1 引言
2 结果与讨论
2.1 AnB8的结构
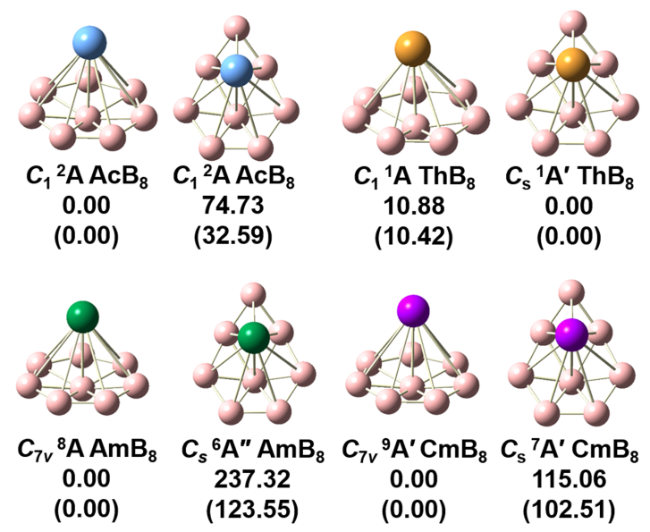
图1 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下优化得到的AnB8结构以及相对能量(括号内为TPSSH方法计算的相对能量, kJ/mol). 粉色球体代表B原子, 蓝色球体代表Ac原子, 橙色球体代表Th原子, 绿色球体代表Am原子以及紫色球体代表Cm原子Figure 1 The optimized geometrical structures and relative energies of AnB8 at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory (The brackets represent the relative energies calculated by the TPSSH method, kJ/mol). The pink spheres represent the B atom, the blue, orange, green, and purple spheres represent the Ac, Th, Am, and Cm atoms, respectively |
表1 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下计算的AnB8自旋态、自旋污染计算值与理论值的差值⟨S2⟩计算值-理论值、Mulliken原子自旋密度(ρAn)以及An—B1和An—Ba键的平均键长(B1原子为中心的硼原子, 而Ba原子为硼环上的硼原子)Table 1 Spin states, the differences between the calculated and theoretical spin contamination ⟨S2⟩计算值-理论值, Mulliken atomic spin densities (ρAn), and average An—B1 and An—Ba average bond distances (the B1 atom is the central boron atom of the boron ring, while the Ba atoms are the peripheral boron atoms of the boron ring) for AnB8 at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory |
| 硼团簇 | 自旋态 | ⟨S2⟩计算值-理论值 | 自旋密度 ρAn | 键长/nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An—B1 | An—Ba | ||||
| AcB8 | 双重态 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.2750 | 0.3017 |
| ThB8 | 单重态 | — | — | 0.2485 | 0.2729 |
| AmB8 | 八重态 | 0.02 | 7.14 | 0.2573 | 0.2882 |
| CmB8 | 九重态 | 0.03 | 8.10 | 0.2588 | 0.2849 |
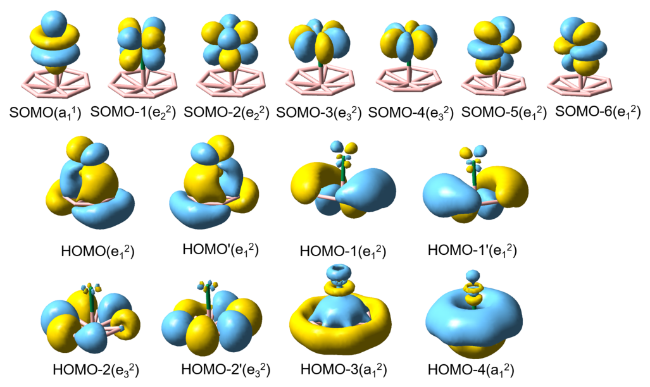
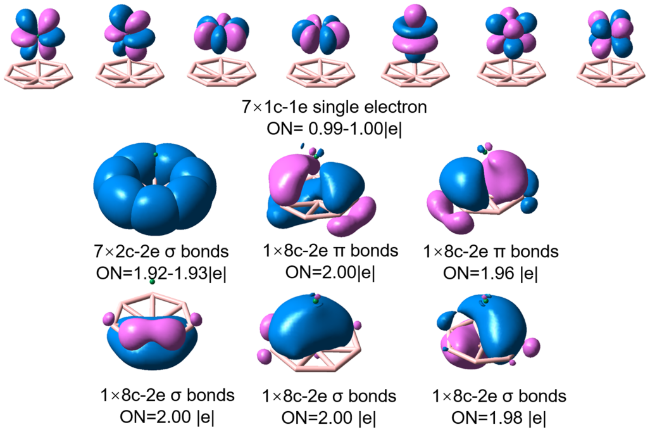
2.2 AnB8的成键性质
表2 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下, 计算得到的AnB8体系An的电荷、An—B键的WBI以及AnB8的SOMO-LUMO能隙(eV)Table 2 The charge analysis of An, WBIs of the An-B bonds, and the SOMO-LUMO gap (eV) of AnB8 at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory |
| 硼团簇 | 原子电荷/a.u. | WBIs | SOMO-LUMO 能隙/eV | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Hirshfeld | An—B1 | An—Ba | α | β | |||||
| AcB8 | 0.743 | 0.796 | 0.620 | 0.421 | 1.20 | 3.45 | ||||
| ThB8 | 0.746 | 0.723 | 0.611 | 0.516 | 1.49 | — | ||||
| AmB8 | 0.766 | 0.807 | 0.638 | 0.346 | 2.91 | 3.50 | ||||
| CmB8 | 0.607 | 0.636 | 0.631 | 0.425 | 2.16 | 3.81 | ||||
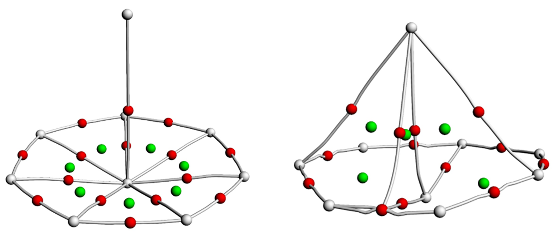
图2 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下, AcB8、AmB8、CmB8(左)和ThB8(右)的QTAIM分析. 红点代表键临界点, 灰线代表键路径, 绿点代表环临界点Figure 2 The QTAIM analysis of AcB8, AmB8, CmB8 (left) and ThB8 (right) at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory. Red points represent bond critical points, grey lines represent bond paths, and green points represent ring critical points |
表3 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下AnB8的QTAIM分析(a.u.)Table 3 The QTAIM analysis (a.u.) of AnB8 at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory |
| 硼团簇 | ρ | H | ∇2ρ | ELF | DItotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcB8 | 0.03987 | -0.00481 | 0.07581 | 0.24085 | 2.387 |
| ThB8 | 0.06165 | -0.01692 | 0.06650 | 0.40489 | 3.628 |
| AmB8 | 0.04167 | -0.00736 | 0.11279 | 0.14418 | 1.800 |
| CmB8 | 0.04180 | -0.00726 | 0.11792 | 0.13616 | 2.226 |
2.3 AnB8的热力学稳定性
表4 在PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP理论水平下计算的AnB8的解离能(kJ/mol)Table 4 The dissociation energy (kJ/mol) of AnB8 at the PBE0/6-311+G*/RECP level of theory |
| 反应方程 | 解离能 |
|---|---|
| AcB8→Ac2++${B}_{8}^{2-}$ | 2055.6 |
| ThB8→Th2++${B}_{8}^{2-}$ | 2384.0 |
| AmB8→Am2++${B}_{8}^{2-}$ | 1988.2 |
| CmB8→Cm2++${B}_{8}^{2-}$ | 2190.7 |