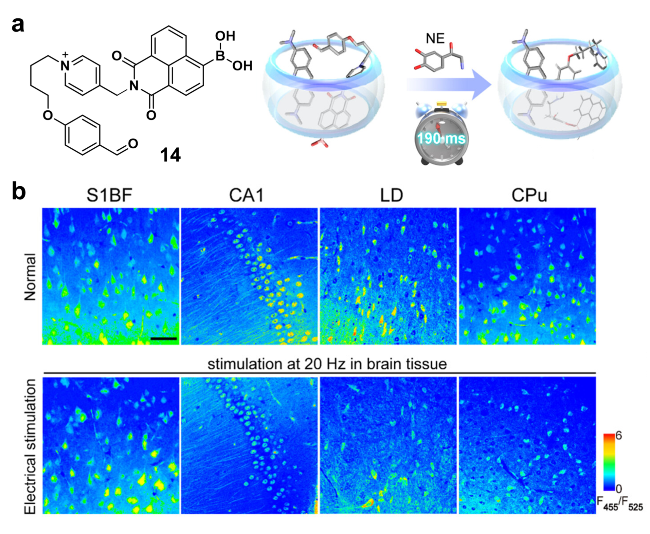
图7 (a)探针14的化学结构及优化的超分子传感器; (b)电刺激后用探针14孵育小鼠S1BF, CA1, LD和CPU区域的脑组织切片的荧光图像[88]Figure 7 (a) Chemical structure of probe 14 and optimized supramolecular probe; (b) fluorescence images of brain tissue slices from S1BF, CA1, LD, and CPU regions incubated with probe 14 after electrical stimulation[88], Copyright 2025, American Chemical Society |
2.1.3 肾上腺素(EP)
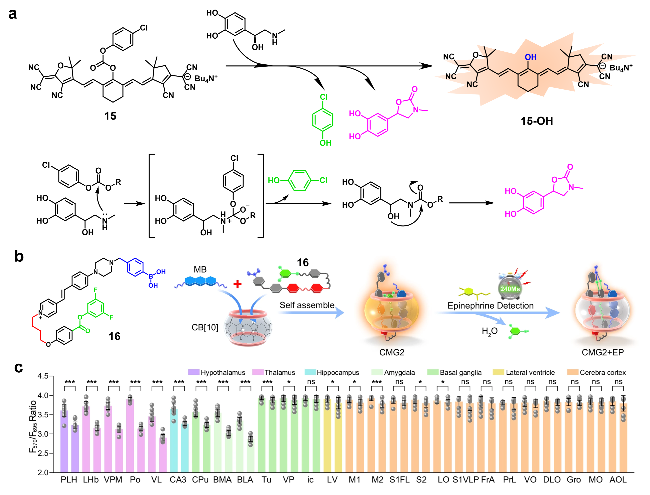
图8 (a)探针15的化学结构及其对肾上腺素的检测机制示意图; (b)探针16的化学结构及其对肾上腺素的检测机制示意图[91]; (c) 26个不同脑区荧光信号的量化图[91]Figure 8 (a) Chemical structure of probe 15 and schematic diagram of the detection mechanism toward EP; (b) chemical structure of probe 16 and its detection mechanism for EP[91]; (c) quantized maps of fluorescence signals in 26 different brain regions[91], reproduced under a CC BY license |
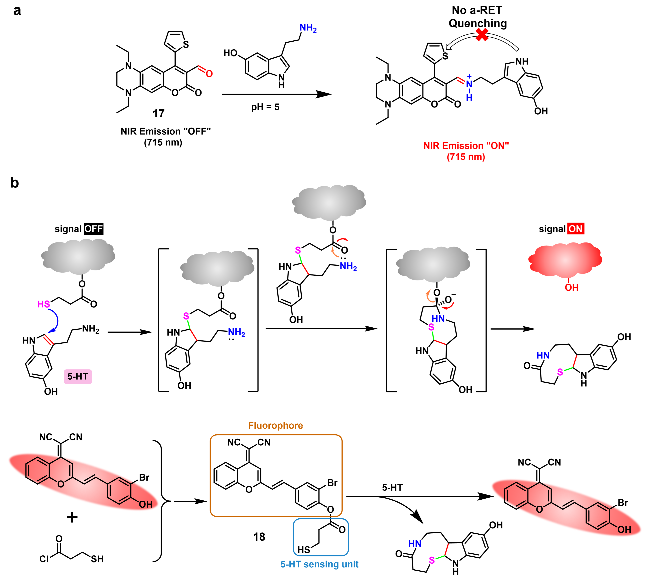
2.1.4 5-羟色胺(5-HT)
2.1.5 组胺(HA)
2.2 胆碱类
2.3 氨基酸类
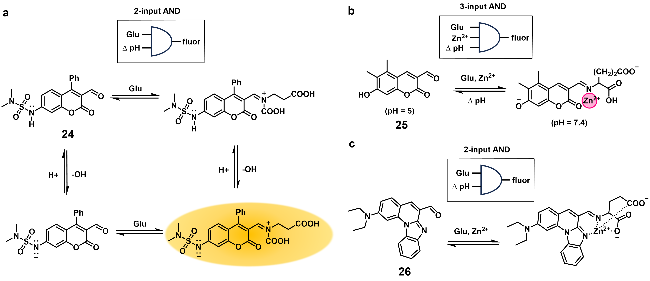
图12 (a)探针22对谷氨酸和天冬氨酸的检测机制示意图及其在HeLa细胞中对天冬氨酸/谷氨酸的成像[113]; (b) 23的化学结构及其对谷氨酸和天冬氨酸的检测机制示意图Figure 12 (a) Schematic diagram of the detection mechanism of probe 22 for glutamate and aspartic acid and its imaging of Asp/Glu in HeLa cells[113], Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society; (b) chemical structures of probe 23 and schematic diagram of the detection mechanism toward Glu and Asp |